Northern Hemisphere – December 2012
... in Taurus in the south, helping us to see it with little atmospheric interference. It is 5 degrees to the upper left of the star Aldebaran at the start of December, moving westwards towards the Pleiades in its retrograde motion during the month. With an angular size of around 48", plenty of detail c ...
... in Taurus in the south, helping us to see it with little atmospheric interference. It is 5 degrees to the upper left of the star Aldebaran at the start of December, moving westwards towards the Pleiades in its retrograde motion during the month. With an angular size of around 48", plenty of detail c ...
red shift blue shift
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
February 2008
... bright and it was easy to mark it’s yearly arrival. On January 1st this year, Sirius was right at due South at midnight. Sirius is twice as large as the Sun and has double it’s mass. It produces more than 20 times the light as the Sun. That isn’t really super bright, but since Sirius is only 8.6 lig ...
... bright and it was easy to mark it’s yearly arrival. On January 1st this year, Sirius was right at due South at midnight. Sirius is twice as large as the Sun and has double it’s mass. It produces more than 20 times the light as the Sun. That isn’t really super bright, but since Sirius is only 8.6 lig ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
PISGAH Dr. Bob Hayward ASTRONOMICAL Astronomer/Educator
... star. This is Sirius the Dog Star. While Sirius appears to be the brightest star in the nighttime sky, it is not intrinsically the brightest nor is it the closest to us. But it is a combination of both so that it appears to be the brightest; it is a white-hot star that is a little less than nine lig ...
... star. This is Sirius the Dog Star. While Sirius appears to be the brightest star in the nighttime sky, it is not intrinsically the brightest nor is it the closest to us. But it is a combination of both so that it appears to be the brightest; it is a white-hot star that is a little less than nine lig ...
Stars - etpt2020s11
... The Sun Located in the center of our solar system is the brightest of all the stars, the sun. The sun is the closest star to the Earth. Due to the spatial arrangement of the Earth and the Sun, it sun is visible to us and responsible for most of the Earth’s energy. ...
... The Sun Located in the center of our solar system is the brightest of all the stars, the sun. The sun is the closest star to the Earth. Due to the spatial arrangement of the Earth and the Sun, it sun is visible to us and responsible for most of the Earth’s energy. ...
City Built Over Caves To be Explored in Mexico
... to the mythological story. Another planet decorates the eastern morning sky just before sunrise. This is Venus, now the "morning star," which rises about four hours before the sun. lt is in the constellation of Virgo, and on the first of December is just north of the star Spica, so that the two will ...
... to the mythological story. Another planet decorates the eastern morning sky just before sunrise. This is Venus, now the "morning star," which rises about four hours before the sun. lt is in the constellation of Virgo, and on the first of December is just north of the star Spica, so that the two will ...
Relative sizes of astronomical objects
... Viewed in comparison to the Sun, Earth dwindles to a speck. Our sun is classified as an unremarkable yellow dwarf main sequence star – one of over 100 million such stars in our galaxy. However, it alone accounts for 99.9% of the mass of our solar system, including all the planets, satellites (moons) ...
... Viewed in comparison to the Sun, Earth dwindles to a speck. Our sun is classified as an unremarkable yellow dwarf main sequence star – one of over 100 million such stars in our galaxy. However, it alone accounts for 99.9% of the mass of our solar system, including all the planets, satellites (moons) ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What is the apparent magnitude of Jupiter ? _____-2.0_______________ How much brighter is the moon than Jupiter ? ____10,000_____________ Can a 15 cm telescope see an object with an apparent magnitude of 18.5 ? _______NO____________ ...
... What is the apparent magnitude of Jupiter ? _____-2.0_______________ How much brighter is the moon than Jupiter ? ____10,000_____________ Can a 15 cm telescope see an object with an apparent magnitude of 18.5 ? _______NO____________ ...
Constellations
... Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? ...
... Imagine you are standing at the North Pole and see a star directly overhead. Where do you think the star would be if you were standing at the equator? ...
The Northern Winter Constellations - Science
... shooting Orion on a bet. When she discovered that she had shot Orion, she quickly lifted him to the heavens and made him immortal, where he now hunts eternally with his two dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor. In front of him is his prey Taurus the Bull. The myths surrounding Auriga the Charioteer var ...
... shooting Orion on a bet. When she discovered that she had shot Orion, she quickly lifted him to the heavens and made him immortal, where he now hunts eternally with his two dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor. In front of him is his prey Taurus the Bull. The myths surrounding Auriga the Charioteer var ...
Chapter 29 Stellar Evolution
... composition & surface temperature of a star. • Explain why stars appear to move to an observer on the earth. • Name & describe the way astronomers measure the distance from the earth to the stars. • Explain the difference between absolute ...
... composition & surface temperature of a star. • Explain why stars appear to move to an observer on the earth. • Name & describe the way astronomers measure the distance from the earth to the stars. • Explain the difference between absolute ...
The Northern Winter Constellations
... shooting Orion on a bet. When she discovered that she had shot Orion, she quickly lifted him to the heavens and made him immortal, where he now hunts eternally with his two dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor. In front of him is his prey Taurus the Bull. The myths surrounding Auriga the Charioteer var ...
... shooting Orion on a bet. When she discovered that she had shot Orion, she quickly lifted him to the heavens and made him immortal, where he now hunts eternally with his two dogs, Canis Major and Canis Minor. In front of him is his prey Taurus the Bull. The myths surrounding Auriga the Charioteer var ...
observingopenclusters-2-2-1
... reason for its brightness is both its intrinsic luminosity and closeness to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You will pick up a large rich field of stars – Open Cluster M41 Procyon (Canis Minor) Locate next large and (also close) Proc ...
... reason for its brightness is both its intrinsic luminosity and closeness to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You will pick up a large rich field of stars – Open Cluster M41 Procyon (Canis Minor) Locate next large and (also close) Proc ...
Homework 7
... 2. Why are carbonaceous chondritic meteorites thought to be the oldest pristine material from the inner solar system? ...
... 2. Why are carbonaceous chondritic meteorites thought to be the oldest pristine material from the inner solar system? ...
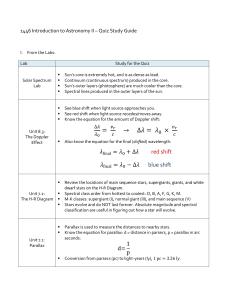
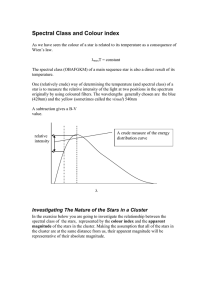
Spectral Class and Colour index
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
1 - Pitt County Schools
... Chapter 25 Concept Questions Name:_______________________________Date:___________________ 1. Absolute magnitude: 2. Apparent magnitude: 3. Big band theory: 4. Binary star: ...
... Chapter 25 Concept Questions Name:_______________________________Date:___________________ 1. Absolute magnitude: 2. Apparent magnitude: 3. Big band theory: 4. Binary star: ...
SNC1PL Celestial Objects and Constellations
... Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
... Ion tail is created by solar wind reacting with material on the comet to produce a tail that is directed away from the comet ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.