Stars Of Orion Essay Research Paper 01
... From the visible perspective, the most obvious things an observer of Orion can tell are the relative size, position and colour of the stars. Studying the colour of stars allows us to determining its temperature, which in turn is related to it’s mass. Temperature determines a star’s colour. Red star ...
... From the visible perspective, the most obvious things an observer of Orion can tell are the relative size, position and colour of the stars. Studying the colour of stars allows us to determining its temperature, which in turn is related to it’s mass. Temperature determines a star’s colour. Red star ...
chapter 14 - Astronomy
... 3. The oscillations of the star’s outer layers result from the ionization of helium in the outer layers when it gets compressed. The resulting gas is opaque, trapping heat from inside the star. This results in an increase of the pressure under the layers, an expansion and subsequent cooling of the l ...
... 3. The oscillations of the star’s outer layers result from the ionization of helium in the outer layers when it gets compressed. The resulting gas is opaque, trapping heat from inside the star. This results in an increase of the pressure under the layers, an expansion and subsequent cooling of the l ...
The Solar Neighborhood
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
Dubhe
... light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s centennial. (shgresources.com) It is also one of the seven brightest stars. ...
... light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s centennial. (shgresources.com) It is also one of the seven brightest stars. ...
Option E Sum Pages
... considered possible signs of extra-terrestrial life. They are more likely to be stars which emit radiation dominantly in one direction, which because of the star's rotation make them appear as regularly flashing beacons, pulsating stars or pulsars. Certain stars emit much more radiation than a star ...
... considered possible signs of extra-terrestrial life. They are more likely to be stars which emit radiation dominantly in one direction, which because of the star's rotation make them appear as regularly flashing beacons, pulsating stars or pulsars. Certain stars emit much more radiation than a star ...
Lab 6
... • This is somewhat tricky: while keeping the axes pointed in the right direction (in other words, without rotating the sheet), slide the transparency over the other graph until the pattern of points on the transparency nearly or exactly matches the pattern of points on the underlying graph (in other ...
... • This is somewhat tricky: while keeping the axes pointed in the right direction (in other words, without rotating the sheet), slide the transparency over the other graph until the pattern of points on the transparency nearly or exactly matches the pattern of points on the underlying graph (in other ...
33-3 - Fremont Peak Observatory
... This object is a very faint planetary nebula but it’s BIG. The outer circumference is about 25 arc minutes, so it fills up a large portion of my field of view. Compared to other planetary nebulae, it’s only 700 light-years from Earth! There are no really bright stars close to the Helix. When I first ...
... This object is a very faint planetary nebula but it’s BIG. The outer circumference is about 25 arc minutes, so it fills up a large portion of my field of view. Compared to other planetary nebulae, it’s only 700 light-years from Earth! There are no really bright stars close to the Helix. When I first ...
CASPEC Observations of the Most Metal-Deficient Main
... give a list of 12 Galactic stars of this type with known distances. If we place these stars in the SMC, their V magnitudes will range from 17 to 22. The brightest one, HD 200775, assumed to lie at 440 pc from the Sun (Whitcomb et al., 1981), may be fainter than 17 if its distance is overestimated. T ...
... give a list of 12 Galactic stars of this type with known distances. If we place these stars in the SMC, their V magnitudes will range from 17 to 22. The brightest one, HD 200775, assumed to lie at 440 pc from the Sun (Whitcomb et al., 1981), may be fainter than 17 if its distance is overestimated. T ...
Ch 28 Class Notes
... The light from Proxima Centauri (the star nearest the sun) left that star more than four years ago. Light from other stars and celestial objects may have taken thousands, millions, or even billions of years to get here. _____________________________are a group of stars that appear to form a pattern ...
... The light from Proxima Centauri (the star nearest the sun) left that star more than four years ago. Light from other stars and celestial objects may have taken thousands, millions, or even billions of years to get here. _____________________________are a group of stars that appear to form a pattern ...
What is a star?
... What is a star? • Stars have different sizes, ranging from 1/100 the size of the sun to 1,000 times the size of the sun. • Two or more stars may be bound together by gravity, which causes them to orbit each other. • Three or more stars that are bound by gravity are called multiple stars or multiple ...
... What is a star? • Stars have different sizes, ranging from 1/100 the size of the sun to 1,000 times the size of the sun. • Two or more stars may be bound together by gravity, which causes them to orbit each other. • Three or more stars that are bound by gravity are called multiple stars or multiple ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... star if it were placed at a distance of 10 pc m – M = 5 log(d/10) - 5 where d is in pc (note: log10 ) • Magnitudes are measured in some wavelength band e.g. UBV. To compare with theory it is more useful to determine bolometric magnitude – defined as absolute magnitude that would be measured by a bol ...
... star if it were placed at a distance of 10 pc m – M = 5 log(d/10) - 5 where d is in pc (note: log10 ) • Magnitudes are measured in some wavelength band e.g. UBV. To compare with theory it is more useful to determine bolometric magnitude – defined as absolute magnitude that would be measured by a bol ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
... square law. Recall that the distance in parsecs is related to the difference between the absolute and apparent magnitude as follows: Distance in parsecs = 10(m-M+5)/5 In this case, we know the distance and apparent magnitude and want to determine the absolute magnitude. The expression can be rewritt ...
