Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... where Fx is the observed flux in the band x, and Fvega is the flux of the star Vega. The star Vega, in the constellation of Lyra is used as a reference in the magnitude system. Vega has the arbitrary definition of zero magnitude at all wavelengths U=B=V=R=I=0 This does not mean tha ...
... where Fx is the observed flux in the band x, and Fvega is the flux of the star Vega. The star Vega, in the constellation of Lyra is used as a reference in the magnitude system. Vega has the arbitrary definition of zero magnitude at all wavelengths U=B=V=R=I=0 This does not mean tha ...
Introduction: The History and Technique of Stellar Classification
... von Fraunhofer early in the 1800’s, but it was not until late in that century that astronomers were able to routinely examine the spectra of stars in large numbers. Astronomers Angelo Secchi and E.C. Pickering were among the first to note that stellar spectra could be divided into groups by their ge ...
... von Fraunhofer early in the 1800’s, but it was not until late in that century that astronomers were able to routinely examine the spectra of stars in large numbers. Astronomers Angelo Secchi and E.C. Pickering were among the first to note that stellar spectra could be divided into groups by their ge ...
HR Diagram - TeacherWeb
... A. Which star group does Proxima Centauri belong to? _________________________ B. On the H-R diagram, which star would Proxima Centauri be near? ______________ 8. Describe: Locate the Sun on the H-R diagram. How will the Sun’s luminosity and temperature change as it ages? How will these changes affe ...
... A. Which star group does Proxima Centauri belong to? _________________________ B. On the H-R diagram, which star would Proxima Centauri be near? ______________ 8. Describe: Locate the Sun on the H-R diagram. How will the Sun’s luminosity and temperature change as it ages? How will these changes affe ...
Stars change over their life cycles.
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... where Fx is the observed flux in the band x, and F vega is the flux of the star Vega. The star Vega, in the constellation of Lyra is used as a reference in the magnitude system. Vega has the arbitrary definition of zero magnitude at all wavelengths U=B=V=R=I=0 This does not mean that Vega show the s ...
... where Fx is the observed flux in the band x, and F vega is the flux of the star Vega. The star Vega, in the constellation of Lyra is used as a reference in the magnitude system. Vega has the arbitrary definition of zero magnitude at all wavelengths U=B=V=R=I=0 This does not mean that Vega show the s ...
Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
... B) shorter than normal (a blue shift) D) longer than normal (a blue shift) ...
... B) shorter than normal (a blue shift) D) longer than normal (a blue shift) ...
Good Vibrations and Stellar Pulsations - Physics
... • Shapley mistook the Pop II Cepheids in globular clusters for Pop I Cepheids, so his Pop II Cepheids in the globular clusters were properly calibrated (luck!). • Shapley’s distances to the globular clusters were correct. • Hubble’s Pop I Cepheids in M31 were underluminous by a factor of 4, so M31(a ...
... • Shapley mistook the Pop II Cepheids in globular clusters for Pop I Cepheids, so his Pop II Cepheids in the globular clusters were properly calibrated (luck!). • Shapley’s distances to the globular clusters were correct. • Hubble’s Pop I Cepheids in M31 were underluminous by a factor of 4, so M31(a ...
All_Stars
... and supergiant stars into various luminosity classes, denoted I-V. Stars that have the same spectral type but different luminosity classes are distinguished by the widths and strengths of the absorption lines in their spectra. ...
... and supergiant stars into various luminosity classes, denoted I-V. Stars that have the same spectral type but different luminosity classes are distinguished by the widths and strengths of the absorption lines in their spectra. ...
DSLR Photometry
... Des says in theory it is advisable to also construct master flat field frames in order to remove the effects of the edge distortions of lens. Des has found, however, that the field of view of a DSLR is so wide that a flat field is not required, if you are using high quality lenses, provided the targ ...
... Des says in theory it is advisable to also construct master flat field frames in order to remove the effects of the edge distortions of lens. Des has found, however, that the field of view of a DSLR is so wide that a flat field is not required, if you are using high quality lenses, provided the targ ...
STEPHAN`S QUINTET
... Stephan's Quintet in the constellation Pegasus is al grouping of five galaxies of which four form the first compact galaxy group ever discovered. The group was discovered by Édouard Stephan in 1877 at Marseilles Observatory. These galaxies are of interest because of their violent collisions. Four of ...
... Stephan's Quintet in the constellation Pegasus is al grouping of five galaxies of which four form the first compact galaxy group ever discovered. The group was discovered by Édouard Stephan in 1877 at Marseilles Observatory. These galaxies are of interest because of their violent collisions. Four of ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... helpful characteristic: The stars are all the same distance away. That means if a star is brighter than another in the cluster, it really is more luminous. That makes comparing the stars directly to each other easier. At first it was assumed that all globulars are very old—as old as the Milky Way it ...
... helpful characteristic: The stars are all the same distance away. That means if a star is brighter than another in the cluster, it really is more luminous. That makes comparing the stars directly to each other easier. At first it was assumed that all globulars are very old—as old as the Milky Way it ...
Binocular Objects (MS Word)
... Sagittarius contains more Messier objects than any other constellation. The best way to identify them is to take them one by one. The beginner will have to be careful not to confuse the various objects. The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the M ...
... Sagittarius contains more Messier objects than any other constellation. The best way to identify them is to take them one by one. The beginner will have to be careful not to confuse the various objects. The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the M ...
