Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... • O B A F G K M L T Subdivide each class into numbered subclasses: ...
... • O B A F G K M L T Subdivide each class into numbered subclasses: ...
Compa ring between Spectroscopic and Photometric Method for
... more than 50% of cases united in a system of two or more stars. Multiple systems consist of stars, which are gravitationally bound and move around a common center of gravity. Systems of multiplicity three an higher are frequent and are representing approximate 20% of the total stellar population, bu ...
... more than 50% of cases united in a system of two or more stars. Multiple systems consist of stars, which are gravitationally bound and move around a common center of gravity. Systems of multiplicity three an higher are frequent and are representing approximate 20% of the total stellar population, bu ...
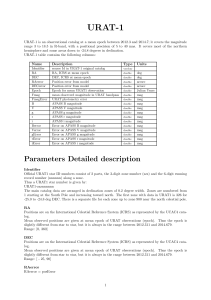
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
Open Clusters
... Open star cluster According to my results: -It is about 3/4 of the Earth’s lifetime old. -It is about 7,603 light years away from us. -Has a metallicity of about 2%---like Sun ...
... Open star cluster According to my results: -It is about 3/4 of the Earth’s lifetime old. -It is about 7,603 light years away from us. -Has a metallicity of about 2%---like Sun ...
galaxies and stars
... 77. Which star is cooler and many times brighter than Earth’s Sun? A Barnard’s Star B Betelgeuse ...
... 77. Which star is cooler and many times brighter than Earth’s Sun? A Barnard’s Star B Betelgeuse ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17)
... If you carry this out for a large number of stars (see Fig. 17.16), you find that most of them have R similar to the sun (these are called “main sequence stars”), but a fraction of them are either: (a) red giants – large L (up to 106 x sun) and small T (i.e. red), so must have large size (up to 100 ...
... If you carry this out for a large number of stars (see Fig. 17.16), you find that most of them have R similar to the sun (these are called “main sequence stars”), but a fraction of them are either: (a) red giants – large L (up to 106 x sun) and small T (i.e. red), so must have large size (up to 100 ...
Star Information ppt.
... stars like our sun that are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
... stars like our sun that are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... Chart can be rotated to any of the 16 compass points and also flipped along the North - South axis. Chart can be "live, realtime", or static for any user selected time. Core positional calculation routines based on "Novas" (Naval Observatory Vector Astrometry Subroutines Version 2.0.1) from the US N ...
... Chart can be rotated to any of the 16 compass points and also flipped along the North - South axis. Chart can be "live, realtime", or static for any user selected time. Core positional calculation routines based on "Novas" (Naval Observatory Vector Astrometry Subroutines Version 2.0.1) from the US N ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... C. Wavelength/temperature increasing to the right. D. Wavelength/temperature decreasing to the right. 15. Refer to the H-R diagram: for stars in general, a higher mass star may be found: A. at higher luminosity and lower temperature. B. at higher luminosity and higher temperature. C. observed at sho ...
... C. Wavelength/temperature increasing to the right. D. Wavelength/temperature decreasing to the right. 15. Refer to the H-R diagram: for stars in general, a higher mass star may be found: A. at higher luminosity and lower temperature. B. at higher luminosity and higher temperature. C. observed at sho ...
Li-cai Deng
... of one galaxy instead of comparing snapshots of many. It is only now that we have large surveys of the whole sky that we are able to comprehend the Milky Way as a whole. Unlike external galaxies, the picture we are building is in three dimensions of position and velocity, with much higher accuracy i ...
... of one galaxy instead of comparing snapshots of many. It is only now that we have large surveys of the whole sky that we are able to comprehend the Milky Way as a whole. Unlike external galaxies, the picture we are building is in three dimensions of position and velocity, with much higher accuracy i ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... Alpha-CV type stars are divided into three main groups depending on which spectral lines are most dominant. These three types of spectral lines are silicon, manganese, or as in Alioth’s case, chromium-strontium lines.8 These stars usually lack the more common elements that are found in stars and hav ...
... Alpha-CV type stars are divided into three main groups depending on which spectral lines are most dominant. These three types of spectral lines are silicon, manganese, or as in Alioth’s case, chromium-strontium lines.8 These stars usually lack the more common elements that are found in stars and hav ...
PHYSICS – Astrophysics Section I
... (astrometry) may be used to determine its distance Define the terms parallax, parsec and light-year Parallax is the apparent movement of an object relative to the background due to a change in position of the observer. A parsec is a unit of astronomical measurement. One parsec is the distance of the ...
... (astrometry) may be used to determine its distance Define the terms parallax, parsec and light-year Parallax is the apparent movement of an object relative to the background due to a change in position of the observer. A parsec is a unit of astronomical measurement. One parsec is the distance of the ...
20_LectureOutline
... Learning Astronomy from History Sirius is the brightest star in the northern sky and has been recorded throughout history. But there is a mystery! All sightings recorded between about 100 BCE and 200 CE describe it as being red—it is now blue-white. Why? Could there have been an intervening dust clo ...
