RFS_315_answers
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
Ch 28 Fact Sheet
... _________________ 24. Synonym for Cepheid variable _________________ 25. The apparent path that the sun (and planets) appear to move along against the star background _________________26. # of crests passing by a spot in a set amount of time. ________________ 27. List, in order, the steps of the li ...
... _________________ 24. Synonym for Cepheid variable _________________ 25. The apparent path that the sun (and planets) appear to move along against the star background _________________26. # of crests passing by a spot in a set amount of time. ________________ 27. List, in order, the steps of the li ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... Southern Cross rising (Centaurus) Taurus (The Bull) Ursa Major (Big Bear) Ursa Minor (Little Bear) Virgo (Maiden) FIRST MAGNITUDE STARS - First magnitude stars are the 20 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale in the 1st century B.C.. A ...
... Southern Cross rising (Centaurus) Taurus (The Bull) Ursa Major (Big Bear) Ursa Minor (Little Bear) Virgo (Maiden) FIRST MAGNITUDE STARS - First magnitude stars are the 20 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale in the 1st century B.C.. A ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... • Neutron Stars are the smallest. They are made of the material left behind after a larger star explodes; about 20 kilometers in diameter. ...
... • Neutron Stars are the smallest. They are made of the material left behind after a larger star explodes; about 20 kilometers in diameter. ...
The 22 First Magnitude Stars
... • Changes orientation of equatorial coordinate system • Pole star changes (Thuban Polaris Vega) • Vernal equinox (“first point of Aries”) is now in Pisces; moving westward into Aquarius • Tropics of Cancer/Capricorn are really Gemini/Sagittarius today • Star charts change orientation or Epoch (1 ...
... • Changes orientation of equatorial coordinate system • Pole star changes (Thuban Polaris Vega) • Vernal equinox (“first point of Aries”) is now in Pisces; moving westward into Aquarius • Tropics of Cancer/Capricorn are really Gemini/Sagittarius today • Star charts change orientation or Epoch (1 ...
How Bright is that Star?
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
Sky Notes - April 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
... moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of _____________________ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of _____________________ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
Stars
... A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the s ...
... A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the s ...
Nights of the Heavenly G With
... sweeping to Aldebaran in the Bull, and then cutting back down to Orion's belt. You will have learned most of the winter stars, and traced out a giant letter "G" taking up nearly half the starry sky! Taking a closer look, let's begin with the "star of middle age," Capella. Even though various distanc ...
... sweeping to Aldebaran in the Bull, and then cutting back down to Orion's belt. You will have learned most of the winter stars, and traced out a giant letter "G" taking up nearly half the starry sky! Taking a closer look, let's begin with the "star of middle age," Capella. Even though various distanc ...
Characteristics of Stars
... luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
Diapositiva 1
... Ursa Minor is a constellation of the northern sky. It is especially known because within it lies the north celestial pole, although its position is subject to a continuous, slow movement due to the precession of the Earth's rotation. The Little Dipper is easily identifiable because, once detected th ...
... Ursa Minor is a constellation of the northern sky. It is especially known because within it lies the north celestial pole, although its position is subject to a continuous, slow movement due to the precession of the Earth's rotation. The Little Dipper is easily identifiable because, once detected th ...
File
... 15) What is an H-R Diagram. (be able to interpret an H-R diagram) 16) List in order the colors of stars from hottest to coolest. 17) What is a binary star system? ...
... 15) What is an H-R Diagram. (be able to interpret an H-R diagram) 16) List in order the colors of stars from hottest to coolest. 17) What is a binary star system? ...
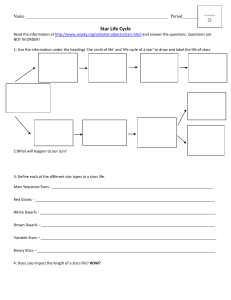
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
The Milky Way
... • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most dramatic cycles in the sky. ...
... • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most dramatic cycles in the sky. ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
January 2012 - Powerhouse Museum
... Jupiter is easily seen as the brightest object towards the north. Venus remains visible in the early evening as a bright object towards the west. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 1st or 31st. The first qua ...
... Jupiter is easily seen as the brightest object towards the north. Venus remains visible in the early evening as a bright object towards the west. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 1st or 31st. The first qua ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... The positions of the constellations appear to change throughout the year because _____. (a) the sun revolves around the galaxy, (b) Earth revolves around the sun, (c) the constellations revolve around Earth, (d) Earth revolves around the stars. ...
... The positions of the constellations appear to change throughout the year because _____. (a) the sun revolves around the galaxy, (b) Earth revolves around the sun, (c) the constellations revolve around Earth, (d) Earth revolves around the stars. ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... Learn the 12 constellations called the signs of the zodiac. Know the history of the signs of the zodiac. ...
... Learn the 12 constellations called the signs of the zodiac. Know the history of the signs of the zodiac. ...
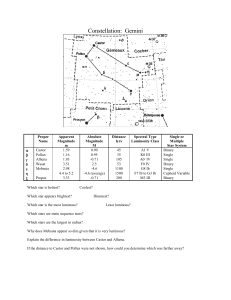
Gemini
... cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and ora ...
... cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and ora ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.