the rest of the univ..
... It is estimated that there are at least 35,000 Kuiper Belt objects greater than 100 km in diameter, which is several hundred times the number (and mass) of similar sized objects in the main asteroid belt. A team of astronomers led by Anita Cochran report that the Hubble Space Telescope has detected ...
... It is estimated that there are at least 35,000 Kuiper Belt objects greater than 100 km in diameter, which is several hundred times the number (and mass) of similar sized objects in the main asteroid belt. A team of astronomers led by Anita Cochran report that the Hubble Space Telescope has detected ...
Why Study Cosmic Near Infrared Background? (1-4um)
... and WMAP data are good enough! It is even plausible that the first convincing evidence for 21-cm from reionization would come from the cross-correlation signal. ...
... and WMAP data are good enough! It is even plausible that the first convincing evidence for 21-cm from reionization would come from the cross-correlation signal. ...
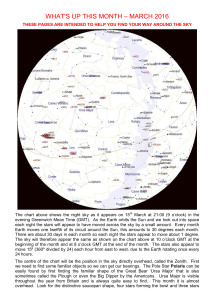
what`s up this month – march 2016
... evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an hour earlier at the end of the month. This is due to the movement of Earth along its orbital path around the Sun. The Sun takes 1 year to complete its or ...
... evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an hour earlier at the end of the month. This is due to the movement of Earth along its orbital path around the Sun. The Sun takes 1 year to complete its or ...
The Next Great Exoplanet Hunt Please share
... are unable to hold a steady pointing except if they are aimed close to the ecliptic, the plane of Earth’s orbit. The mission has recently been re-christened “K2” and is now surveying various star fields in the ecliptic. This will turn up more transiting exoplanets around bright stars, but leaves mos ...
... are unable to hold a steady pointing except if they are aimed close to the ecliptic, the plane of Earth’s orbit. The mission has recently been re-christened “K2” and is now surveying various star fields in the ecliptic. This will turn up more transiting exoplanets around bright stars, but leaves mos ...
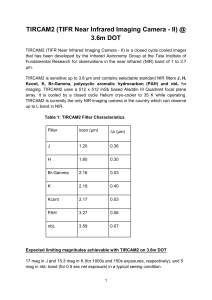
TIRCAM2 (TIFR Near Infrared Imaging Camera - II) @ 3.6m
... The observation procedure on TIRCAM2 is mostly standard NIR observation strategy which involves taking flats in the morning and evening twilight. Dithered short exposure observations of the target star as well as nearby NIR photometric standard star with 5-point dithered pattern is sufficient. Only ...
... The observation procedure on TIRCAM2 is mostly standard NIR observation strategy which involves taking flats in the morning and evening twilight. Dithered short exposure observations of the target star as well as nearby NIR photometric standard star with 5-point dithered pattern is sufficient. Only ...
First astronomical unit scale image of the GW Orionis triple system
... epoch bins allowed us to neglect orbital motions within each fit (even for the longest epoch, 2004, the eight days of observations only span 3% of the orbit, and therefore the orbital motion introduces negligible errors). We first fitted simultaneously V 2 and CP data with a binary model. To achieve ...
... epoch bins allowed us to neglect orbital motions within each fit (even for the longest epoch, 2004, the eight days of observations only span 3% of the orbit, and therefore the orbital motion introduces negligible errors). We first fitted simultaneously V 2 and CP data with a binary model. To achieve ...
Document
... Bellatrix: "Gamma Orionis“ is the twenty-second brightest star in the night sky. Bellatrix is considered a blue giant, though it is too small to explode in a supernova. Its luminosity is derived from its high temperature rather than its radius. Bellatrix serves as Orion's "left shoulder. ...
... Bellatrix: "Gamma Orionis“ is the twenty-second brightest star in the night sky. Bellatrix is considered a blue giant, though it is too small to explode in a supernova. Its luminosity is derived from its high temperature rather than its radius. Bellatrix serves as Orion's "left shoulder. ...
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Stars and Gas in Galaxies
... • Compressing gas (e.g. in collisions, or spiral arms) triggers gravitational collapse to form stars. – Ellipticals: very little gas ...
... • Compressing gas (e.g. in collisions, or spiral arms) triggers gravitational collapse to form stars. – Ellipticals: very little gas ...
Introduction - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... • Photons are emitted at the characteristic energy of particles in a system. • For a blackbody, we have Wien’s Law: – Wavelength of peak (Ang) = 2.9 x 107 / T(K) • In general, a system tends to produce radiation up to around the maximum energy of its particles • Thus, high energy photons are probes ...
... • Photons are emitted at the characteristic energy of particles in a system. • For a blackbody, we have Wien’s Law: – Wavelength of peak (Ang) = 2.9 x 107 / T(K) • In general, a system tends to produce radiation up to around the maximum energy of its particles • Thus, high energy photons are probes ...