... Learning Astronomy from History Sirius is the brightest star in the northern sky and has been recorded throughout history. But there is a mystery! All sightings recorded between about 100 BCE and 200 CE describe it as being red—it is now blue-white. Why? Could there have been an intervening dust clo ...
Slide 1
... Other Constellations you should know Killed by a scorpion and placed in the sky. Source: Dr. Islam’s Constellation page http://www2.potsdam.edu/islamma/Phys335Constellations.htm ...
... Other Constellations you should know Killed by a scorpion and placed in the sky. Source: Dr. Islam’s Constellation page http://www2.potsdam.edu/islamma/Phys335Constellations.htm ...
Surveying the Stars
... stars are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores like the Sun Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
... stars are fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores like the Sun Luminous mainsequence stars are hot (blue) Less luminous ones are cooler (yellow or red) ...
Oct 06, 2001
... 13. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two stars marked α and β? A. Star α is hotter than star β. B. Star α is less luminous than star β. C. Star α is larger in radius than star β. D. Star α appears brighter that star β. 14. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two st ...
... 13. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two stars marked α and β? A. Star α is hotter than star β. B. Star α is less luminous than star β. C. Star α is larger in radius than star β. D. Star α appears brighter that star β. 14. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two st ...
SGL 9 NGC Galaxy magnitude 9/10 observing challenge Up for
... It is Friday the 4th April. It is 9.30pm and its dark and the sky is clear. Time to start. Due South, almost overhead is Lynx. Use the TAKI charts and detailed CDC charts attached to find the objects. Object 1 – NGC 2683 (Taki page 53) A lovely edge of spiral galaxy some 30 million light years away. ...
... It is Friday the 4th April. It is 9.30pm and its dark and the sky is clear. Time to start. Due South, almost overhead is Lynx. Use the TAKI charts and detailed CDC charts attached to find the objects. Object 1 – NGC 2683 (Taki page 53) A lovely edge of spiral galaxy some 30 million light years away. ...
Lesson 4. Wiens and Stefans Laws
... Questions 1. The peak intensity of thermal radiation from the Sun is at a wavelength of 500 nm, calculate the surface temperature of the Sun. 2. A star has a power output of 6.0 x 1028 W and a surface temperature of 3400K, calculate its radius and the ratio to the Sun’s radius (rsun = 7 x 108 m) ...
... Questions 1. The peak intensity of thermal radiation from the Sun is at a wavelength of 500 nm, calculate the surface temperature of the Sun. 2. A star has a power output of 6.0 x 1028 W and a surface temperature of 3400K, calculate its radius and the ratio to the Sun’s radius (rsun = 7 x 108 m) ...
What is a white dwarf?
... life, it can begin to transfer mass to its companion. This mass exchange can then change the remaining life histories of both stars. • Sun ...
... life, it can begin to transfer mass to its companion. This mass exchange can then change the remaining life histories of both stars. • Sun ...
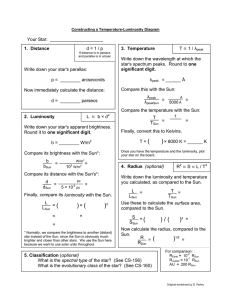
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... Once you have determined the luminosity and temperature of each star, please go to the board and plot that star on the class H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Calculating the radius and spectral type is optional, but strongly encouraged. ...
... Once you have determined the luminosity and temperature of each star, please go to the board and plot that star on the class H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Calculating the radius and spectral type is optional, but strongly encouraged. ...
Triangulation Trigonometric Parallax
... – Some stars are hundreds of times larger than the Sun and are referred to as giants – Stars smaller than the giants are called dwarfs ...
... – Some stars are hundreds of times larger than the Sun and are referred to as giants – Stars smaller than the giants are called dwarfs ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... e) Population I star Cepheids (called Type I or classical Cepheids) have a slightly different period-luminosity relationship than the Population II star cepheids (called Type II Cepheids or W Virginis stars). 3. Lower mass versions of Cepheids exist called RR Lyrae type variables, which change in br ...
... e) Population I star Cepheids (called Type I or classical Cepheids) have a slightly different period-luminosity relationship than the Population II star cepheids (called Type II Cepheids or W Virginis stars). 3. Lower mass versions of Cepheids exist called RR Lyrae type variables, which change in br ...
Notes
... The Lower Main Sequence – UV Ceti Stars • M dwarf flare stars • About half of M dwarfs are flare stars (and a few K dwarfs, too) • A flare star brightens by a few tenths up to a magnitude in V (more in the UV) in a few seconds, returning to its normal luminosity within a few hours • Flare temperatu ...
... The Lower Main Sequence – UV Ceti Stars • M dwarf flare stars • About half of M dwarfs are flare stars (and a few K dwarfs, too) • A flare star brightens by a few tenths up to a magnitude in V (more in the UV) in a few seconds, returning to its normal luminosity within a few hours • Flare temperatu ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.