The Future Sun
... Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Perseus has hotter stars than Pleiades. b. Most stars are one the main sequence. c. Perseus has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
... Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Perseus has hotter stars than Pleiades. b. Most stars are one the main sequence. c. Perseus has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
Stars
... • Earth rotates on its axis, this makes most constellations appear to rise in the east and set in the west during the night. • Most constellations appear in many different positions in the sky as the Earth revolves around the sun. • There is a group of stars that appear in the sky all night long and ...
... • Earth rotates on its axis, this makes most constellations appear to rise in the east and set in the west during the night. • Most constellations appear in many different positions in the sky as the Earth revolves around the sun. • There is a group of stars that appear in the sky all night long and ...
E3 – Stellar distances
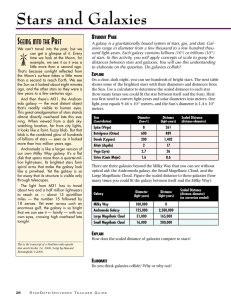
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... Patterns of stars: Constellations Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations. Constellations: Patterns of stars in the night sky ...
... Patterns of stars: Constellations Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations. Constellations: Patterns of stars in the night sky ...
Star Jeopardy Review #2
... Event Horizon Math problem: Calculate the Scharzchild radius for the sun using the following: R=2GM/c2 M=1.9x1030 kg G=6.67x10-11 Nm2/kg2 C=3x108 m/sec ...
... Event Horizon Math problem: Calculate the Scharzchild radius for the sun using the following: R=2GM/c2 M=1.9x1030 kg G=6.67x10-11 Nm2/kg2 C=3x108 m/sec ...
Astr604-Ch1
... A star can be defined as a body that satisfies two conditions: (a) it is bound by self-gravity; (b) it radiates energy supplied by an internal source. From the first condition it follows that the shape of such a body must be a spherical, for gravity is a spherical symmetric force field. Or, it might ...
... A star can be defined as a body that satisfies two conditions: (a) it is bound by self-gravity; (b) it radiates energy supplied by an internal source. From the first condition it follows that the shape of such a body must be a spherical, for gravity is a spherical symmetric force field. Or, it might ...
Double Stars in Scorpio`s Claws
... but you should be able to see two dim red stars that form a line with brighter ρ Scorpii between them. ...
... but you should be able to see two dim red stars that form a line with brighter ρ Scorpii between them. ...
www.aavso.org
... The most popularly accepted model for this companion object is a binary star system surrounded by a massive, opaque disk of dust ...
... The most popularly accepted model for this companion object is a binary star system surrounded by a massive, opaque disk of dust ...
Star in a Box Worksheet - Beginning with solutions
... 1. What stages of their lives are the two stars in? Deneb is between the main sequence and the Hertzsprung Gap. Betelgeuse is between the Hertzsprung Gap and core helium burning. 2. How long does each star have to live? D eneb has about 1 million years left to live and Betelgeuse has about 400 th ...
... 1. What stages of their lives are the two stars in? Deneb is between the main sequence and the Hertzsprung Gap. Betelgeuse is between the Hertzsprung Gap and core helium burning. 2. How long does each star have to live? D eneb has about 1 million years left to live and Betelgeuse has about 400 th ...
Astro 210 Lecture 4 Sept. 4, 2013 Announcements: • PS 1 available
... Recall: color related to Temperature Dr. Wien’s amazing law says colder: redder; hotter: bluer ...
... Recall: color related to Temperature Dr. Wien’s amazing law says colder: redder; hotter: bluer ...
10.5 The Hertzsprung
... The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
... The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
STUDY GUIDE:
... system explode in the course of a day. Temporarily, this can make their system 300,000 times brighter than the sun. This brightness lasts for a few days or weeks, and then lessens gradually, leaving the stars about the same as they were before. In 1992, Nova Cygni, in the northern constellation Cygn ...
... system explode in the course of a day. Temporarily, this can make their system 300,000 times brighter than the sun. This brightness lasts for a few days or weeks, and then lessens gradually, leaving the stars about the same as they were before. In 1992, Nova Cygni, in the northern constellation Cygn ...
1-1 H. Color Index: A color index is the difference of two color
... Distance modulus is an indicator of the distance of an object expressed in terms of its absolute and apparent magnitudes. More specifically, distance modulus is defined as m-M. If the distance modulus is 0, the object is 10 parsecs distant. If m-M is less than zero or negative, this means the object ...
... Distance modulus is an indicator of the distance of an object expressed in terms of its absolute and apparent magnitudes. More specifically, distance modulus is defined as m-M. If the distance modulus is 0, the object is 10 parsecs distant. If m-M is less than zero or negative, this means the object ...
Astronomy Unit Period
... __________ 34. Which of the following statements is NOT true of supernovas? a. They are explosions in which a massive star collapses. b. They are explosions that occur at the beginning of a star’s life. c. They can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days. d. They are explosions in which a ...
... __________ 34. Which of the following statements is NOT true of supernovas? a. They are explosions in which a massive star collapses. b. They are explosions that occur at the beginning of a star’s life. c. They can be brighter than an entire galaxy for several days. d. They are explosions in which a ...
Stars and Galaxies
... little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the Sun as it looked about eight minutes ago, and the other stars as they were a few years to a few centuries ago. And then there’s M31, the Andromeda gal ...
... little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the Sun as it looked about eight minutes ago, and the other stars as they were a few years to a few centuries ago. And then there’s M31, the Andromeda gal ...
Stars in the night Sky - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the ...
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the ...
Quiz Chapter 10 Answers
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
Print Activity - Let`s Talk Science
... 4. If you don’t have access to glow-in-the-dark stickers, you can cover the end of a flashlight with red cellophane and shine this on the image when you’re outside (this way you can look at the image and the night sky without losing your ‘night vision’). 5. Go outside to a dark area where you have a ...
... 4. If you don’t have access to glow-in-the-dark stickers, you can cover the end of a flashlight with red cellophane and shine this on the image when you’re outside (this way you can look at the image and the night sky without losing your ‘night vision’). 5. Go outside to a dark area where you have a ...
1. absolute brightness -
... to their spectral characteristics. • They are classified according to the spectral lines observed, originally the amount of Hydrogen the lines seemed to indicate. • Today they are ranked in order of surface temperature. O, B, A, F, G, K, M from hottest to coolest. ...
... to their spectral characteristics. • They are classified according to the spectral lines observed, originally the amount of Hydrogen the lines seemed to indicate. • Today they are ranked in order of surface temperature. O, B, A, F, G, K, M from hottest to coolest. ...
Galaxy Powerpoint
... • A. Different constellations can be seen at different times of the year.. • i. Due to the Earth’s revolution around the Sun. • Ii. Ex. Orion can be seen in the winter and spring . Pegasus can only be seen in summer and fall. ...
... • A. Different constellations can be seen at different times of the year.. • i. Due to the Earth’s revolution around the Sun. • Ii. Ex. Orion can be seen in the winter and spring . Pegasus can only be seen in summer and fall. ...
16. Properties of Stars
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
... When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, and then black dwarfs. For stars larger than our sun, after main sequence and giant s ...
... When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, and then black dwarfs. For stars larger than our sun, after main sequence and giant s ...
Russell Diagram
... massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
... massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.