Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Absolute Magnitude Brightness from 32.6 ly Ex: If the sun was 32.6 ly away, it would be a fifth magnitude star. Its absolute magnitude = +5 Most stars are between a -5 and +15 ...
... Absolute Magnitude Brightness from 32.6 ly Ex: If the sun was 32.6 ly away, it would be a fifth magnitude star. Its absolute magnitude = +5 Most stars are between a -5 and +15 ...
Section 2
... temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
... temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid v ...
... E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid v ...
THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF
... THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF Lupus is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for wolf. Lupus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It lies between Centaurus and Scorpius. STARS Lupus has ...
... THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF Lupus is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for wolf. Lupus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It lies between Centaurus and Scorpius. STARS Lupus has ...
Stars and Galaxies - Earth Science: Astronomy
... A. Galaxy—gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar ...
... A. Galaxy—gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar ...
North Star
... Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
... Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
PH507 - University of Kent
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
F03HW09
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
Quiz #4 – The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Stars
... The explosion of a massive star at the end of its life is called a _____________________. ...
... The explosion of a massive star at the end of its life is called a _____________________. ...
g9u4c12part3
... star lasts only about 10 billion years. long period of stability expands into a red giant. slowly shrinking into a small, dim white dwarf. it cools into a black dwarf, a dense, dark body made up mostly of carbon and oxygen. ...
... star lasts only about 10 billion years. long period of stability expands into a red giant. slowly shrinking into a small, dim white dwarf. it cools into a black dwarf, a dense, dark body made up mostly of carbon and oxygen. ...
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star
... Exit Slip: Stars 1. What 5 characteristics are used to classify stars? 2. What can the color of a star tell you about it? ...
... Exit Slip: Stars 1. What 5 characteristics are used to classify stars? 2. What can the color of a star tell you about it? ...
The Stars
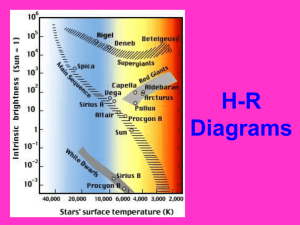
... Plotting the Properties of Stars Two astronomers created a special kind of graph that compares star brightness with their ________________ ________________. When this was plotted it showed that these properties are related. For example, as the temperature of a star __________________, its colour bec ...
... Plotting the Properties of Stars Two astronomers created a special kind of graph that compares star brightness with their ________________ ________________. When this was plotted it showed that these properties are related. For example, as the temperature of a star __________________, its colour bec ...
Beauty and the beast - University of Wyoming
... horizon of the North Star are the same. For example, the latitude of Cody is 44.5°, so Polaris is directly north and 44.5° above the horizon there. Continue the line from the Big Dipper through Polaris and the constellation Cassiopeia is seen. I once heard it referred to as the Wyoming constellation ...
... horizon of the North Star are the same. For example, the latitude of Cody is 44.5°, so Polaris is directly north and 44.5° above the horizon there. Continue the line from the Big Dipper through Polaris and the constellation Cassiopeia is seen. I once heard it referred to as the Wyoming constellation ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.