Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... diagram? The mass of the gas cloud (nebula) 23. Name the forces involved in the following processes: A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equilibrium): Gravity (inward) and Gas Pressure (outward) 24. Put the followin ...
... diagram? The mass of the gas cloud (nebula) 23. Name the forces involved in the following processes: A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equilibrium): Gravity (inward) and Gas Pressure (outward) 24. Put the followin ...
AST 207 Test 2 Answers 20 October 2010
... star A. Prof. Adams says he discovered a new type of star that is fainter than white dwarfs. Has he discovered a new type of star? Explain. The clues are very much like Walter Adams’ discovery that Sirius B is a white dwarf. However, there is a crucial missing clue. Since Sirius A and B were known t ...
... star A. Prof. Adams says he discovered a new type of star that is fainter than white dwarfs. Has he discovered a new type of star? Explain. The clues are very much like Walter Adams’ discovery that Sirius B is a white dwarf. However, there is a crucial missing clue. Since Sirius A and B were known t ...
Name
... 21. If the universe expands forever, what will happen? Will it eventually collapse or remain just as it is? Explain ...
... 21. If the universe expands forever, what will happen? Will it eventually collapse or remain just as it is? Explain ...
Name: ______________________________# __________ Study Guide is due WEDNESDAY November 2
... 1. What branch of earth science deals with studying the objects in space? ...
... 1. What branch of earth science deals with studying the objects in space? ...
Sun, Star Types and Luminosity
... d. Most stars (about 90%) are Main Sequence Stars. e. For these stars, the hotter, the brighter ...
... d. Most stars (about 90%) are Main Sequence Stars. e. For these stars, the hotter, the brighter ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
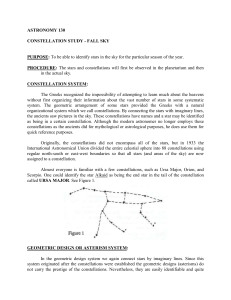
... slightly farther south than the other, is Schedar. The bright star at the end of the " W ", the one near Schedar is known as Caph. Include Cassiopeia in your previous drawing. The husband of Cassiopeia, Cepheus, is located counterclockwise from Cassiopeia. Cepheus, the King, looks like a drawing of ...
... slightly farther south than the other, is Schedar. The bright star at the end of the " W ", the one near Schedar is known as Caph. Include Cassiopeia in your previous drawing. The husband of Cassiopeia, Cepheus, is located counterclockwise from Cassiopeia. Cepheus, the King, looks like a drawing of ...
ASTRONOMY 130
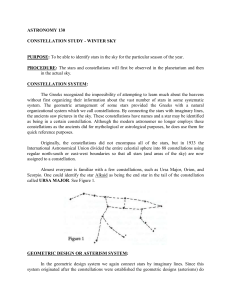
... Turn to face the south or southeastern part of the sky. You should find three bright stars that form the apexes of a large equilateral triangle. The star to the right is Betelgeuse (in Orion), the one to the left is Procyon (in Canis Minor), and the one farthest south is Sirius (in Canis Major). The ...
... Turn to face the south or southeastern part of the sky. You should find three bright stars that form the apexes of a large equilateral triangle. The star to the right is Betelgeuse (in Orion), the one to the left is Procyon (in Canis Minor), and the one farthest south is Sirius (in Canis Major). The ...
Day-6
... Temperature rises in the core. Hydrogen fusion begins in the core, and the star begins its life on the main sequence. Very low-mass stars (< 0.08 M) never start hydrogen fusion. These are called brown dwarfs. ...
... Temperature rises in the core. Hydrogen fusion begins in the core, and the star begins its life on the main sequence. Very low-mass stars (< 0.08 M) never start hydrogen fusion. These are called brown dwarfs. ...
Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System
... dwarf, and finally, a black dwarf. • White dwarfs are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. • Neutron stars, which are smaller and more massive than white dwarfs, are thought to be the remnants of supernova events. • A spinning neutron star that appears to give off pulses of radio waves is ...
... dwarf, and finally, a black dwarf. • White dwarfs are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. • Neutron stars, which are smaller and more massive than white dwarfs, are thought to be the remnants of supernova events. • A spinning neutron star that appears to give off pulses of radio waves is ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
ASTR-1020 Exam 2 Review Questions
... these two stars are farther from Earth? (Remember that the parallax angle is inversely proportional to the distance.) 4. What is the moving cluster method? Which star cluster is the foundation of the distance indicator method of figuring out the distance to external galaxies? 5. What is the differen ...
... these two stars are farther from Earth? (Remember that the parallax angle is inversely proportional to the distance.) 4. What is the moving cluster method? Which star cluster is the foundation of the distance indicator method of figuring out the distance to external galaxies? 5. What is the differen ...
On my webpage, find the link Star Life Cycle and use it to answer the
... A Solar Mass is equal to the mass of the Sun. If, for example, a star has 2 solar masses, it means it has twice as much mass as the Sun. Click the “brown dwarf” link in Option 1 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
... A Solar Mass is equal to the mass of the Sun. If, for example, a star has 2 solar masses, it means it has twice as much mass as the Sun. Click the “brown dwarf” link in Option 1 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
EMS, HR, Star Lives classwork/homework
... 9. Both stars are yellow in color but Alpha Centauri A is slightly brighter than our sun. Our sun is slightly hotter than Alpha Centauri A. 10. They both have about the same surface temperature and color. 11. Algol, Regulus, Spica, Rigel, Zeta Eridani 12. Deneb is an extremely bright star, white in ...
... 9. Both stars are yellow in color but Alpha Centauri A is slightly brighter than our sun. Our sun is slightly hotter than Alpha Centauri A. 10. They both have about the same surface temperature and color. 11. Algol, Regulus, Spica, Rigel, Zeta Eridani 12. Deneb is an extremely bright star, white in ...
Characteristics of Stars
... 4. In relation to the brightness of other stars how bright is the Sun? What are the three characteristics astronomers use to classify stars? 5. What size is the Sun compared to other stars? What are very large stars called? How far would the supergiant Betelgeuse reach if it were to replace our Sun? ...
... 4. In relation to the brightness of other stars how bright is the Sun? What are the three characteristics astronomers use to classify stars? 5. What size is the Sun compared to other stars? What are very large stars called? How far would the supergiant Betelgeuse reach if it were to replace our Sun? ...
Summer Triangle (Winter in the south hemisphere) Lyra
... Deneb is a blue-white giant star at the tip of the Northern Cross. It is 1400 light-years away, and is the 19th brightest star in the sky - more than 54,00 times the Sun's luminosity - making it one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. Due to precession, Deneb was a pole star 18,000 years ag ...
... Deneb is a blue-white giant star at the tip of the Northern Cross. It is 1400 light-years away, and is the 19th brightest star in the sky - more than 54,00 times the Sun's luminosity - making it one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. Due to precession, Deneb was a pole star 18,000 years ag ...
Stars Powerpoint
... core is unable to support itself and it will collapse further to become a neutron star ...
... core is unable to support itself and it will collapse further to become a neutron star ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
... narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.