16. Magnitude Systems
... • In this system, the zero-point source is a theoretical source defined such that it truly has a flat SED • In the AB system, the flux zero-point in every filter is defined to be 3631 Jy (Janskys; 1 Jy = 10-26 WHz-1m-2) • Thus, AB magnitude in any passband is given by – m = -2.5log10f +8.9 (magnitud ...
... • In this system, the zero-point source is a theoretical source defined such that it truly has a flat SED • In the AB system, the flux zero-point in every filter is defined to be 3631 Jy (Janskys; 1 Jy = 10-26 WHz-1m-2) • Thus, AB magnitude in any passband is given by – m = -2.5log10f +8.9 (magnitud ...
3.2 Spectra and Spectral Classification
... Φ(R) = Φ(r)/δ2 where δ = R/r is the angular radius of the star ...
... Φ(R) = Φ(r)/δ2 where δ = R/r is the angular radius of the star ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances f ...
... Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances f ...
Interstellar medium, birth and life of stars
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
Lecture 8: The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Out to a distance of 4 pc, 12 light, from the Sun, there are 30 stars. The brightest is Sirius, which can be seen in the night sky. Only 10 are bright enough to see with the naked eye. The rest have been discovered through telescopic surveys of the sky. ...
... Out to a distance of 4 pc, 12 light, from the Sun, there are 30 stars. The brightest is Sirius, which can be seen in the night sky. Only 10 are bright enough to see with the naked eye. The rest have been discovered through telescopic surveys of the sky. ...
Arcturus - bYTEBoss
... Exactly whom Boötes is supposed to represent is not clear. According to one version, he was a ploughman who drove the oxen in the constellation Ursa Major using his two dogs Chara and Asterion (from the constellation Canes Venatici). The oxen were tied to the polar axis and so the action of Boötes k ...
... Exactly whom Boötes is supposed to represent is not clear. According to one version, he was a ploughman who drove the oxen in the constellation Ursa Major using his two dogs Chara and Asterion (from the constellation Canes Venatici). The oxen were tied to the polar axis and so the action of Boötes k ...
Distant Stars - How far away is it
... RR Lyrae – 854 light years RR Lyrae is a variable star like Delta Cephei. As the brightest star in its class, it became the namesake for the RR Lyrae variable class of stars. The relationship between pulsation period and absolute magnitude of RR Lyraes makes them good standard candles. They are not ...
... RR Lyrae – 854 light years RR Lyrae is a variable star like Delta Cephei. As the brightest star in its class, it became the namesake for the RR Lyrae variable class of stars. The relationship between pulsation period and absolute magnitude of RR Lyraes makes them good standard candles. They are not ...
IND 6 - 1 Stars and Stellar Evolution In order to better understand
... layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( > 8 Msun), will eventually explode as a massive star supernova (often known as a “Type II” sup ...
... layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( > 8 Msun), will eventually explode as a massive star supernova (often known as a “Type II” sup ...
Variable star information
... Classical Cepheid variables are highly luminous, yellow giant or supergiant stars that pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses ra ...
... Classical Cepheid variables are highly luminous, yellow giant or supergiant stars that pulsate on a very regular basis. Some of them change in brightness very quickly, over a period of only one day, whereas others are characterised by slower changes and have periods of up to 70 days. Their masses ra ...
uniview glossary - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... Saturn was named for the Roman god of agriculture and lies 885 million miles from the Sun, (9.6 AU). Saturn takes 29.5 years to orbit, but only 10.7 hours to rotate (day). Its diameter is 75,000 miles, making it the second largest planet. Its mass is 95 times that of Earth. It is the second of the f ...
... Saturn was named for the Roman god of agriculture and lies 885 million miles from the Sun, (9.6 AU). Saturn takes 29.5 years to orbit, but only 10.7 hours to rotate (day). Its diameter is 75,000 miles, making it the second largest planet. Its mass is 95 times that of Earth. It is the second of the f ...
Assignment 3 - Physics Internal Website
... Orion (Bellatrix) — B2III, β Orion (Rigel) — B8I, α Canis Major (Sirius) — A1V, α Canis Minor (Procyon) — F5V, α Auriga (Capella) — G6III, β Gemini (Pollux) — K0III, α Taurus (Aldebaran) — K5III, and α Orion (Betelgeuse) — M2I. Display these spectral along a spectral classification sequence so that ...
... Orion (Bellatrix) — B2III, β Orion (Rigel) — B8I, α Canis Major (Sirius) — A1V, α Canis Minor (Procyon) — F5V, α Auriga (Capella) — G6III, β Gemini (Pollux) — K0III, α Taurus (Aldebaran) — K5III, and α Orion (Betelgeuse) — M2I. Display these spectral along a spectral classification sequence so that ...
Modified True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true or false
... ____ 16. HS-ESS1-1 The process in which smaller atomic nuclei combine into larger atomic nuclei is known as a. Gravitational attraction. c. The Doppler effect. b. Parallax. d. Nuclear fusion. ____ 17. HS-ESS1-2 The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called __ ...
