Earth
... What is known about stars? What is the sun made of? The sun is a huge, glowing sphere of hot gas. Most of this gas is hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silic ...
... What is known about stars? What is the sun made of? The sun is a huge, glowing sphere of hot gas. Most of this gas is hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silic ...
stars - science1d
... 4. What is the name of the constellation that has three bright stars in a row? 5. What is the name of the star that seems to form the tail of the swan-shaped constellation known as Cygnus? 6. Is the star Aldebaran located east or west of Betelgeuse? 7. What is the name of the star cluster located mi ...
... 4. What is the name of the constellation that has three bright stars in a row? 5. What is the name of the star that seems to form the tail of the swan-shaped constellation known as Cygnus? 6. Is the star Aldebaran located east or west of Betelgeuse? 7. What is the name of the star cluster located mi ...
Star`s ReadingStar`s Reading(es)
... Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature, and brightness. Sizes of Stars When you look at stars in the sky, they all appear to be the same size. Many stars are actually about the size of the sun, whi ...
... Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature, and brightness. Sizes of Stars When you look at stars in the sky, they all appear to be the same size. Many stars are actually about the size of the sun, whi ...
January SKY Newsletter 2012
... southern horizon below Canis Major between 10:00 and 11:00 p.m. The Winter Hexagon will move across the southern sky over the course of the night. Other constellations in the south at this time are very large and fairly dim, but if you are in a dark site you may want to check for observing details ...
... southern horizon below Canis Major between 10:00 and 11:00 p.m. The Winter Hexagon will move across the southern sky over the course of the night. Other constellations in the south at this time are very large and fairly dim, but if you are in a dark site you may want to check for observing details ...
MS Word
... are no O stars anywhere near the Sun). Recall that each letter category is also broken into ten subcatagories. Thus you can have a B2 star, as well as a G8 star. There are A0 stars and F7 stars. Look at each of the tables and under ‘spectral type’ you will see these classifications. Remember that B0 ...
... are no O stars anywhere near the Sun). Recall that each letter category is also broken into ten subcatagories. Thus you can have a B2 star, as well as a G8 star. There are A0 stars and F7 stars. Look at each of the tables and under ‘spectral type’ you will see these classifications. Remember that B0 ...
PREVIEW-Reading Quiz 06 - Chapter 12
... The vast majority of these giant stars are part of a binary system and mass ends up being dumped on the other star. These giant stars have convection occurring throughout their interior, and this motion causes gas ejection. These stars are so huge that the force of gravity at their surfaces is less ...
... The vast majority of these giant stars are part of a binary system and mass ends up being dumped on the other star. These giant stars have convection occurring throughout their interior, and this motion causes gas ejection. These stars are so huge that the force of gravity at their surfaces is less ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 4. Large, massive stars will have a _____________ main sequence stage while less massive stars will have a _________ main sequence stage. 5. What is a red giant? ...
... 4. Large, massive stars will have a _____________ main sequence stage while less massive stars will have a _________ main sequence stage. 5. What is a red giant? ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
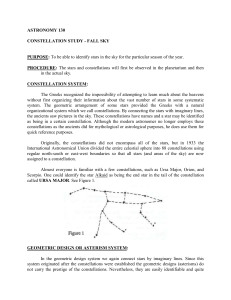
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
... point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle, this is Alkaid. Continue down the handle, the next star is Mizar. Look carefully at Mizar with the naked eye and then through one of the telescopes that are set on Mizar. Note your ob ...
AST101_lect_12
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... In the mid-19th century the French comet-hunter Charles Messier (17301817) compiled his famous list of 110 “faint fuzzies”, non-comet “nuisances” for him but popular targets for astronomers ever since. Sir William Herschel (1738-1822) and other astronomers would turn larger and larger telescopes tow ...
... In the mid-19th century the French comet-hunter Charles Messier (17301817) compiled his famous list of 110 “faint fuzzies”, non-comet “nuisances” for him but popular targets for astronomers ever since. Sir William Herschel (1738-1822) and other astronomers would turn larger and larger telescopes tow ...
life cycle of stars notes
... • Hotter core causes star to expand up to 100x original size due to ‘radiative pressure’ • Surface temp gets cooler – star becomes red • Core becomes “degenerate” - can’t be crushed ...
... • Hotter core causes star to expand up to 100x original size due to ‘radiative pressure’ • Surface temp gets cooler – star becomes red • Core becomes “degenerate” - can’t be crushed ...
30.2 PowerPoint Stellar Evolution
... gases and reveals a core An expanding shell of gases shed by this dying star forms a PLANETARY NEBULA ...
... gases and reveals a core An expanding shell of gases shed by this dying star forms a PLANETARY NEBULA ...
The Milky Way - Midlandstech
... B. The Evolution of Star Clusters IV. Evidence of Evolution: Variable Stars A. Cepheid and RR Lyrae Variable Stars B. Pulsating Stars C. Period Changes in Variable Stars ...
... B. The Evolution of Star Clusters IV. Evidence of Evolution: Variable Stars A. Cepheid and RR Lyrae Variable Stars B. Pulsating Stars C. Period Changes in Variable Stars ...
P2_5 The Apparent Magnitude of α Orionis Supernova
... The star α Orionis (Betelgeuse) is to become a type II supernova at the end of its life. Some have postulated that this supernova will be bright enough that it will be visible during the day. Betelgeuse will have an apparent magnitude of around -8.7, brighter than Venus, which can be seen when the s ...
... The star α Orionis (Betelgeuse) is to become a type II supernova at the end of its life. Some have postulated that this supernova will be bright enough that it will be visible during the day. Betelgeuse will have an apparent magnitude of around -8.7, brighter than Venus, which can be seen when the s ...
Exercise 4
... radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position of the peak, astronomers can deduce the surface temperature of the star. In general, the spectra of hot stars peak at shorter wavelengths and therefore ...
... radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position of the peak, astronomers can deduce the surface temperature of the star. In general, the spectra of hot stars peak at shorter wavelengths and therefore ...
A stars
... Around Epsilon Indi (Spectral type K5: about one-tenth the Sun's luminosity), an Earth-sized planet would have to orbit at about the distance of Mercury from the star. ...
... Around Epsilon Indi (Spectral type K5: about one-tenth the Sun's luminosity), an Earth-sized planet would have to orbit at about the distance of Mercury from the star. ...
Wednesday, November 7, 2007
... • The central object continues to shed matter slowly. • The ejected matter forms a cloud around the star. ...
... • The central object continues to shed matter slowly. • The ejected matter forms a cloud around the star. ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.