Characteristics of Stars
... Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) ...
... Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) ...
chap17_s05_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
chap17_f04_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
Astronomy
... Ursa Major and Ursa Minor • Artemis, the moon goddess and goddess of the hunt, always had hunting companions with her when she went on the hunt. One such companion was Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself ...
... Ursa Major and Ursa Minor • Artemis, the moon goddess and goddess of the hunt, always had hunting companions with her when she went on the hunt. One such companion was Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself ...
Astronomy Problems – Color Index Nov. 2011
... Colors of Stars Astronomers measure the brightness of stars at three colors of light: The "U" band at 360 nm The "B" band at 440 nm The "V" band at 540 nm The "color index" of a star is defined as the magnitude in the B filter, minus the magnitude in the V filter. Color Index = B-V, where B an ...
... Colors of Stars Astronomers measure the brightness of stars at three colors of light: The "U" band at 360 nm The "B" band at 440 nm The "V" band at 540 nm The "color index" of a star is defined as the magnitude in the B filter, minus the magnitude in the V filter. Color Index = B-V, where B an ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
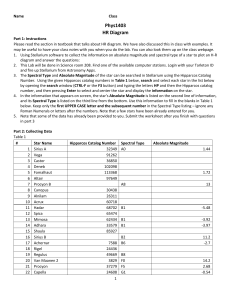
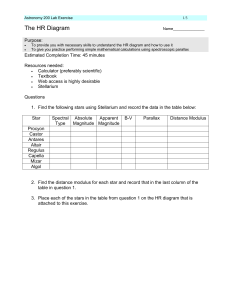
... 4. In the information that appears on screen, the star's Absolute Magnitude is listed on the second line of information, and its Spectral Type is listed on the third line from the bottom. Use this information to fill in the blanks in Table 1 below. Keep only the first UPPER CASE letter and the subse ...
... 4. In the information that appears on screen, the star's Absolute Magnitude is listed on the second line of information, and its Spectral Type is listed on the third line from the bottom. Use this information to fill in the blanks in Table 1 below. Keep only the first UPPER CASE letter and the subse ...
User`s Guide to the Sky Notes
... As you observe the night sky, your view is limited to a few thousand stars that are close enough, big enough, and bright enough for us to see from our vantage point in the galaxy. Some things you think are stars are actually distant galaxies that are so far away, the light from its billions of stars ...
... As you observe the night sky, your view is limited to a few thousand stars that are close enough, big enough, and bright enough for us to see from our vantage point in the galaxy. Some things you think are stars are actually distant galaxies that are so far away, the light from its billions of stars ...
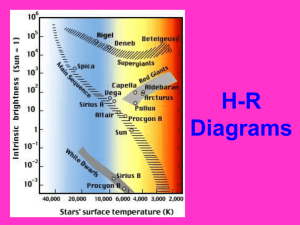
H-R Diagrams
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
9 spectroscopic parallax
... Absolute magnitude = how bright (what magnitude) a star would appear at 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) ...
... Absolute magnitude = how bright (what magnitude) a star would appear at 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... The term magnitude is used to describe the brightness of a star' Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the ...
... The term magnitude is used to describe the brightness of a star' Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the ...
The Constellation Microscopium, the Microscope Microscopium is a
... Piscis Austrinus and Grus to the west, Sagittarius to the east, Indus to the south, and touching on Telescopium to the southeast. The recommended three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted Seen in the 1824 star chart set Urania's Mirror (lower left) by the International Astronomical ...
... Piscis Austrinus and Grus to the west, Sagittarius to the east, Indus to the south, and touching on Telescopium to the southeast. The recommended three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted Seen in the 1824 star chart set Urania's Mirror (lower left) by the International Astronomical ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
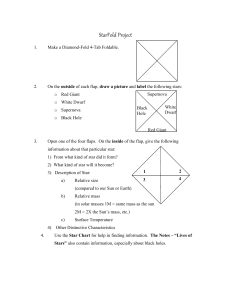
206a StarFold Lab Instructions
... On the outside of each flap, draw a picture and label the following stars: o Red Giant ...
... On the outside of each flap, draw a picture and label the following stars: o Red Giant ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
chapter 18
... A faint white dwarf that temporarily increases in brightness as a consequence of nuclear explosions on its surface is termed a) a nova. b) a Type II supernova. c) a bright nebula. d) a red giant. ...
... A faint white dwarf that temporarily increases in brightness as a consequence of nuclear explosions on its surface is termed a) a nova. b) a Type II supernova. c) a bright nebula. d) a red giant. ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
labex7
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
Earth
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.