Night Sky Checklist April–May–June Unaided Eye Astronomy
... Omega Centauri is a globular cluster, a family of close to a million stars whose gravity holds the whole group together in what appears in binoculars or a low power telescope as a ball of stars. It can be seen as a faint fuzzy with the unaided eye under clear, dark conditions, but a very clear south ...
... Omega Centauri is a globular cluster, a family of close to a million stars whose gravity holds the whole group together in what appears in binoculars or a low power telescope as a ball of stars. It can be seen as a faint fuzzy with the unaided eye under clear, dark conditions, but a very clear south ...
solution
... apparent magnitude of 13.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Explain your answer. Zubenelgenubi appears to be brighter, since it has a lower apparent magnitude (remember that a negative apparent magnitude is very ...
... apparent magnitude of 13.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Explain your answer. Zubenelgenubi appears to be brighter, since it has a lower apparent magnitude (remember that a negative apparent magnitude is very ...
Badge Day - GBT
... 4. Cosmic Clues 1.Analyze the spectrum for three stars. What are the 2 most prominent differences between the spectra? Which star is hottest? ...
... 4. Cosmic Clues 1.Analyze the spectrum for three stars. What are the 2 most prominent differences between the spectra? Which star is hottest? ...
The Life of a Star
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star
... gas and dust in my Solar Nursery and begins to Shine! When the cool masses of dust and gas combine, a star has a temperature of 1,800,000 degrees F! http://www.virginmedia.com/images/ ...
... gas and dust in my Solar Nursery and begins to Shine! When the cool masses of dust and gas combine, a star has a temperature of 1,800,000 degrees F! http://www.virginmedia.com/images/ ...
Lives and Deaths of Stars (middle school)
... Outer layers expand due to radiation pressure from a hot core • Surface temperature drops by a factor of ~ 2 • The radius increases by a factor of ~ 100 • Luminosity increases ~ R2 T4 ~ 100-1000 times ...
... Outer layers expand due to radiation pressure from a hot core • Surface temperature drops by a factor of ~ 2 • The radius increases by a factor of ~ 100 • Luminosity increases ~ R2 T4 ~ 100-1000 times ...
29.2 - Stars - s3.amazonaws.com
... Star • A star is a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat • Appear to be tiny specks of white light • Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth ...
... Star • A star is a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat • Appear to be tiny specks of white light • Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth ...
SNC 1D Astonomy
... revolution around the sun is 365.24 days. • It takes one day for Earth to make one rotation on its axis. • The first clocks were pillars and sticks in the ground and people used the shadows they made to tell the time. ...
... revolution around the sun is 365.24 days. • It takes one day for Earth to make one rotation on its axis. • The first clocks were pillars and sticks in the ground and people used the shadows they made to tell the time. ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
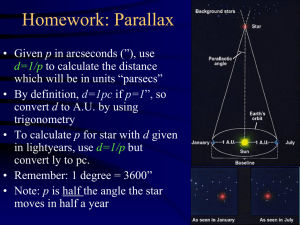
... of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least luminous stars are quite common, but are so faint they are hard to see even if they are close. 2. The parallax of the bright star Vega is 0.129 seconds of arc. What is the distance of Vega in parsecs ? In light-years ? We have ...
... of space because these stars are very rare. On the other hand, the least luminous stars are quite common, but are so faint they are hard to see even if they are close. 2. The parallax of the bright star Vega is 0.129 seconds of arc. What is the distance of Vega in parsecs ? In light-years ? We have ...
Mr. Scharff
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
Stellar Evolution
... massive stars after a supernova. • Very small ~ 30 km across • Density of 2 x 1014 • Would be comparative to 1 sugar cube = mass of humanity ...
... massive stars after a supernova. • Very small ~ 30 km across • Density of 2 x 1014 • Would be comparative to 1 sugar cube = mass of humanity ...
Review Game
... 44) A cluster where the turn-off point fell in spectral type B must be very: 45) ________ is the means of transport of energy outward by circulating currents of material between hotter and cooler regions inside a star. 46) Collapsed white dwarfs are typically about as big as the: 47) A neutron star ...
... 44) A cluster where the turn-off point fell in spectral type B must be very: 45) ________ is the means of transport of energy outward by circulating currents of material between hotter and cooler regions inside a star. 46) Collapsed white dwarfs are typically about as big as the: 47) A neutron star ...
SECTION 30.2 Measuring the Stars 1. Constellations are a. the
... 3. Scientists measure distances to stars and observe how stars interact with one another to a. determine if stars are right next to each other. b. determine if stars are touching. c. determine the names of constellations. d. determine which stars are gravitationally bound to each other. 4. Astronome ...
... 3. Scientists measure distances to stars and observe how stars interact with one another to a. determine if stars are right next to each other. b. determine if stars are touching. c. determine the names of constellations. d. determine which stars are gravitationally bound to each other. 4. Astronome ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.