Stellar Continua
... I. The Paschen Continuum • The Paschen continuum slope (B-V) is a good temperature indicator • Varies smoothly with changing temperature • Slope is negative (blue is brighter) for hot stars and positive (visual is brighter) for cooler stars • B-V works as a temperature indicator from 3500K to 9000K ...
... I. The Paschen Continuum • The Paschen continuum slope (B-V) is a good temperature indicator • Varies smoothly with changing temperature • Slope is negative (blue is brighter) for hot stars and positive (visual is brighter) for cooler stars • B-V works as a temperature indicator from 3500K to 9000K ...
The masses of stars
... Thus most easily measured quantities of a star’s brightness at different colours enable us to characterise it in terms of its surface temperature (T) and luminosity (L), which are related to one another through the radius of the star. If we want to understand more about the differences between star ...
... Thus most easily measured quantities of a star’s brightness at different colours enable us to characterise it in terms of its surface temperature (T) and luminosity (L), which are related to one another through the radius of the star. If we want to understand more about the differences between star ...
Here
... together by gravity. They orbit their common center of mass. • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use sp ...
... together by gravity. They orbit their common center of mass. • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use sp ...
A Walk through the Southern Sky: A Guide to Stars and
... Rigel is actually thousands of times brighter than Sirius. It appears fainter because it is over a thousand light years away, while Sirius is only 81⁄2 light years from us. We measure the brightness of the stars as seen with the naked eye on a scale called the magnitude scale. Hipparchus, a Greek as ...
... Rigel is actually thousands of times brighter than Sirius. It appears fainter because it is over a thousand light years away, while Sirius is only 81⁄2 light years from us. We measure the brightness of the stars as seen with the naked eye on a scale called the magnitude scale. Hipparchus, a Greek as ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way • We use a statistical approach to determine and describe the spatial distribution of stars in the Galaxy • This approach allows us to derive the structure of the disk and spheroidal components (density distribution and extent). • This information can ...
... Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way • We use a statistical approach to determine and describe the spatial distribution of stars in the Galaxy • This approach allows us to derive the structure of the disk and spheroidal components (density distribution and extent). • This information can ...
Observational properties of stars
... atmosphere of the Earth blocking some light, as well as stuff out in space blocking other types of light. So any apparent magnitude that you measure will not give you the full energy output of a star. Of course you could try to work around this by measuring light from stars in as many wavelengths as ...
... atmosphere of the Earth blocking some light, as well as stuff out in space blocking other types of light. So any apparent magnitude that you measure will not give you the full energy output of a star. Of course you could try to work around this by measuring light from stars in as many wavelengths as ...
LAB #5 - GEOCITIES.ws
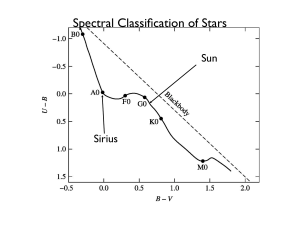
... A, F, G, K, and M, and though the letter designations have no meaning other than that imposed on them by history, the names have stuck to this day. Each spectral class is divided into tenths, so that a B0 star follows an O9, and an A0, a B9. The early spectral classification system was based on the ...
... A, F, G, K, and M, and though the letter designations have no meaning other than that imposed on them by history, the names have stuck to this day. Each spectral class is divided into tenths, so that a B0 star follows an O9, and an A0, a B9. The early spectral classification system was based on the ...
Stellar Census
... Objects with masses between 1/100 and 1/12 that of the Sun are called brown dwarfs They may produce energy for a brief time by nuclear reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
... Objects with masses between 1/100 and 1/12 that of the Sun are called brown dwarfs They may produce energy for a brief time by nuclear reactions, but do not become hot enough to fuse protons They are intermediate in mass between stars and planets ...
Exploring the Mystery of Sirius – the Bright Isis and the Dark Nephthys
... mysteries of Isis. As Robert Temple writes, "the Black Ritual" probably referred to the concept of the Night which was an object moving in the sky together with other mysteries which orbited in a harmonic way. It reputedly had less light than the Sun and "weave the web with fast light" – which could ...
... mysteries of Isis. As Robert Temple writes, "the Black Ritual" probably referred to the concept of the Night which was an object moving in the sky together with other mysteries which orbited in a harmonic way. It reputedly had less light than the Sun and "weave the web with fast light" – which could ...
THE PHYSICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE STARS 1
... therefore the absolute individual masses can be derived. The double-lined eclipsing binaries are extremely important, since they are the only case providing simultaneous determinations of individual masses and radii (see Sect. 3). The best reached precisions are of the order of 1-5% ([27], [4]). Suc ...
... therefore the absolute individual masses can be derived. The double-lined eclipsing binaries are extremely important, since they are the only case providing simultaneous determinations of individual masses and radii (see Sect. 3). The best reached precisions are of the order of 1-5% ([27], [4]). Suc ...
Stellar Evolution – Cosmic Cycles of Formation and Destruction
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
The Southern Fall PDF - Treasures of the Southern Sky
... The vast Carina Nebula contains over a dozen stars with masses between 50 to 100 times that of the Sun, and these are the main source of illumination of the nebula itself. However, by far the most exotic star here is Eta Carinae. It is shrouded in a tiny nebula — the expanding, dumbbell-shaped Homu ...
