3.1 Introduction
... In the case of a halo globular cluster, with little foreground contamination, the density of points in the HR diagram approximately reflects the length of time a star spends in different evolutionary stages. Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence (MS), burning hydrogen in their cores. ...
... In the case of a halo globular cluster, with little foreground contamination, the density of points in the HR diagram approximately reflects the length of time a star spends in different evolutionary stages. Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence (MS), burning hydrogen in their cores. ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... star, causing it to glow more brightly, too. Some dwarf novae such as U Geminorum can jump from magnitude 15 to 9.5 in just 1-2 days. After an outburst, the star slowly returns to its original quiet state and then flares up again weeks or months later. SS Cygni's two stars whirl like stellar Tilt-A- ...
... star, causing it to glow more brightly, too. Some dwarf novae such as U Geminorum can jump from magnitude 15 to 9.5 in just 1-2 days. After an outburst, the star slowly returns to its original quiet state and then flares up again weeks or months later. SS Cygni's two stars whirl like stellar Tilt-A- ...
1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 1031 W. The apparent brightness of the star is 1.4 10–9 W m–2. These data can be used to determine the distance of the star from Earth. (i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 1031 W. The apparent brightness of the star is 1.4 10–9 W m–2. These data can be used to determine the distance of the star from Earth. (i) ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... the H-R diagram above the Mira variables and are generally spectral class K, M, C or S. Since stars are plotted on the H-R diagram by absolute magnitude and/or luminosity and surface temperature (stellar classification), each star is plotted as one data point. Main sequence stars, giants and supergi ...
... the H-R diagram above the Mira variables and are generally spectral class K, M, C or S. Since stars are plotted on the H-R diagram by absolute magnitude and/or luminosity and surface temperature (stellar classification), each star is plotted as one data point. Main sequence stars, giants and supergi ...
Stellarium Astronomy Software
... Raise or lower the planetarium until the stars are in sharp focus. 2. Rotate your planetarium so that N (North) on the compass lines up with the raised dot. This allows your planetarium to project the stars in the same directional orientation as they are in the real night sky outside. Your planetari ...
... Raise or lower the planetarium until the stars are in sharp focus. 2. Rotate your planetarium so that N (North) on the compass lines up with the raised dot. This allows your planetarium to project the stars in the same directional orientation as they are in the real night sky outside. Your planetari ...
white dwarf supernova
... More massive white dwarfs are smaller than less massive white dwarfs. (Degeneracy pressure only depends on density) ...
... More massive white dwarfs are smaller than less massive white dwarfs. (Degeneracy pressure only depends on density) ...
Star Types - College of Engineering and Computer Science
... Up the red giant branch As hydrogen in the core is being used up, it starts to contract, raising temperature in the surrounding. Eventually, hydrogen will burn only in a shell. There is less gravity from above to balance this pressure. The Sun will then swell to enormous size and luminosity, and it ...
... Up the red giant branch As hydrogen in the core is being used up, it starts to contract, raising temperature in the surrounding. Eventually, hydrogen will burn only in a shell. There is less gravity from above to balance this pressure. The Sun will then swell to enormous size and luminosity, and it ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... stars do not fall randomly on the graph; rather they are confined to specific regions. This tells you that there is some physical relationship between the luminosity and temperature of a star. From the figure, one sees that most stars fall along a diagonal strip from high temperature, high lumi ...
... stars do not fall randomly on the graph; rather they are confined to specific regions. This tells you that there is some physical relationship between the luminosity and temperature of a star. From the figure, one sees that most stars fall along a diagonal strip from high temperature, high lumi ...
b. - UW Canvas
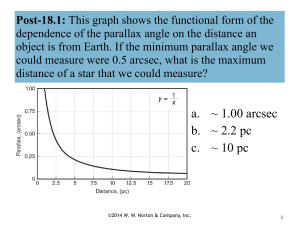
... dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? ...
... dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? ...
Distance Ladder
... Spectroscopic parallax applied to a cluster of stars How it works: •Measure brightness and spectral type of stars in a cluster •Deduce age from turn off point •Adjust H-R diagram accordingly •Deduce distance from: L = 4d2B •Having multiple stars also reduces statistical errors Still limited by lumi ...
... Spectroscopic parallax applied to a cluster of stars How it works: •Measure brightness and spectral type of stars in a cluster •Deduce age from turn off point •Adjust H-R diagram accordingly •Deduce distance from: L = 4d2B •Having multiple stars also reduces statistical errors Still limited by lumi ...
