Patterns in the night sky - Laureate International College
... If you watch the stars for a whole night they appear to move from east to west (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s rotation causes the illusion of movement. The stars appear to rotate around a single point in the sky – the North Star ...
... If you watch the stars for a whole night they appear to move from east to west (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s rotation causes the illusion of movement. The stars appear to rotate around a single point in the sky – the North Star ...
Theoretical Modeling of Massive Stars Mr. Russell University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
The Evening Sky in February 2016
... In February bright stars are nearly overhead. Sirius, the brightest star, is north of the zenith. Canopus, the second brightest star, is south of the zenith. Below and left of Sirius are Orion's bright stars: bluish Rigel and reddish Betelgeuse. Between them is the line of three stars making Orion's ...
... In February bright stars are nearly overhead. Sirius, the brightest star, is north of the zenith. Canopus, the second brightest star, is south of the zenith. Below and left of Sirius are Orion's bright stars: bluish Rigel and reddish Betelgeuse. Between them is the line of three stars making Orion's ...
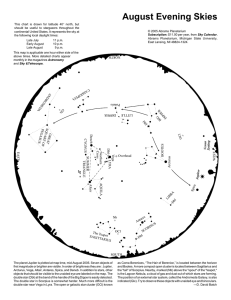
August Evening Skies
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... MA045 Basic Math Skills, or MA050 Introductory Mathematics This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolution of stars, pulsars, and black holes. Laboratory sessions may be sc ...
... MA045 Basic Math Skills, or MA050 Introductory Mathematics This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolution of stars, pulsars, and black holes. Laboratory sessions may be sc ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
... • A star’s apparent brightness depends on its luminosity and distance from Earth. • Hertzsprung and Russell independently discovered that each type of star has specific properties. They organized their findings into what is now called a Hertzsprung and Russell ( H-R) diagram ...
... • A star’s apparent brightness depends on its luminosity and distance from Earth. • Hertzsprung and Russell independently discovered that each type of star has specific properties. They organized their findings into what is now called a Hertzsprung and Russell ( H-R) diagram ...
properties of stars 2012
... Wien’s Law T = c/λm where T = temperature in kelvins, c is the speed of light, λm is the wavelength of maximum brightness. Spectral Classes There is a relationship between the temperature of a star and the appearance of the dark lines on its absorption spectrum. Star temperatures are classified, fro ...
... Wien’s Law T = c/λm where T = temperature in kelvins, c is the speed of light, λm is the wavelength of maximum brightness. Spectral Classes There is a relationship between the temperature of a star and the appearance of the dark lines on its absorption spectrum. Star temperatures are classified, fro ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... have important implications for the formation of planets around these stars. According to some theoretical models, large flares could produce strong turbulence in a planet-forming disk around a young star. Such turbulence might affect the position of rocky, Earth-like planets as they form and preven ...
... have important implications for the formation of planets around these stars. According to some theoretical models, large flares could produce strong turbulence in a planet-forming disk around a young star. Such turbulence might affect the position of rocky, Earth-like planets as they form and preven ...
Chapter 13 Notes – The Deaths of Stars
... Sun will expand to a red giant in ______________ billion years Expands to ______________ radius Earth will then be ___________________ Sun MAY form a ________________ nebula (but uncertain) Sun’s C, O core will become a ______________ dwarf VIII. The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae F ...
... Sun will expand to a red giant in ______________ billion years Expands to ______________ radius Earth will then be ___________________ Sun MAY form a ________________ nebula (but uncertain) Sun’s C, O core will become a ______________ dwarf VIII. The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae F ...
Sample Assessment Items
... c. The stars are much farther away than Mars, so they appear not to move. d. Earth and the stars move in one direction, and Mars moves in the other. Answer: The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly moving because _______________. a. the Earth is moving b. they rotate around the Sun c. t ...
... c. The stars are much farther away than Mars, so they appear not to move. d. Earth and the stars move in one direction, and Mars moves in the other. Answer: The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly moving because _______________. a. the Earth is moving b. they rotate around the Sun c. t ...
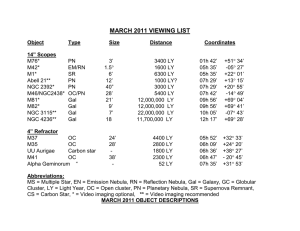
March
... M1 The Crab Nebula in the constellation Taurus (TAW-rus) is the brightest and most famous supernova remnant in the sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 da ...
... M1 The Crab Nebula in the constellation Taurus (TAW-rus) is the brightest and most famous supernova remnant in the sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 da ...
Lab Document - University of Iowa Astronomy and Astrophysics
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
FSA school wide Science Olympiad 12/8/2007
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
... C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova ...
07-01TheColsmologicalDistanceLadder
... Cepheid Variables: How to measure the distance to a galaxy using Cepheid variable stars: 1. Find the Cepheid, measure its spectrum 2. Measure a couple periods, and its apparent magnitude m 3. Look up its absolute magnitude 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
... Cepheid Variables: How to measure the distance to a galaxy using Cepheid variable stars: 1. Find the Cepheid, measure its spectrum 2. Measure a couple periods, and its apparent magnitude m 3. Look up its absolute magnitude 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
Constellations - Mayo Dark Sky Park
... knows what stories are ancestors here created when they saw this giant in the night sky? Let your imagination wander as you learn about the patterns of stars forming constellations and the legends and myths that have been attached to them over thousands of years. ...
... knows what stories are ancestors here created when they saw this giant in the night sky? Let your imagination wander as you learn about the patterns of stars forming constellations and the legends and myths that have been attached to them over thousands of years. ...
Practice Homework 2: Properties of Stars 1. Star A is 100 times more
... 1. Star A is 100 times more luminous than star B. Star A is 100 times nearer to us than star B. how Do the apparent brightness of the two stars compare 2. The temperature of gas filled in box A is more than the temperature of gas filled in box B. whose molecules have more average kinetic energy? Which ...
... 1. Star A is 100 times more luminous than star B. Star A is 100 times nearer to us than star B. how Do the apparent brightness of the two stars compare 2. The temperature of gas filled in box A is more than the temperature of gas filled in box B. whose molecules have more average kinetic energy? Which ...
Chapter 25 - Notes Super Size
... Stars & Galaxies Stars Constellations • _________________ of stars representing mythological characters, animals, or familiar objects. • Most constellations come from the _________________. • The stars in a constellation may appear close, however each star can be _________________ of light-years awa ...
... Stars & Galaxies Stars Constellations • _________________ of stars representing mythological characters, animals, or familiar objects. • Most constellations come from the _________________. • The stars in a constellation may appear close, however each star can be _________________ of light-years awa ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.