... The vast Carina Nebula contains over a dozen stars with masses between 50 to 100 times that of the Sun, and these are the main source of illumination of the nebula itself. However, by far the most exotic star here is Eta Carinae. It is shrouded in a tiny nebula — the expanding, dumbbell-shaped Homu ...
Evolved Stellar Populations
... To understand the history of formation and evolution of galaxies we need to understand the distribution of age, chemical abundance and kinematics of both the stars and gas. The best laboratories for these studies are galaxies of the Local Group and in particular the Magellanic Clouds (nearby, kn ...
... To understand the history of formation and evolution of galaxies we need to understand the distribution of age, chemical abundance and kinematics of both the stars and gas. The best laboratories for these studies are galaxies of the Local Group and in particular the Magellanic Clouds (nearby, kn ...
Spectral Classification of Stars
... "If, on the contrary, two stars should really be situated very near each other, and at the same time so far insulated as not to be materially affected by the attractions of neighbouring stars, they will then compose a separate system, and remain united by the bond of their own mutual gravitation tow ...
... "If, on the contrary, two stars should really be situated very near each other, and at the same time so far insulated as not to be materially affected by the attractions of neighbouring stars, they will then compose a separate system, and remain united by the bond of their own mutual gravitation tow ...
Physics- HSC- Module 9.7 Astrophysics
... During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers obtained spectra and parallax distances for many stars, a powerful tool was discovered for classifying and understanding stars. Around 1911-13, Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell independently found that stars could be divided into t ...
... During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers obtained spectra and parallax distances for many stars, a powerful tool was discovered for classifying and understanding stars. Around 1911-13, Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell independently found that stars could be divided into t ...
A near IR adaptive optics search for faint companions to early
... about the fainter sources, the P component is very likely physical, judging by its proximity to C and its brightness. Its colour J − K = 1.24 is too red for a normal star, but not unusual for young low-mass T Tau stars as found in the compilation of Strom et al. (1989). This object may be similar to ...
... about the fainter sources, the P component is very likely physical, judging by its proximity to C and its brightness. Its colour J − K = 1.24 is too red for a normal star, but not unusual for young low-mass T Tau stars as found in the compilation of Strom et al. (1989). This object may be similar to ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved the universe was expanding like a big balloon. In 1930, Einstein visited Wilson Observato ...
... up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved the universe was expanding like a big balloon. In 1930, Einstein visited Wilson Observato ...
Project 8 : Stellar Spectra: Classification
... Absorption lines occur when an electron absorbs energy from the spectrum to move up the energy levels in the atom. Since hydrogen has only one electron, this electron is usually in the ground state. But as the temperature rises, the average electron gains m ...
... Absorption lines occur when an electron absorbs energy from the spectrum to move up the energy levels in the atom. Since hydrogen has only one electron, this electron is usually in the ground state. But as the temperature rises, the average electron gains m ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... absolute magnitude for Cepheid variables. E.3.15. Explain how Cepheid variables may be used as “standard candles”. E.3.16. Determine the distance to a Cepheid variable using the luminosity-period relationship. ...
... absolute magnitude for Cepheid variables. E.3.15. Explain how Cepheid variables may be used as “standard candles”. E.3.16. Determine the distance to a Cepheid variable using the luminosity-period relationship. ...
Small star patterns for telescopes and binoculars Demelza Ramakers
... chevron. It’s located just above the galaxy NGC 2217 in Canis Major, a bit right of the back paw. The asterism is pretty big, and the stars in the chevron have a magnitude of 7 to 10, which makes this a beautiful binocular object. Through telescopes you will see the color of the stars (yellow-orange ...
... chevron. It’s located just above the galaxy NGC 2217 in Canis Major, a bit right of the back paw. The asterism is pretty big, and the stars in the chevron have a magnitude of 7 to 10, which makes this a beautiful binocular object. Through telescopes you will see the color of the stars (yellow-orange ...
Agenda - Relativity Group
... a. Yes, all stars create heavier elements than carbon when they become a supernova. b. Yes, but there would be far fewer heavier elements because high-mass stars form elements like iron far more prolifically than low-mass stars. c. No, the core temperatures of low-mass stars are too low to fuse othe ...
... a. Yes, all stars create heavier elements than carbon when they become a supernova. b. Yes, but there would be far fewer heavier elements because high-mass stars form elements like iron far more prolifically than low-mass stars. c. No, the core temperatures of low-mass stars are too low to fuse othe ...
1. The catalogue structure
... We have partially processed this enormous body of material. First of all, it is very useful to indicate the location of the constellations mentioned in Ptolemy’s star catalogue geometrically. Let us use a modern map that specifies constellation boundaries for this end. In fig. 2.1. these boundaries ...
... We have partially processed this enormous body of material. First of all, it is very useful to indicate the location of the constellations mentioned in Ptolemy’s star catalogue geometrically. Let us use a modern map that specifies constellation boundaries for this end. In fig. 2.1. these boundaries ...
12 Introduction to Cepheid Variable Stars Exercise
... If you know the distance to the bulb and measure its apparent brightness then you can calculate the wattage of the bulb. Likewise, if you know the wattage of the bulb and measure the observed brightness you can calculate the distance to the bulb. This can be applied to stars, if you determine the ap ...
... If you know the distance to the bulb and measure its apparent brightness then you can calculate the wattage of the bulb. Likewise, if you know the wattage of the bulb and measure the observed brightness you can calculate the distance to the bulb. This can be applied to stars, if you determine the ap ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.