Using Star Charts Introduction A Digression on Star Names
... as nebulae and galaxies. We will use the Pocket Sky Atlas for this last purpose later in the semester. An analogy can make the function of the Pocket Sky Atlas clearer. The star wheel and SC1 Chart are similar in function to a map of the entire world. The Pocket Sky Atlas is more like an atlas which ...
... as nebulae and galaxies. We will use the Pocket Sky Atlas for this last purpose later in the semester. An analogy can make the function of the Pocket Sky Atlas clearer. The star wheel and SC1 Chart are similar in function to a map of the entire world. The Pocket Sky Atlas is more like an atlas which ...
A little bit more to do. Stefan
... second you would need to add up all the intensity at each wavelength. In other words, find the area underneath the curve. ...
... second you would need to add up all the intensity at each wavelength. In other words, find the area underneath the curve. ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
... Mark scheme for Extension Worksheet – Option E, Worksheet 1 ...
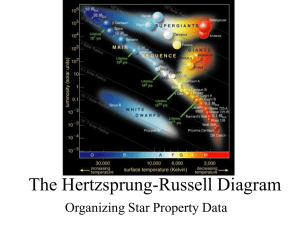
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Project Packet - Montville.net
... 1. Time of year when it is visible 2. What direction you should look and at what time 3. How high above the horizon you should look. Part 2 1. What does your constellation look like? 2. Draw a diagram or include an image in the space on the results pages. Part 3 Look up what stars are in your conste ...
... 1. Time of year when it is visible 2. What direction you should look and at what time 3. How high above the horizon you should look. Part 2 1. What does your constellation look like? 2. Draw a diagram or include an image in the space on the results pages. Part 3 Look up what stars are in your conste ...
Luminosity - UCF Physics
... Life expectancy of 10 MSun star: 10 times as much fuel, uses it 104 times as fast ...
... Life expectancy of 10 MSun star: 10 times as much fuel, uses it 104 times as fast ...
2017 MIT Invitational
... system with a period of 50 hours. For simplicity, assume that both of the stars in the system are on circular orbits, that stellar occultations completely block the disk of the eclipsed star (but not that both stars have the same radius), and that stellar luminosity scales with mass as L ∝ M 3.5 . ...
... system with a period of 50 hours. For simplicity, assume that both of the stars in the system are on circular orbits, that stellar occultations completely block the disk of the eclipsed star (but not that both stars have the same radius), and that stellar luminosity scales with mass as L ∝ M 3.5 . ...
Star and Galaxies
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
Star Powerpoint notes
... The intensity of light emitted by three hypothetical stars is plotted against wavelength. The range of visible wavelengths is indicated. Where the peak of a star’s intensity curve lies relative to the visible light band determines the apparent color of its visible light. ...
... The intensity of light emitted by three hypothetical stars is plotted against wavelength. The range of visible wavelengths is indicated. Where the peak of a star’s intensity curve lies relative to the visible light band determines the apparent color of its visible light. ...
Stars and Light
... bright they looked to his eye. • Herschel (1800s) first measured the brightness of stars quantitatively and matched his measurements onto Ptolemy’s magnitude groups and assigned a number for the magnitude of each star. ...
... bright they looked to his eye. • Herschel (1800s) first measured the brightness of stars quantitatively and matched his measurements onto Ptolemy’s magnitude groups and assigned a number for the magnitude of each star. ...
binary star
... Death of Massive Stars • In contrast to sunlike stars, stars that are over three times the sun’s mass have relatively short life spans, which end in a supernova event. • A supernova is an exploding massive star that increases in brightness many thousands of times. • The massive star’s interior con ...
... Death of Massive Stars • In contrast to sunlike stars, stars that are over three times the sun’s mass have relatively short life spans, which end in a supernova event. • A supernova is an exploding massive star that increases in brightness many thousands of times. • The massive star’s interior con ...
Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers
... wavelengths and therefore hot stars appear bluer. (More precisely, according to Wien’s displacement law, λmax and T of a black body are related by max T 2.90 10 3 m K . Thus, we can calculate the surface temperature of a star from the spectrum.) (b) When the spectrum of a star is examined clo ...
... wavelengths and therefore hot stars appear bluer. (More precisely, according to Wien’s displacement law, λmax and T of a black body are related by max T 2.90 10 3 m K . Thus, we can calculate the surface temperature of a star from the spectrum.) (b) When the spectrum of a star is examined clo ...
ASTRONOMY: WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW
... It is a spinning neutron star that emits radio waves form excited gases trapped in the star’s magnetic field. It doesn’t actually pulse, rather it appears to blink on and off as it rotates towards and away from the sight-line of Earth What is a pulsar wind? The high energy particles blowing away fro ...
... It is a spinning neutron star that emits radio waves form excited gases trapped in the star’s magnetic field. It doesn’t actually pulse, rather it appears to blink on and off as it rotates towards and away from the sight-line of Earth What is a pulsar wind? The high energy particles blowing away fro ...
Main Sequence stars
... The star Rigel is about 100,000 times brighter than the Sun and belongs to spectral type B8. The star Sirius B is about 3000 times dimmer than the Sun and also belongs to spectral type B8. Which star has the greatest surface temperature? 1. Rigel 2. Sirius B 3. They have the same temperature. 4. Th ...
... The star Rigel is about 100,000 times brighter than the Sun and belongs to spectral type B8. The star Sirius B is about 3000 times dimmer than the Sun and also belongs to spectral type B8. Which star has the greatest surface temperature? 1. Rigel 2. Sirius B 3. They have the same temperature. 4. Th ...
Directed Reading A
... _____ 1. Which of the following statements is NOT true about stars? a. A star begins its life as a ball of gas and dust. b. As stars get older, they lose some of their material. c. Stars last forever. d. New stars form from the material of old stars. 2. During a star’s life cycle, hydrogen changes t ...
... _____ 1. Which of the following statements is NOT true about stars? a. A star begins its life as a ball of gas and dust. b. As stars get older, they lose some of their material. c. Stars last forever. d. New stars form from the material of old stars. 2. During a star’s life cycle, hydrogen changes t ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.