using a cepheid variable to determine distance
... USING A CEPHEID VARIABLE TO DETERMINE DISTANCE ...
... USING A CEPHEID VARIABLE TO DETERMINE DISTANCE ...
The surface composition of Beta Pictoris
... Why does the signature of accretion not show up in the surface composition of β Pic? Accretion of gas depleted in refractory elements is thought to be responsible for the deficiency pattern of λ Boo stars, and direct evidence for the presence of CS matter is accumulating (e.g. Stürenburg 1993; HRH9 ...
... Why does the signature of accretion not show up in the surface composition of β Pic? Accretion of gas depleted in refractory elements is thought to be responsible for the deficiency pattern of λ Boo stars, and direct evidence for the presence of CS matter is accumulating (e.g. Stürenburg 1993; HRH9 ...
2016 Spring, VAS Newsletter
... is to engage kids' interest in Space and Earth science, as well as the technologies that scientists use. Our site offers interactive games and demonstrations, hands-on projects, fun facts and short videos. It is a U.S. government-sponsored website; there are no advertisements or pop-up windows, and ...
... is to engage kids' interest in Space and Earth science, as well as the technologies that scientists use. Our site offers interactive games and demonstrations, hands-on projects, fun facts and short videos. It is a U.S. government-sponsored website; there are no advertisements or pop-up windows, and ...
D2 Stellar characteristics and stellar evolution
... dimming) which is caused by periodic expansion and contraction of outer surface (brighter as it expands). This is to do with the balance between the nuclear and gravitational forces within the star. In most stars these forces are balanced over long periods but in Cepheid variables they seem to take ...
... dimming) which is caused by periodic expansion and contraction of outer surface (brighter as it expands). This is to do with the balance between the nuclear and gravitational forces within the star. In most stars these forces are balanced over long periods but in Cepheid variables they seem to take ...
Chapter three: The properties of Stars
... Chapter three: The properties of Stars When we look up into the sky in a clear night, all of the stars locate at the inner surface of a sphere called celestial sphere and they seem to be at same distance from us. However this is just a projection effect. For the stars we can see with our unaided eye ...
... Chapter three: The properties of Stars When we look up into the sky in a clear night, all of the stars locate at the inner surface of a sphere called celestial sphere and they seem to be at same distance from us. However this is just a projection effect. For the stars we can see with our unaided eye ...
Procedurally Generating an Artificial Galaxy
... common. In the same way that you can choose how many times to run the seeds through the middle-square algorithm, the linear congruential generator can be configured in different ways with different results, some of which are better than others. It is slightly more complicated than the middle-square ...
... common. In the same way that you can choose how many times to run the seeds through the middle-square algorithm, the linear congruential generator can be configured in different ways with different results, some of which are better than others. It is slightly more complicated than the middle-square ...
Slide 1
... scattered light contribution, which accounts for flux scattered off an equatorial accretion disk to the observer including time delays in the scattered light. We give limits to mass and radius for XTE J1807-294 and compare these to limits determined for SAX J1808-3658 and XTE J1814-334 previously de ...
... scattered light contribution, which accounts for flux scattered off an equatorial accretion disk to the observer including time delays in the scattered light. We give limits to mass and radius for XTE J1807-294 and compare these to limits determined for SAX J1808-3658 and XTE J1814-334 previously de ...
Wien`s Law and Temperature
... in the Astronomy folder. Determine the wavelengths of the strongest absorption lines for this star. List them in the table below from shortest wavelength to longest and then identify the element associated with each absorption line. Repeat this process for each of the other stars on the list. 9. A c ...
... in the Astronomy folder. Determine the wavelengths of the strongest absorption lines for this star. List them in the table below from shortest wavelength to longest and then identify the element associated with each absorption line. Repeat this process for each of the other stars on the list. 9. A c ...
The Final Flight of Atlantis - Westchester Amateur Astronomers
... inexpensive Meade Electronic Eyepiece, to shoot this image of the Sun. The scope was mounted on a Tech200/Giro-2 "track and train" drive. He captured a one-minute avi file using Deepsky Imaging on a netbook with an inexpensive USB-video adaptor. Larry ran the avi through Registax 5 to stack the imag ...
... inexpensive Meade Electronic Eyepiece, to shoot this image of the Sun. The scope was mounted on a Tech200/Giro-2 "track and train" drive. He captured a one-minute avi file using Deepsky Imaging on a netbook with an inexpensive USB-video adaptor. Larry ran the avi through Registax 5 to stack the imag ...
Critical Thinking Questions: (work on these with a partner) Post
... 2. Protostars & Main Sequence Stars A. Why is a protostar not classified as an actual star? & what needs to occur for a star to transform from a Protostar to an actual star? A protostar is not an actual star because fusion doesn't occur. To become an actual star, nuclear fusion needs to occur. B. Wh ...