Chemical abundances and winds of massive stars in M31: a Btype
... achieved by observing HR4074 within an air mass of 0.10 from HD 92809. A standard data reduction was again carried out with IRAF. These observations were supplemented by high resolution (HIRES), International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE ), large aperture, short-(SWP) and long-wavelength (LWP, LWR) ult ...
... achieved by observing HR4074 within an air mass of 0.10 from HD 92809. A standard data reduction was again carried out with IRAF. These observations were supplemented by high resolution (HIRES), International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE ), large aperture, short-(SWP) and long-wavelength (LWP, LWR) ult ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... “free” electrons for every Fe • electrons are “degenerate” as so close together provide most of the pressure resisting gravity • enormous stress. electrons “give way” leaves “hole” size of Earth in center of star ...
... “free” electrons for every Fe • electrons are “degenerate” as so close together provide most of the pressure resisting gravity • enormous stress. electrons “give way” leaves “hole” size of Earth in center of star ...
What is the life cycle of a star?
... compressed into a single point, which is called a black hole. • A black hole is an invisible object with gravity so great that nothing, not even light, can escape it. ...
... compressed into a single point, which is called a black hole. • A black hole is an invisible object with gravity so great that nothing, not even light, can escape it. ...
The Sky
... – Although some stars emit large amounts of infrared or ultraviolet light, humans can’t see it. It is not included in the apparent visual magnitude. – The subscript ‘v’ reminds you that you are including only light you can see. ...
... – Although some stars emit large amounts of infrared or ultraviolet light, humans can’t see it. It is not included in the apparent visual magnitude. – The subscript ‘v’ reminds you that you are including only light you can see. ...
ANTARES - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... science that is done with supernovae, the key is not the discovery of a single, unique object, but rather the detailed follow up of large samples. The resources to conduct observational follow up of astronomical objects are limited, especially when it comes to transient objects that are only availab ...
... science that is done with supernovae, the key is not the discovery of a single, unique object, but rather the detailed follow up of large samples. The resources to conduct observational follow up of astronomical objects are limited, especially when it comes to transient objects that are only availab ...
Chapter 7: The Galaxy, structure and content File
... of stars around the Sun in the Galaxy, and they can be measured from simple velocity and distance data. But now that we have accurate proper motions from the Hipparcos satellite mission, and hence (combining with ground-based line-of-sight velocities) three-dimensional stellar velocities in the sola ...
... of stars around the Sun in the Galaxy, and they can be measured from simple velocity and distance data. But now that we have accurate proper motions from the Hipparcos satellite mission, and hence (combining with ground-based line-of-sight velocities) three-dimensional stellar velocities in the sola ...
Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences
... CCD cameras, imaging polarimeter, three channel fast photometer and an optical multichannel analyzer. ARIES also has two 15-cm reflectors equipped with Hα , Ca II K and CN filters and CCD cameras for carrying out observations of solar activities with a time resolution of up to 25 millisecond. For op ...
... CCD cameras, imaging polarimeter, three channel fast photometer and an optical multichannel analyzer. ARIES also has two 15-cm reflectors equipped with Hα , Ca II K and CN filters and CCD cameras for carrying out observations of solar activities with a time resolution of up to 25 millisecond. For op ...
The Bible and big bang cosmology
... “Stars are formed by the gravitational collapse of cool dense gas and dust clouds…. There are problems, however, in initiating the collapse of a gas cloud. It resists collapse because of firstly its internal motions and the heating effects of nearby stars, secondly the centrifugal support due to rot ...
... “Stars are formed by the gravitational collapse of cool dense gas and dust clouds…. There are problems, however, in initiating the collapse of a gas cloud. It resists collapse because of firstly its internal motions and the heating effects of nearby stars, secondly the centrifugal support due to rot ...
Joining the Party - Lincoln-Sudbury Regional High School
... collapse of a cool molecular cloud. In the final stages of this collapse, the cloud’s core becomes sufficiently hot and the gas is under enough pressure for fusion reactions to begin: this is a young stellar object (YSO), a baby star. Obviously, astronomers are very interested in the stages of the c ...
... collapse of a cool molecular cloud. In the final stages of this collapse, the cloud’s core becomes sufficiently hot and the gas is under enough pressure for fusion reactions to begin: this is a young stellar object (YSO), a baby star. Obviously, astronomers are very interested in the stages of the c ...
Galileo & the Telescope—Sept 21
... planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name Midicean Stars. Venice ...
... planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name Midicean Stars. Venice ...
Grzegorz Nowak, Andrzej Niedzielski, Aleksander Wolszczan, Pawe
... The main objective of the PTPS is detection of planets around GK subgiants and giants through precision radial velocity (RV) measurements with iodine absorption cell using HET HRS spectrograph. However, the long period RV variations of red giants may also have other than planetary nature (e.g. a non ...
... The main objective of the PTPS is detection of planets around GK subgiants and giants through precision radial velocity (RV) measurements with iodine absorption cell using HET HRS spectrograph. However, the long period RV variations of red giants may also have other than planetary nature (e.g. a non ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.