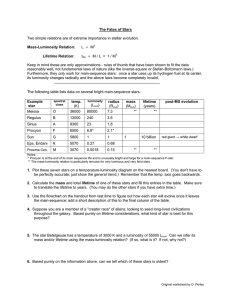
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
April
... Galaxy for it’s elongated shape, M82 is also about 12 million Light Years distant. The close encounter with M81 described above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. ...
... Galaxy for it’s elongated shape, M82 is also about 12 million Light Years distant. The close encounter with M81 described above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. ...
source
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... • There are several classes of stars with known power output. • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with mo ...
... • There are several classes of stars with known power output. • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with mo ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... sun. Example: Betelgeuse is 38000 LSUN, and emits 1.4 x 1031 watts 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner pl ...
... sun. Example: Betelgeuse is 38000 LSUN, and emits 1.4 x 1031 watts 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner pl ...
Stars - Weebly
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
... • The objects that heat and light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars (H He) – Energy from the nuclear reactions is released as electromagnetic radiation ...
Life Cycle of Stars - Faulkes Telescope Project
... the rest of its fuel is gone. At this point, the outward pressure of the nuclear reactions in the star is not strong enough to equalize the inward gravitational force, so the star begins to collapse. Most stars (including our Sun) will blow away their outer layers to form a planetary nebula; their c ...
... the rest of its fuel is gone. At this point, the outward pressure of the nuclear reactions in the star is not strong enough to equalize the inward gravitational force, so the star begins to collapse. Most stars (including our Sun) will blow away their outer layers to form a planetary nebula; their c ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... inspection shows that Mizar (2.5) has a fainter companion named Alcor (4.0). The pair provide a good test for reasonable eyesight. The pair form a optical double ie. they are not physically associated. Through large binoculars or small telescopes Mizar itself is shown to have a fourth magnitude comp ...
... inspection shows that Mizar (2.5) has a fainter companion named Alcor (4.0). The pair provide a good test for reasonable eyesight. The pair form a optical double ie. they are not physically associated. Through large binoculars or small telescopes Mizar itself is shown to have a fourth magnitude comp ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. October 2005
... Beta () Persei, Algol. +2.2 to +3.4, period 2.7 days. Favourable evening minima this month occur on the 17th and 20th. Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standa ...
... Beta () Persei, Algol. +2.2 to +3.4, period 2.7 days. Favourable evening minima this month occur on the 17th and 20th. Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standa ...
Magnitude Scale
... Absolute Magnitude • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
... Absolute Magnitude • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... universe began 15 to 20 billion years ago. Scientist have viewed thousands of galaxies and can measure the fact that all galaxies are moving away from each other. If you could run the film “backwards”, it would appear that all of the galaxies come together at a single incredibly dense point. Scienti ...
... universe began 15 to 20 billion years ago. Scientist have viewed thousands of galaxies and can measure the fact that all galaxies are moving away from each other. If you could run the film “backwards”, it would appear that all of the galaxies come together at a single incredibly dense point. Scienti ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.























