Stars - Haag
... But stars actually do move in space, this can be seen by the movement of stars over a time period of thousands of years. This is called Actual Motion ...
... But stars actually do move in space, this can be seen by the movement of stars over a time period of thousands of years. This is called Actual Motion ...
Main Sequence Star
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • Matter started to “clump” back together • This was due to gravity • The galaxies, stars and planets formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of billions of stars ...
... • Matter started to “clump” back together • This was due to gravity • The galaxies, stars and planets formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of billions of stars ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 10
... density (the number of atoms per unit volume), and also to the average speed of the atoms (measured by the gas temperature). 3. Using the Hertzprung-Russell diagram in Figure ...
... density (the number of atoms per unit volume), and also to the average speed of the atoms (measured by the gas temperature). 3. Using the Hertzprung-Russell diagram in Figure ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
Mon Oct 22, 2012 MOON IN CAPRICORNUS The moon is waxing
... What’s the farthest thing you can see without a telescope? Off in the northeastern sky late this evening, you can find the answer to this question, but only if the skies are very clear, and very dark, and you know just where to look. It’s a very dim smudge of light that lies in the direction of the ...
... What’s the farthest thing you can see without a telescope? Off in the northeastern sky late this evening, you can find the answer to this question, but only if the skies are very clear, and very dark, and you know just where to look. It’s a very dim smudge of light that lies in the direction of the ...
How is a Star`s Color Related to Its temperature?
... different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color. temperature, and class are related. ~Vlaterials: Colored pencils (red, orange, yellow, blue) Procedur ...
... different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color. temperature, and class are related. ~Vlaterials: Colored pencils (red, orange, yellow, blue) Procedur ...
Lesson 2 Power Notes Outline
... When astronomers use the word luminosity, they mean the actual brightness of a star. They measure it on a scale called absolute magnitude. ...
... When astronomers use the word luminosity, they mean the actual brightness of a star. They measure it on a scale called absolute magnitude. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell used spectral class against absolute magnitude. Their resultant plots showed that the relationship between temperature and luminosity of a star was not random but instead appeared t ...
... against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell used spectral class against absolute magnitude. Their resultant plots showed that the relationship between temperature and luminosity of a star was not random but instead appeared t ...
Chapter 21 Study Guide
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
The Sun . . .
... 90% of stars are main sequence. Supergiant: 20 to 200 times larger than the Sun, but also much brighter, cooler and less dense. Dwarf: Small stars; fairly hot but very dim. Diameter is about the same as Earth, but their mass is equal to the sun . . . ...
... 90% of stars are main sequence. Supergiant: 20 to 200 times larger than the Sun, but also much brighter, cooler and less dense. Dwarf: Small stars; fairly hot but very dim. Diameter is about the same as Earth, but their mass is equal to the sun . . . ...
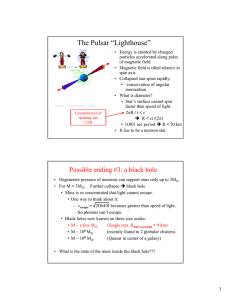
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... • Outer layers of star gradually contract onto core which becomes too massive to be held up by degenerate electron pressure • e- + p Î n • Sudden core collapse: 104 km Î 20 km • Then core rebounds • Outer layers fall in, then get hit by rebounding core. ...
... • Outer layers of star gradually contract onto core which becomes too massive to be held up by degenerate electron pressure • e- + p Î n • Sudden core collapse: 104 km Î 20 km • Then core rebounds • Outer layers fall in, then get hit by rebounding core. ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 16. Star A and star B have the same absolute brightness, but star A is about twice as far from Earth as star B. Describe the apparent magnitude of the stars? 17. Describe the reason for having a leap year? 18. The picture shows sand used to make a model of a galaxy. In the model, each grain of sand ...
... 16. Star A and star B have the same absolute brightness, but star A is about twice as far from Earth as star B. Describe the apparent magnitude of the stars? 17. Describe the reason for having a leap year? 18. The picture shows sand used to make a model of a galaxy. In the model, each grain of sand ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.