... 2. Protostars & Main Sequence Stars A. Why is a protostar not classified as an actual star? & what needs to occur for a star to transform from a Protostar to an actual star? A protostar is not an actual star because fusion doesn't occur. To become an actual star, nuclear fusion needs to occur. B. Wh ...
The Motion of Celestial Bodies
... So far we have discussed how to compute positions and velocities of celestial bodies at specific times given their orbital elements. The inverse problem is considerably more complex and can only be solved by iteration. Here we will limit ourselves to a sketch of how to proceed. The classical methods ...
... So far we have discussed how to compute positions and velocities of celestial bodies at specific times given their orbital elements. The inverse problem is considerably more complex and can only be solved by iteration. Here we will limit ourselves to a sketch of how to proceed. The classical methods ...
Unit 13―The “Fixed” Stars
... each other and so their apparent grouping into constellations is more of a function of their accidental, visual alignment as viewed from Earth. So clearly the Celestial Sphere, with all the stars stuck to it, is merely a convenient illusion to make locating them simple for us. Follow up sightings wi ...
... each other and so their apparent grouping into constellations is more of a function of their accidental, visual alignment as viewed from Earth. So clearly the Celestial Sphere, with all the stars stuck to it, is merely a convenient illusion to make locating them simple for us. Follow up sightings wi ...
Instructor`s Guide
... • Ptolemy, an Egyptian astronomer living in the second century A.D., devised a powerful mathematical model of the universe based on continuous motion in perfect circles, and in circles on circles. With the model, he was able to predict the motions of the sun, moon, and stars, and even of the irregu ...
... • Ptolemy, an Egyptian astronomer living in the second century A.D., devised a powerful mathematical model of the universe based on continuous motion in perfect circles, and in circles on circles. With the model, he was able to predict the motions of the sun, moon, and stars, and even of the irregu ...
astep - Institut d`Astrophysique de Paris
... +Ellipsoidal variability of close binaries (Sirko & Paczynski 2003) + Photocenter of the fluctuation ...
... +Ellipsoidal variability of close binaries (Sirko & Paczynski 2003) + Photocenter of the fluctuation ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... for locating a number of objects scattered across the sky. After finding that most of the objects on their list were a bit too faint, a new list was put together and the test re-started. The GoTo telescope was very accurate and the object being observed was always near the centre of the field of vie ...
... for locating a number of objects scattered across the sky. After finding that most of the objects on their list were a bit too faint, a new list was put together and the test re-started. The GoTo telescope was very accurate and the object being observed was always near the centre of the field of vie ...
HST Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant from
... – EG: correlation between the stellar velocity dispersion and the intrinsic luminosity – EGs found to occupy a “fundamental plane” in which a defined effective radius is tightly correlated with the surface brightness with that radius and central velocity dispersion – Scatter ~10-20% distance for ind ...
... – EG: correlation between the stellar velocity dispersion and the intrinsic luminosity – EGs found to occupy a “fundamental plane” in which a defined effective radius is tightly correlated with the surface brightness with that radius and central velocity dispersion – Scatter ~10-20% distance for ind ...
observing cards - NC Science Festival
... doubles, but aren’t “true binaries.” They may be very far apart but lie on the same line of sight from our perspective. It’s common for stars to come in pairs but they’re not often identical twins. Double stars of different sizes and colors beautifully illustrate the variety of our stellar neighbors ...
... doubles, but aren’t “true binaries.” They may be very far apart but lie on the same line of sight from our perspective. It’s common for stars to come in pairs but they’re not often identical twins. Double stars of different sizes and colors beautifully illustrate the variety of our stellar neighbors ...
Astronomical Filters on Skynet Telescopes
... stars look bluer. By quantifying how red or blue a star looks, we can relate this measurement to its temperature, which can then give us some insight into other properties like its mass and age. What filters do and how they are used Filters are colored glass disks that are placed, one at a time, in ...
... stars look bluer. By quantifying how red or blue a star looks, we can relate this measurement to its temperature, which can then give us some insight into other properties like its mass and age. What filters do and how they are used Filters are colored glass disks that are placed, one at a time, in ...
EXAM II REVIEW - University of Maryland: Department of
... • Textbook, lecture notes, discussion section activities! ...
... • Textbook, lecture notes, discussion section activities! ...
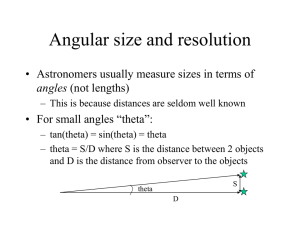
angles_telescopes
... magnification of 10 (typical of binoculars) – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10’s of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use a small telescope w/ magnification of 100-300 – w/ small telescope can distinguish large craters (angular sizes of ...
... magnification of 10 (typical of binoculars) – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10’s of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use a small telescope w/ magnification of 100-300 – w/ small telescope can distinguish large craters (angular sizes of ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.