Main Sequence Stars
... They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is widely used in modern ...
... They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is widely used in modern ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
observingopenclusters-2-2-1
... to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You will pick up a large rich field of stars – Open Cluster M41 Procyon (Canis Minor) Locate next large and (also close) Procyon This points the way to 2 very different open clusters in Monocerous, ...
... to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You will pick up a large rich field of stars – Open Cluster M41 Procyon (Canis Minor) Locate next large and (also close) Procyon This points the way to 2 very different open clusters in Monocerous, ...
Classifying Stars
... Absolute magnitude is the actual amount of light that a star gives off. Apparent magnitude is the amount of a star’s light that is observed on Earth. If two stars are the same distance from Earth, the one with the greatest absolute magnitude will be the brightest. If one star is farther away than th ...
... Absolute magnitude is the actual amount of light that a star gives off. Apparent magnitude is the amount of a star’s light that is observed on Earth. If two stars are the same distance from Earth, the one with the greatest absolute magnitude will be the brightest. If one star is farther away than th ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... a display of colors and lines called a spectrum. ...
... a display of colors and lines called a spectrum. ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
The Stars
... Telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the moon and the planets. The number of stars that can be seen through telescopes is dramatically greater than can be seen by the unaided eye. Planets change their positions against the background of stars. Stars a ...
... Telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the moon and the planets. The number of stars that can be seen through telescopes is dramatically greater than can be seen by the unaided eye. Planets change their positions against the background of stars. Stars a ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... and your position on Earth. However it’s oriented, once you’ve come to know its distinctive zigzag pattern, you’ll spot it with ease. The plane of the Milky Way runs right through Cassiopeia, so it’s full of deep sky objects—in particular, a lot of open star clusters. Cassiopeia is named for the qu ...
... and your position on Earth. However it’s oriented, once you’ve come to know its distinctive zigzag pattern, you’ll spot it with ease. The plane of the Milky Way runs right through Cassiopeia, so it’s full of deep sky objects—in particular, a lot of open star clusters. Cassiopeia is named for the qu ...
Dark Sky Scotland - Constellation Project
... distances were radically updated based on data from the Hipparchus Satellite. Stars and history If anyone is standing on Alpha Centauri today (not very likely!) looking at Earth through a hugely powerful telescope (not yet built!) they would see the light that left here four years ago. So they would ...
... distances were radically updated based on data from the Hipparchus Satellite. Stars and history If anyone is standing on Alpha Centauri today (not very likely!) looking at Earth through a hugely powerful telescope (not yet built!) they would see the light that left here four years ago. So they would ...
Name: Notes – #45 The Diverse Sizes of Stars 1. A Hertzsprung
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
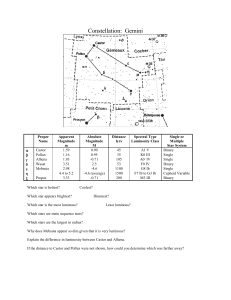
Gemini
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.