The Night Sky
... Annual motion of the stars The same stars are not visible all year long. Any given non-circumpolar star will set 4 minutes early each day until it becomes lost in the glare of the setting Sun. ...
... Annual motion of the stars The same stars are not visible all year long. Any given non-circumpolar star will set 4 minutes early each day until it becomes lost in the glare of the setting Sun. ...
iClicker Questions
... Discovering the Universe, Eighth Edition by Neil F. Comins and William J. Kaufmann III Chapter 12 12-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust * c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are al ...
... Discovering the Universe, Eighth Edition by Neil F. Comins and William J. Kaufmann III Chapter 12 12-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust * c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are al ...
Chapter 9 “The Family of Stars “
... Mars' orbit is larger than Earth's, and stars would show a larger parallax when observed from Mars as compared to Earth. We would be able to determine the distance to nearby stars more accurately and determine the distance to stars that are currently too far to be measured using parallax from Earth. ...
... Mars' orbit is larger than Earth's, and stars would show a larger parallax when observed from Mars as compared to Earth. We would be able to determine the distance to nearby stars more accurately and determine the distance to stars that are currently too far to be measured using parallax from Earth. ...
File - Adopt A Constellation
... • Constellations - A pattern or group of stars in the sky that humans observe in a pattern and give a name. • People of ancient time saw the constellations as character or animals in the sky. They made up stories to explain how the object, animal, or character came into the night sky • Earth rotate ...
... • Constellations - A pattern or group of stars in the sky that humans observe in a pattern and give a name. • People of ancient time saw the constellations as character or animals in the sky. They made up stories to explain how the object, animal, or character came into the night sky • Earth rotate ...
Northern and Southern Hemisphere Star Chart
... the Sun, actually small and dim M type stars called red dwarfs (stars physically smaller than our Sun are classed as dwarf stars) seem to be the most common stars in space, at least in our part of the Milky Way galaxy. Of the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 are M-type red dwarf stars, too dim be se ...
... the Sun, actually small and dim M type stars called red dwarfs (stars physically smaller than our Sun are classed as dwarf stars) seem to be the most common stars in space, at least in our part of the Milky Way galaxy. Of the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 are M-type red dwarf stars, too dim be se ...
ReviewQuestionsForClass
... Where are the red giants? White dwarfs? Why are they where they are on an HR diagram? How do size, temperature, and distance to a star affect its brightness? Which stars on the main sequence are the brightest? Hottest? Biggest? Bluest? Live the longest? What are the different astronomical objects? C ...
... Where are the red giants? White dwarfs? Why are they where they are on an HR diagram? How do size, temperature, and distance to a star affect its brightness? Which stars on the main sequence are the brightest? Hottest? Biggest? Bluest? Live the longest? What are the different astronomical objects? C ...
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... The night-adapted naked eye, under dark, moonless skies at sea level, may discern stars as faint as magnitude 6. (In the astronomical apparent-magnitude scale, increasing brightest corresponds to smaller numbers.) However, these conditions rarely exist on Rapa Nui, even in pre-historic times. It se ...
... The night-adapted naked eye, under dark, moonless skies at sea level, may discern stars as faint as magnitude 6. (In the astronomical apparent-magnitude scale, increasing brightest corresponds to smaller numbers.) However, these conditions rarely exist on Rapa Nui, even in pre-historic times. It se ...
1st EXAM VERSION C - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... bluer and fainter than the cooler object C. redder and brighter than the cooler object D. redder and fainter than the cooler object E. None of the above can be true. 33. The following table gives the name, absolute magnitude (M), apparent magnitude (m), and spectral type for five stars. Answer the f ...
... bluer and fainter than the cooler object C. redder and brighter than the cooler object D. redder and fainter than the cooler object E. None of the above can be true. 33. The following table gives the name, absolute magnitude (M), apparent magnitude (m), and spectral type for five stars. Answer the f ...
Lecture notes -- pdf file - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... in 1838 (Friedrich Bessel) • Closest star is Alpha Centauri, p=0.75 arcseconds, d=1.33 parsecs= 4.35 light years • Nearest stars are a few to many parsecs, 5 - 20 light years ...
... in 1838 (Friedrich Bessel) • Closest star is Alpha Centauri, p=0.75 arcseconds, d=1.33 parsecs= 4.35 light years • Nearest stars are a few to many parsecs, 5 - 20 light years ...
08 September: How far away are the closest stars?
... • If the distance between the Earth and Sun were shrunk to 1 cm (0.4 inches), Alpha Centauri would be 2.75 km (1.7 miles) away ...
... • If the distance between the Earth and Sun were shrunk to 1 cm (0.4 inches), Alpha Centauri would be 2.75 km (1.7 miles) away ...
1 Sep: 6.13am BST 15 Sep: 6.43am BST 30 Sep: 7.14am BST
... Looking southwest the sky is dominated by the constellations of Cygnus (the Swan), Lyra (the Lyre) and Aquila (the Eagle) whose brightest stars of Deneb, Vega and Altair respectively make up the Summer Triangle. The Swan’s beak is marked by Albireo and halfway between Albireo and Altair is Sagitta ( ...