... ____ 16. HS-ESS1-1 The process in which smaller atomic nuclei combine into larger atomic nuclei is known as a. Gravitational attraction. c. The Doppler effect. b. Parallax. d. Nuclear fusion. ____ 17. HS-ESS1-2 The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called __ ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B PMS star
... Observational and theoretical evidence is accumulating that massive stars form through disk accretion, similar to low-mass stars. Accretion persists despite the strong radiation pressure and ionizing power produced by the massive young stellar object (YSO) that may prevent matter from accreting (e.g ...
... Observational and theoretical evidence is accumulating that massive stars form through disk accretion, similar to low-mass stars. Accretion persists despite the strong radiation pressure and ionizing power produced by the massive young stellar object (YSO) that may prevent matter from accreting (e.g ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
Preview Sample 2
... The names of stars usually come from ancient Arabic, although modern astronomers often refer to a star by its constellation and a Greek letter assigned according to its brightness within the constellation. How can you compare the brightness of the stars? The magnitude system is the astronomer’s brig ...
... The names of stars usually come from ancient Arabic, although modern astronomers often refer to a star by its constellation and a Greek letter assigned according to its brightness within the constellation. How can you compare the brightness of the stars? The magnitude system is the astronomer’s brig ...
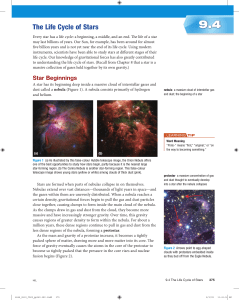
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Stars Like the Sun: Red Giant to White Dwarf After spending approximately 10 billion years as a main sequence star, a star’s available hydrogen will have been converted to helium by nuclear fusion. This results in the formation of a helium-rich core, surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. With le ...
... Stars Like the Sun: Red Giant to White Dwarf After spending approximately 10 billion years as a main sequence star, a star’s available hydrogen will have been converted to helium by nuclear fusion. This results in the formation of a helium-rich core, surrounded by an outer layer of hydrogen. With le ...
V - ESO
... This is generally assumed to be the reason why, though star formation proceeds on a typical scale comparable to the size of a giant molecular cloud (~80 pc, Efremov 1995, AJ 100, 2757), Milky Way massive clusters tend to be much smaller. Image taken from class by James Schombert, University of Oreg ...
... This is generally assumed to be the reason why, though star formation proceeds on a typical scale comparable to the size of a giant molecular cloud (~80 pc, Efremov 1995, AJ 100, 2757), Milky Way massive clusters tend to be much smaller. Image taken from class by James Schombert, University of Oreg ...
Part I: Shining a Light on Visual Magnitude
... the sky, the brightness of the objects it’s looking at is called apparent magnitude. If we’re only considering what the human eye can see, then we’re measuring visual magnitude. This is a relative measurement on a log scale. It’s a ratio of the irradiance (which is the energy of the source over a gi ...
... the sky, the brightness of the objects it’s looking at is called apparent magnitude. If we’re only considering what the human eye can see, then we’re measuring visual magnitude. This is a relative measurement on a log scale. It’s a ratio of the irradiance (which is the energy of the source over a gi ...
TISHTRIYA - Earth`s second Sun
... tint. Sirius B is a ’White Dwarf’ star, invisible to the naked eye, intensely dense about 4 times the diameter of our Earth. This suggests that at some previous time, having used up all its hydrogen reserve, it expanded as a ‘Red Giant’ during its dying moments and then suddenly collapsed into the s ...
... tint. Sirius B is a ’White Dwarf’ star, invisible to the naked eye, intensely dense about 4 times the diameter of our Earth. This suggests that at some previous time, having used up all its hydrogen reserve, it expanded as a ‘Red Giant’ during its dying moments and then suddenly collapsed into the s ...
This Book of Hours calculation is a possible
... highly regarded amongst occult researchers and even the likes of John Dee and Giordano Bruno are known to have consulted his work. He is even mentioned in famous books of fiction like Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein and even briefly mentioned in the Harry Potter series. His famous quote is: “Seeing ther ...
... highly regarded amongst occult researchers and even the likes of John Dee and Giordano Bruno are known to have consulted his work. He is even mentioned in famous books of fiction like Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein and even briefly mentioned in the Harry Potter series. His famous quote is: “Seeing ther ...
black holes activity
... In this lab you will examine the spectra of a few elements and compare them with some spectra of stars and galaxies taken by astronomers. In this way we can learn what is going on in atoms that are millions of light years away. Exercises: A. Using figure 3.5 on page 97 in your text, make a complex v ...
... In this lab you will examine the spectra of a few elements and compare them with some spectra of stars and galaxies taken by astronomers. In this way we can learn what is going on in atoms that are millions of light years away. Exercises: A. Using figure 3.5 on page 97 in your text, make a complex v ...
Slide 1
... Studying stars from an astrobiological perspective A-F stars: ~3% of all stars Timescales Life spans of 1—2 billion years, enough time for at least primitive life to form. Radiation Significant amounts of sterilizing ultraviolet radiation. Life would need to seek shelter under ice, rocks, or perhap ...
... Studying stars from an astrobiological perspective A-F stars: ~3% of all stars Timescales Life spans of 1—2 billion years, enough time for at least primitive life to form. Radiation Significant amounts of sterilizing ultraviolet radiation. Life would need to seek shelter under ice, rocks, or perhap ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.