... square law. Recall that the distance in parsecs is related to the difference between the absolute and apparent magnitude as follows: Distance in parsecs = 10(m-M+5)/5 In this case, we know the distance and apparent magnitude and want to determine the absolute magnitude. The expression can be rewritt ...
Camelopardalis-Better-Know-A-Constellation
... reveal many of these regions that seem to take on likeliness to M33. Three supernovae have been spotted in this galaxy, one in 1954 (SN 1954J) with the others, a half a century later in 2002 (SN 2002kg) and in 2004 (SN 2004DJ). ...
... reveal many of these regions that seem to take on likeliness to M33. Three supernovae have been spotted in this galaxy, one in 1954 (SN 1954J) with the others, a half a century later in 2002 (SN 2002kg) and in 2004 (SN 2004DJ). ...
astrocoursespring2012lec4
... In cosmological redshift, the wavelength at which the radiation is originally emitted is (only) lengthened as it travels through (expanding) space. A Cosmological redshift results from the expansion of space itself and not from the motion of the object. So the recessional velocity is not the galaxie ...
... In cosmological redshift, the wavelength at which the radiation is originally emitted is (only) lengthened as it travels through (expanding) space. A Cosmological redshift results from the expansion of space itself and not from the motion of the object. So the recessional velocity is not the galaxie ...
CHAPTER 14
... (b) Type II: their spectrum contains prominent hydrogen lines; they originate from the explosion of a single star. 5. Type I supernovae are divided into three subclasses: (a) Type Ib, and Ic are caused by massive stars that have lost different proportions of their outer layers before exploding. (b) ...
... (b) Type II: their spectrum contains prominent hydrogen lines; they originate from the explosion of a single star. 5. Type I supernovae are divided into three subclasses: (a) Type Ib, and Ic are caused by massive stars that have lost different proportions of their outer layers before exploding. (b) ...
Masers and high mass star formation Claire Chandler
... research • Let´s look at some possible examples. ...
... research • Let´s look at some possible examples. ...
Classifying Spectra PDF version - the Home Page for Voyager2
... The spectral classes are specified by the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, M, L, T going hotter to colder. Each letter is subdivided by assigning a number 0 through 9 following the letter and going from hotter to colder. So B0 is colder than O9 and hotter than B1. Obviously not every type is shown. Origina ...
... The spectral classes are specified by the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, M, L, T going hotter to colder. Each letter is subdivided by assigning a number 0 through 9 following the letter and going from hotter to colder. So B0 is colder than O9 and hotter than B1. Obviously not every type is shown. Origina ...
DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. The distances to more remote stars are determined using spect ...
... to understanding the nature of the stars. Distances to the nearer stars can be determined by stellar parallax, which is the apparent shift of a star’s location against the background stars while Earth moves along its orbit around the Sun. The distances to more remote stars are determined using spect ...
Article Reference - Archive ouverte UNIGE
... are located in Table 1. The mass function f(m) and the log gp are directly obtained from fitting the data. They indicate we have discovered a new transiting planet. Using the stellar mass we obtain a mass and radius for our object and find 0.55 ± 0.04 Mjup and 0.95 ± 0.03 Rjup . The Rossiter-McLaugh ...
... are located in Table 1. The mass function f(m) and the log gp are directly obtained from fitting the data. They indicate we have discovered a new transiting planet. Using the stellar mass we obtain a mass and radius for our object and find 0.55 ± 0.04 Mjup and 0.95 ± 0.03 Rjup . The Rossiter-McLaugh ...
Patterns in the Night Sky
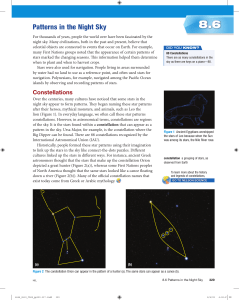
... night sky appear to form patterns. They began naming these star patterns after their heroes, mythical monsters, and animals, such as Leo the lion (Figure 1). In everyday language, we often call these star patterns constellations. However, in astronomical terms, constellations are regions of the sky. ...
... night sky appear to form patterns. They began naming these star patterns after their heroes, mythical monsters, and animals, such as Leo the lion (Figure 1). In everyday language, we often call these star patterns constellations. However, in astronomical terms, constellations are regions of the sky. ...
Spectral Classification: The First Step in Quantitative Spectral Analysis
... Spectral Analysis begins with the estimation of the physical parameters: Teff, log(g), [M/H]. How can Spectral Classification help? • Spectral classification in conjunction with photometry is the best way to determine the interstellar reddening because it does not depend on an extinction model. • C ...
... Spectral Analysis begins with the estimation of the physical parameters: Teff, log(g), [M/H]. How can Spectral Classification help? • Spectral classification in conjunction with photometry is the best way to determine the interstellar reddening because it does not depend on an extinction model. • C ...
Whiteq
... dwarf yet discovered is type K. No type M stars have been found. This has implications for the age of the universe, since the coolest white dwarves are believed to be the remains of the first stars formed. There may be no class M white dwarves, because no stars have yet had time to cool that much. T ...
... dwarf yet discovered is type K. No type M stars have been found. This has implications for the age of the universe, since the coolest white dwarves are believed to be the remains of the first stars formed. There may be no class M white dwarves, because no stars have yet had time to cool that much. T ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.