Stars
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it ...
... • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it ...
Nov - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... Auriga is some 50° above the horizon, whilst below it Taurus, Orion and Gemini are now fully risen. Above Capella lies the constellation of Perseus, with the double cluster only 10° from the zenith. Looking south both Andromeda and Pisces are straddling the meridian with the largely faint constellat ...
... Auriga is some 50° above the horizon, whilst below it Taurus, Orion and Gemini are now fully risen. Above Capella lies the constellation of Perseus, with the double cluster only 10° from the zenith. Looking south both Andromeda and Pisces are straddling the meridian with the largely faint constellat ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... • most stars (90%) are in a band that runs from the upper left (high, high) to the lower right (low, low) – main sequence stars – main sequence stars vary in surface temperature and absolute magnitudes – commonality: actively fusing hydrogen into helium ...
... • most stars (90%) are in a band that runs from the upper left (high, high) to the lower right (low, low) – main sequence stars – main sequence stars vary in surface temperature and absolute magnitudes – commonality: actively fusing hydrogen into helium ...
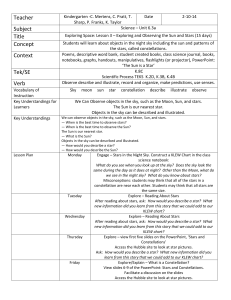
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... Objects in the sky can be described and illustrated. We can observe objects in the sky, such as the Moon, Sun, and stars. — When is the best time to observe stars? — When is the best time to observe the Sun? The Sun is our nearest star. — What is the Sun? Objects in the sky can be described and illu ...
... Objects in the sky can be described and illustrated. We can observe objects in the sky, such as the Moon, Sun, and stars. — When is the best time to observe stars? — When is the best time to observe the Sun? The Sun is our nearest star. — What is the Sun? Objects in the sky can be described and illu ...
Celestial Bodies
... The Sun The Sun provides our world with the warmth and light needed to survive. Our Sun is an average ...
... The Sun The Sun provides our world with the warmth and light needed to survive. Our Sun is an average ...
H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
File
... as they orbit the Sun, material ________ forming the tail the tail _______ points away from the Sun Halley's comet orbits the Sun every ____ years (1986) Meteors and Meteorites Earth is bombarded everyday by _____ and ______ fragments from space when one of the objects _______ up generatin ...
... as they orbit the Sun, material ________ forming the tail the tail _______ points away from the Sun Halley's comet orbits the Sun every ____ years (1986) Meteors and Meteorites Earth is bombarded everyday by _____ and ______ fragments from space when one of the objects _______ up generatin ...
Light from stars part II
... 1) Blackbody – all solids, liquids and gases radiate EM waves at all wavelengths with a distribution of energy over the wavelengths that depends on temperature T ...
... 1) Blackbody – all solids, liquids and gases radiate EM waves at all wavelengths with a distribution of energy over the wavelengths that depends on temperature T ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
Objects Beyond our Solar System
... A supernova is an enormous explosion that occurs at the end of a large star’s life. As a star runs out of fuel its core collapses inward due to the lack of pressure. This core now becomes a neutron star or a black hole. When this change occurs the shock wave created explodes outward in a rapid ...
... A supernova is an enormous explosion that occurs at the end of a large star’s life. As a star runs out of fuel its core collapses inward due to the lack of pressure. This core now becomes a neutron star or a black hole. When this change occurs the shock wave created explodes outward in a rapid ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while? Realize that once our Sun starts to run out of hydrogen fuel and has exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to env ...
... mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while? Realize that once our Sun starts to run out of hydrogen fuel and has exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to env ...
source
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.