... Looking southwest the sky is dominated by the constellations of Cygnus (the Swan), Lyra (the Lyre) and Aquila (the Eagle) whose brightest stars of Deneb, Vega and Altair respectively make up the Summer Triangle. The Swan’s beak is marked by Albireo and halfway between Albireo and Altair is Sagitta ( ...
The Stars - University of Redlands
... the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI prod ...
... the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI prod ...
Properties of Stars
... 10. Our Sun has a temperature of 5800 K (which is 6073°Celsius) and an absolute magnitude of +4.7. Use a “” symbol to plot the location of the Sun on your diagram. To which group does the Sun belong? (label it “Sun” on your graph also) 11. Compare the absolute magnitude and temperature of the Sun w ...
... 10. Our Sun has a temperature of 5800 K (which is 6073°Celsius) and an absolute magnitude of +4.7. Use a “” symbol to plot the location of the Sun on your diagram. To which group does the Sun belong? (label it “Sun” on your graph also) 11. Compare the absolute magnitude and temperature of the Sun w ...
Introduction to the sky
... are very small fractions of a degree each year. Thus, we can make a star catalogue or star chart that is useful for observers at any location on the Earth. For example, the coordinates of Betelgeuse in the year 2000 were RA = 5 hours 55 minutes 10.3 seconds, DEC = +7 deg 24' 25”. ...
... are very small fractions of a degree each year. Thus, we can make a star catalogue or star chart that is useful for observers at any location on the Earth. For example, the coordinates of Betelgeuse in the year 2000 were RA = 5 hours 55 minutes 10.3 seconds, DEC = +7 deg 24' 25”. ...
Introduction to the sky
... If we draw a line from the zenith through a celestial object and extend that line to the horizon, we obtain the azimuth angle of the object. By convention, the north point on the horizon has azimuth 0 degrees, the east point has azimuth 90 degrees, the south point has azimuth 180 degrees, and the w ...
... If we draw a line from the zenith through a celestial object and extend that line to the horizon, we obtain the azimuth angle of the object. By convention, the north point on the horizon has azimuth 0 degrees, the east point has azimuth 90 degrees, the south point has azimuth 180 degrees, and the w ...
Astrology, calendars and the dating of Christian festivals.
... earth. It is much more luminous, intrinsically, than the sole star that appears brighter than it from Earth—Sirius which is a mere 22 times more luminous than our sun, and depends on being much closer to us to beat its rival in apparent magnitude. In fact, for a large fraction of stars in the local ...
... earth. It is much more luminous, intrinsically, than the sole star that appears brighter than it from Earth—Sirius which is a mere 22 times more luminous than our sun, and depends on being much closer to us to beat its rival in apparent magnitude. In fact, for a large fraction of stars in the local ...
Constellations and the Galactic Plane
... cities, that forms the plane of our galaxy. Altair and Deneb are very close to this plane. In fact the plane is best seen during the summer-fall months. In November, the milky way is spanned, from southwest to northeast through the zenith, by the constellations Aquila (with Altair), Cygnus (the “nor ...
... cities, that forms the plane of our galaxy. Altair and Deneb are very close to this plane. In fact the plane is best seen during the summer-fall months. In November, the milky way is spanned, from southwest to northeast through the zenith, by the constellations Aquila (with Altair), Cygnus (the “nor ...
Highlights of the Month - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, simila ...
... Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, simila ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... This is a large bright star with a cool surface. It is formed during the later stages of the evolution of a star like the Sun, as it runs out of hydrogen fuel at its center. Red giants have diameters between 10 and 100 times that of the Sun. They are very bright because they are so large, although t ...
... This is a large bright star with a cool surface. It is formed during the later stages of the evolution of a star like the Sun, as it runs out of hydrogen fuel at its center. Red giants have diameters between 10 and 100 times that of the Sun. They are very bright because they are so large, although t ...
Science Olympiad 2008 Reach for the Stars Division B
... 43,44. Give the name of the two brightest stars in this constellation: 45,46. Give these stars' position on the HR diagram: 47. Identify the single DSO by number in this constellation 48,49. What is the name and Messier Number of this DSO: 50. What type of Object is this DSO (refer to the ...
... 43,44. Give the name of the two brightest stars in this constellation: 45,46. Give these stars' position on the HR diagram: 47. Identify the single DSO by number in this constellation 48,49. What is the name and Messier Number of this DSO: 50. What type of Object is this DSO (refer to the ...
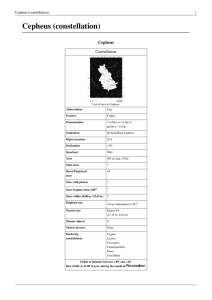
Cepheus (constellation)
... δ Cephei is the prototype Cepheid variable, a yellow-hued supergiant star 980 light-years from Earth. It was discovered to be variable by John Goodricke in 1784. It varies between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei ha ...
... δ Cephei is the prototype Cepheid variable, a yellow-hued supergiant star 980 light-years from Earth. It was discovered to be variable by John Goodricke in 1784. It varies between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei ha ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.