Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... D. T-Tauri stars E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR ...
... D. T-Tauri stars E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR ...
Other Objects in Space
... Meteorites are any objects that fall to Earth. The sun is the largest kind of star. All stars become supernovas. ...
... Meteorites are any objects that fall to Earth. The sun is the largest kind of star. All stars become supernovas. ...
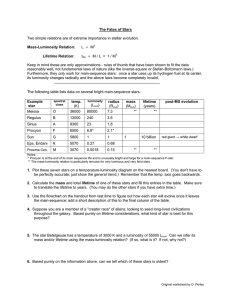
Calculating Main Sequence Lifetimes
... If we remember that the Sun’s mass is 2 × 10 Kg, and knowing the stellar mass, we can calculate the period in which the star burns Hydrogen, which the time it stays as a main sequence star. The star turns off: the star exhausts the Hydrogen in its core and it continues to burn it in shells.. For a ‘ ...
... If we remember that the Sun’s mass is 2 × 10 Kg, and knowing the stellar mass, we can calculate the period in which the star burns Hydrogen, which the time it stays as a main sequence star. The star turns off: the star exhausts the Hydrogen in its core and it continues to burn it in shells.. For a ‘ ...
F03HW09
... What does luminosity measure that is different from what absolute visual magnitude measure? The luminosity is a measure of the total amount of energy emitted by a star in one second. The absolute visual magnitude is related to the portion of the total luminosity emitted only in the visible portion o ...
... What does luminosity measure that is different from what absolute visual magnitude measure? The luminosity is a measure of the total amount of energy emitted by a star in one second. The absolute visual magnitude is related to the portion of the total luminosity emitted only in the visible portion o ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-7. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from Earth, which one looks brighter in the night sky? Explain why.? The blue star, being hotter than the red star, will appear brighter since the two stars are the same size and same distance from the earth ...
... 10-7. If a red star and a blue star both have the same radius and both are the same distance from Earth, which one looks brighter in the night sky? Explain why.? The blue star, being hotter than the red star, will appear brighter since the two stars are the same size and same distance from the earth ...
I. Parallax
... _______________. Because of Earth’s orbit around the Sun, this happens when astronomers view a “nearby” star at ___ _________________________. C. An example of this is when you hold your finger ___________ ________________and view it first with ________ and then the _________. D. The term parallax i ...
... _______________. Because of Earth’s orbit around the Sun, this happens when astronomers view a “nearby” star at ___ _________________________. C. An example of this is when you hold your finger ___________ ________________and view it first with ________ and then the _________. D. The term parallax i ...
HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
January
... dog) and Canis Minor (the little dog) to the West follow Orion. Other constellations to note: Taurus, Perseus, Andromeda, Pegasus (the great square of Pegasus the flying horse - the symbol of Mobil gas - is to the Northeast near the horizon), Gemini, Canis Major, Aurica and Leo. Stars: Betelgense (r ...
... dog) and Canis Minor (the little dog) to the West follow Orion. Other constellations to note: Taurus, Perseus, Andromeda, Pegasus (the great square of Pegasus the flying horse - the symbol of Mobil gas - is to the Northeast near the horizon), Gemini, Canis Major, Aurica and Leo. Stars: Betelgense (r ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables to count. A._________________ B._________________ 2. In Table 10.1, the brightest stars, how many stars are brighter than the sun? Brighter means lower magnitude (M) not higher. If double both must be consi ...
... (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables to count. A._________________ B._________________ 2. In Table 10.1, the brightest stars, how many stars are brighter than the sun? Brighter means lower magnitude (M) not higher. If double both must be consi ...
Stars, Constellations, and Quasars
... Great Bear), which includes the Big Dipper, and Ursa Minor (the Little Bear), which includes the Little Dipper. Polaris, which is also known as the North Star or the Pole Star, is an important star in the handle of Ursa Minor. Polaris takes its name from the fact that Earth’s rotational axis (north ...
... Great Bear), which includes the Big Dipper, and Ursa Minor (the Little Bear), which includes the Little Dipper. Polaris, which is also known as the North Star or the Pole Star, is an important star in the handle of Ursa Minor. Polaris takes its name from the fact that Earth’s rotational axis (north ...
Astronomy - The-A-List
... answer questions relating to orbital motions of binary and multiple star systems Use parallax, spectroscopic parallax, and the distance modulus to calculate distances to Type I and II Cepheids ...
... answer questions relating to orbital motions of binary and multiple star systems Use parallax, spectroscopic parallax, and the distance modulus to calculate distances to Type I and II Cepheids ...
File
... Use language we can comprehend. Tell us what elements you blend. It gives us strangely little aid, But does tell something in the end. And steadfast as Keats' Eremite, Not even stooping from its sphere, It asks a little of us here. It asks of us a certain height, So when at times the mob is swayed T ...
... Use language we can comprehend. Tell us what elements you blend. It gives us strangely little aid, But does tell something in the end. And steadfast as Keats' Eremite, Not even stooping from its sphere, It asks a little of us here. It asks of us a certain height, So when at times the mob is swayed T ...
Sun and Stars
... nuclear fusion in its core. This nuclear fusion releases energy which travels through the star's different layers and then radiates into outer space. ...
... nuclear fusion in its core. This nuclear fusion releases energy which travels through the star's different layers and then radiates into outer space. ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
... and size. Supergiant star, giant star, medium-sized star, white dwarf star, neutron star A star’s color reveals its temperature. Red, yellow - white, blue - white Brightness depends on the star’s size and temperature. It’s brightness as seen from Earth. Apparent brightness is how bright it appears t ...
ref H-R Spectral types
... Sirius A is a type A star, but it has a dwarf companion (Sirius B) which is a type O but is too small to see here. Other examples include Meissa, or Orionis lambda in the constellation Orion (actually, in Orion’s helmet!). ...
... Sirius A is a type A star, but it has a dwarf companion (Sirius B) which is a type O but is too small to see here. Other examples include Meissa, or Orionis lambda in the constellation Orion (actually, in Orion’s helmet!). ...
lifedeath - University of Glasgow
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Friday, August 29
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... The Hyades is the nearest open star cluster to the Solar System at about 150 lightyears away and thus, one of the beststudied of all star clusters. It consists of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its b ...
... The Hyades is the nearest open star cluster to the Solar System at about 150 lightyears away and thus, one of the beststudied of all star clusters. It consists of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its b ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... How Is a Star’s Color Related to Its Temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell ...
... How Is a Star’s Color Related to Its Temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Stars, Galaxies, and Constellations Stars = objects in space, made of gases, which produce their own light and heat. Earth’s nearest star is the sun (149,600,000 km away) The next nearest star is Proxima Centauri (4.24 light years away) Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light trave ...
... Stars, Galaxies, and Constellations Stars = objects in space, made of gases, which produce their own light and heat. Earth’s nearest star is the sun (149,600,000 km away) The next nearest star is Proxima Centauri (4.24 light years away) Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light trave ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.