Stellar Evolution
... • These tiny stars are much smaller than planet Earth -- in fact, they are about the diameter of a large city (~20 km). • One cubic centimeter (like a sugar cube) of a neutron star, would have a mass of about 1011 kg! (hundreds of billions of pounds!) ...
... • These tiny stars are much smaller than planet Earth -- in fact, they are about the diameter of a large city (~20 km). • One cubic centimeter (like a sugar cube) of a neutron star, would have a mass of about 1011 kg! (hundreds of billions of pounds!) ...
Assignment 7 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... c. luminosity is proportional to mass to the fourth power (luminosity increases strongly with mass) d. bright stars have more mass around them in the form of planets, comets, and asteroids e. the brightest stars are made of such light materials they hardly have any mass at all ____ 22. For what typ ...
... c. luminosity is proportional to mass to the fourth power (luminosity increases strongly with mass) d. bright stars have more mass around them in the form of planets, comets, and asteroids e. the brightest stars are made of such light materials they hardly have any mass at all ____ 22. For what typ ...
Proficiency Step #5--
... We tend to think of constellations as a group of related stars that form a pattern, when in fact, most of the constellations consist of stars that are not related—that is, they are varying distances from Earth and their relative positions are simply a coincidence. It might be convenient to note her ...
... We tend to think of constellations as a group of related stars that form a pattern, when in fact, most of the constellations consist of stars that are not related—that is, they are varying distances from Earth and their relative positions are simply a coincidence. It might be convenient to note her ...
Chapter 13 section 3
... its helium and the outer layers escape into space. This leaves only the hot, dense core. At this stage in a star’s life cycle, it is about the size of Earth. It is called a white dwarf. In time, the white dwarf will cool and stop giving off light. The length time it takes for a star to go through it ...
... its helium and the outer layers escape into space. This leaves only the hot, dense core. At this stage in a star’s life cycle, it is about the size of Earth. It is called a white dwarf. In time, the white dwarf will cool and stop giving off light. The length time it takes for a star to go through it ...
April - Magic Valley Astronomical Society
... and more may reveal its cigar-shaped profile surrounding circular core. Next, try for M99, just south of the kite's tail. It’s not significantly easier to see, glowing dimly at 10th magnitude. Can you spot it, as well? If you can, then try your luck with an even more challenging target. M100 is rate ...
... and more may reveal its cigar-shaped profile surrounding circular core. Next, try for M99, just south of the kite's tail. It’s not significantly easier to see, glowing dimly at 10th magnitude. Can you spot it, as well? If you can, then try your luck with an even more challenging target. M100 is rate ...
Constellation
... (from Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2006. © 1993-2005 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved) ...
... (from Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2006. © 1993-2005 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved) ...
Making Visual Estimates
... Now Wasn't That Easy! However…. A Lot Of Times There Will Not Be A Comp Star With The Same Magnitude As The Variable Star. When ...
... Now Wasn't That Easy! However…. A Lot Of Times There Will Not Be A Comp Star With The Same Magnitude As The Variable Star. When ...
February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
... brightest stars are called Pollux (β) and Castor (α) and are known as the Gemini Twins. The twins originated in a Greek myth which told that they had one mother but two fathers. Castor was the mortal son of King Tyndareus but Pollux was the immortal son of the God Zeus who had disguised himself as C ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... material is dumped onto the surface of the white dwarf causing an outburst or flare called a nova. The outbursts causes a sharp increase in magnitude and a plot of the change in brightness over time is called a light curve. SS Cygni was also observed by Chandra in X-ray following an outburst in the ...
... material is dumped onto the surface of the white dwarf causing an outburst or flare called a nova. The outbursts causes a sharp increase in magnitude and a plot of the change in brightness over time is called a light curve. SS Cygni was also observed by Chandra in X-ray following an outburst in the ...
Constellation Classification Cards*
... 7. Family members can live nearby or farther away. Again, begin the U-shape in the front left corner of the room, starting with the closest stars. Ask the students with distances less than 25 light-years to start the line. If 20 cards are used, there should be one student representing 8.3 light-minu ...
... 7. Family members can live nearby or farther away. Again, begin the U-shape in the front left corner of the room, starting with the closest stars. Ask the students with distances less than 25 light-years to start the line. If 20 cards are used, there should be one student representing 8.3 light-minu ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.