Photometry – I. “All sky”
... So far, we have looked at the concept of magnitude in a rather generalised way. When we come to actually make photometric measurements, we usually need to use a specified system. This is because different observers will often use different sized telescopes at different sites (which means different a ...
... So far, we have looked at the concept of magnitude in a rather generalised way. When we come to actually make photometric measurements, we usually need to use a specified system. This is because different observers will often use different sized telescopes at different sites (which means different a ...
June 2015 - Bristol Astronomical Society
... the centre of M87 is a supermassive black hole with a jet of extremely energetic plasma extending outwards for at least 5000 light-years. The galaxy is therefore an interesting object for both professional and amateur astronomers alike. With an apparent magnitude of +8.6, M87 is the second brightest ...
... the centre of M87 is a supermassive black hole with a jet of extremely energetic plasma extending outwards for at least 5000 light-years. The galaxy is therefore an interesting object for both professional and amateur astronomers alike. With an apparent magnitude of +8.6, M87 is the second brightest ...
Navigating the Night Sky – Teacher Guide Argos Online Subject
... • Identify limitations of the map: o Do the constellations near the horizon on the star map look like the constellations in the sky? If not, how do they look different? -If you are using the star maps in Stardate Magazine, the answer is obviously No. If you are using the star maps from Starmaps.com, ...
... • Identify limitations of the map: o Do the constellations near the horizon on the star map look like the constellations in the sky? If not, how do they look different? -If you are using the star maps in Stardate Magazine, the answer is obviously No. If you are using the star maps from Starmaps.com, ...
star
... Objects with masses between 1/100 and 1/12 that of the Sun are called brown dwarfs They may produce energy for a brief time by nuclear reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
... Objects with masses between 1/100 and 1/12 that of the Sun are called brown dwarfs They may produce energy for a brief time by nuclear reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
18 are exactly the same ones as for galactic star clusters of early
... NGC 6067 is 15-20 times richer. The cluster has red supergiants brighter than those in the otherwise similar cluster Mil. A few supergiants straddle across a very well-defined Hertzsprung gap, including the brighest central star which is classified GO lb. There can be no doubt about the membership o ...
... NGC 6067 is 15-20 times richer. The cluster has red supergiants brighter than those in the otherwise similar cluster Mil. A few supergiants straddle across a very well-defined Hertzsprung gap, including the brighest central star which is classified GO lb. There can be no doubt about the membership o ...
LET THE STARS GET IN YOUR EYES SKY MOTIONS
... constellations requires a constellation chart, a red flashlight and your willingness to explore the sky. A red flashlight is a basic tool of astronomers because it won't ruin your night vision. You can paint your light red, or cover your light with a red filter. Red flashlights can also be purchased ...
... constellations requires a constellation chart, a red flashlight and your willingness to explore the sky. A red flashlight is a basic tool of astronomers because it won't ruin your night vision. You can paint your light red, or cover your light with a red filter. Red flashlights can also be purchased ...
key for the HR Diagram Lab Handout
... Geminorum have brightness of 9,000 Suns and 310 Suns respectively; these stars are much larger than Proxima and Barnard s with brightness of 0.00005 and 0.0003 Suns. The significant difference in brightness with no change in temperature means that Betelgeuse and Mu Geminorum are much larger than the ...
... Geminorum have brightness of 9,000 Suns and 310 Suns respectively; these stars are much larger than Proxima and Barnard s with brightness of 0.00005 and 0.0003 Suns. The significant difference in brightness with no change in temperature means that Betelgeuse and Mu Geminorum are much larger than the ...
pkt 14 Astrophysics
... Originally nebula was a general name for any extended astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way (some examples of the older usage survive; for example, the Andromeda Galaxy was referred to as the Andromeda Nebula before galaxies were discovered by Edwin Hubble). Nebulae often form ...
... Originally nebula was a general name for any extended astronomical object, including galaxies beyond the Milky Way (some examples of the older usage survive; for example, the Andromeda Galaxy was referred to as the Andromeda Nebula before galaxies were discovered by Edwin Hubble). Nebulae often form ...
Astronomical Formulae
... Where D is the diameter of the objective in inches Atmospheric conditions seldom permit Theta > 0.5". The Dawes Limit is one half the angular diameter of the Airy (diffraction) disc, so that the edge of one disc does not extend beyond the center of the other). The working value is two times the Dawe ...
... Where D is the diameter of the objective in inches Atmospheric conditions seldom permit Theta > 0.5". The Dawes Limit is one half the angular diameter of the Airy (diffraction) disc, so that the edge of one disc does not extend beyond the center of the other). The working value is two times the Dawe ...
The birth and life of stars
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
... The most massive pre–main-sequence stars take the shortest time to become main-sequence stars (O and B stars). In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that eje ...
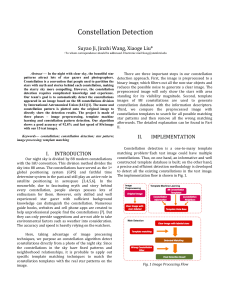
Constellation Detection
... missing or out of frame; we set the matching threshold NUM_MATCH to be half of the total star numbers in the constellation template. If the matching number is above the threshold, we decide the constellation is detected in the test image. Finding the proper scale of the template improves the accurac ...
... missing or out of frame; we set the matching threshold NUM_MATCH to be half of the total star numbers in the constellation template. If the matching number is above the threshold, we decide the constellation is detected in the test image. Finding the proper scale of the template improves the accurac ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.