guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... young stars are nearly spherical. New stars are created when knots of dust and gas collapse. In the nebula, however, this process stopped when the young central stars reached their full power. The radiation they produce is so strong that it prevents new stars from forming. ...
... young stars are nearly spherical. New stars are created when knots of dust and gas collapse. In the nebula, however, this process stopped when the young central stars reached their full power. The radiation they produce is so strong that it prevents new stars from forming. ...
Lecture16
... When we say temperature, we really mean the surface temperature. There are two ways to determine a star’s temperature, 1) its color, and 2) its ...
... When we say temperature, we really mean the surface temperature. There are two ways to determine a star’s temperature, 1) its color, and 2) its ...
Level 6 Stars and Constellations
... passes successively through 12 constellations. All planets (except Pluto at certain times) can be observed only in these 12 constellations, which form the so-called zodiac, and the Sun also moves through the zodiacal signs, though the Sun's apparent movement is actually caused by the movement of Ear ...
... passes successively through 12 constellations. All planets (except Pluto at certain times) can be observed only in these 12 constellations, which form the so-called zodiac, and the Sun also moves through the zodiacal signs, though the Sun's apparent movement is actually caused by the movement of Ear ...
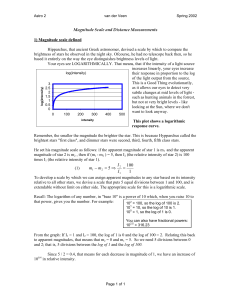
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... 2) Finding the distance to a star from its absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude: The visual magnitude you observe for a star depends both on its intrinsic luminosity and its distance. In order to bring all stars to the same "reference distance" so that we can really compare their magnitudes, we ...
... 2) Finding the distance to a star from its absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude: The visual magnitude you observe for a star depends both on its intrinsic luminosity and its distance. In order to bring all stars to the same "reference distance" so that we can really compare their magnitudes, we ...
Deducing Temperatures and Luminosities of Stars
... • Two otherwise identical stars (same radius, same temperature ⇒ same luminosity) will still appear vastly different in brightness if their distances from Earth are different • Reason: intensity of light inversely proportional to the square of the distance the light has to travel – Light waves from ...
... • Two otherwise identical stars (same radius, same temperature ⇒ same luminosity) will still appear vastly different in brightness if their distances from Earth are different • Reason: intensity of light inversely proportional to the square of the distance the light has to travel – Light waves from ...
How it works:
... big “W” in the northern sky. The “W” represents the outline of Queen Cassiopeia tied to a throne. According to the Greek myth, this was her punishment for being extremely vain. Depending on the time of night and the season, the “W” will be right-side up, on one of its sides, or hanging upside-down. ...
... big “W” in the northern sky. The “W” represents the outline of Queen Cassiopeia tied to a throne. According to the Greek myth, this was her punishment for being extremely vain. Depending on the time of night and the season, the “W” will be right-side up, on one of its sides, or hanging upside-down. ...
Assignment Worksheet
... 1. Your full name, last name first, first name last, and remember to bubble in the letters. 2. Bubble in the 5-digit homework code, 11111, on the form under "Identification Number" in columns A-E (lower left-hand corner of the form). Do not enter your Student ID or any other info into this area, jus ...
... 1. Your full name, last name first, first name last, and remember to bubble in the letters. 2. Bubble in the 5-digit homework code, 11111, on the form under "Identification Number" in columns A-E (lower left-hand corner of the form). Do not enter your Student ID or any other info into this area, jus ...
The HR Diagram - Faculty Web Pages
... its Hipparcos Catalog Number. The Hipparcos Catalog is a standard reference list of about 100,000 stars in the sky. Every star you can see with the naked eye, and many thousands that you can't see, were all carefully organized in the Hipparcos Catalog in the 1980's and 90's by the Hipparcos spacecra ...
... its Hipparcos Catalog Number. The Hipparcos Catalog is a standard reference list of about 100,000 stars in the sky. Every star you can see with the naked eye, and many thousands that you can't see, were all carefully organized in the Hipparcos Catalog in the 1980's and 90's by the Hipparcos spacecra ...
Aspire: Star Life Cycle - Easy Peasy All-in
... Our Sun Vega Sirius B I. Click on the image to start the next activity. ...
... Our Sun Vega Sirius B I. Click on the image to start the next activity. ...
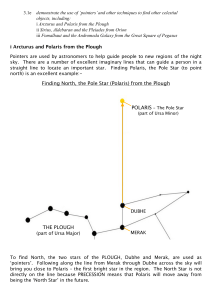
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... To find Sirius, the Dog Star and the brightest star in the night sky, the three stars of Orion’s Belt are used as ‘pointers’. Following along the line down from Orion’s Belt across the sky will bring you to Sirius. Using Orion’s Belt as ‘pointers’, but this time moving in the opposite direction, you ...
... To find Sirius, the Dog Star and the brightest star in the night sky, the three stars of Orion’s Belt are used as ‘pointers’. Following along the line down from Orion’s Belt across the sky will bring you to Sirius. Using Orion’s Belt as ‘pointers’, but this time moving in the opposite direction, you ...
temperature - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... The most important PhD thesis in modern astrophysics: the stars are MOSTLY hydrogen (and helium) with trace levels of other elements. We only see those strong lines from the trace elements when there are variations in stellar temperature. ...
... The most important PhD thesis in modern astrophysics: the stars are MOSTLY hydrogen (and helium) with trace levels of other elements. We only see those strong lines from the trace elements when there are variations in stellar temperature. ...
WEBDA - a tool for CP star research in open clusters
... success of WEBDA is documented by its worldwide usage and the related acknowledgements in the literature: more than 450 refereed publications within the last seven years acknowledge its use. It collects all published data for stars in open clusters that may be useful either to determine membership, ...
... success of WEBDA is documented by its worldwide usage and the related acknowledgements in the literature: more than 450 refereed publications within the last seven years acknowledge its use. It collects all published data for stars in open clusters that may be useful either to determine membership, ...
14.5 Yellow Giants and Pulsating Stars Variable Stars Not all stars
... becomes an RR Lyrae variable star. When a highmass star crosses the instability strip in its red giant phase, being more luminous it instead becomes a Cepheid variable. The amount of time a given star spends in the instability strip depends on its mass. Massive stars such as the highly luminous Cep ...
... becomes an RR Lyrae variable star. When a highmass star crosses the instability strip in its red giant phase, being more luminous it instead becomes a Cepheid variable. The amount of time a given star spends in the instability strip depends on its mass. Massive stars such as the highly luminous Cep ...
ppt document
... luminosity, but hotter tends to increase luminosity. The position of the newly forming star on the H-R diagram will move to the left as it heats up but wander up and down somewhat as its size shrinks. This process takes about 50 million years for a star like the sun, but may take a much shorter time ...
... luminosity, but hotter tends to increase luminosity. The position of the newly forming star on the H-R diagram will move to the left as it heats up but wander up and down somewhat as its size shrinks. This process takes about 50 million years for a star like the sun, but may take a much shorter time ...
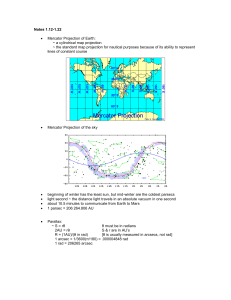
Notes 1 - cloudfront.net
... 7 milimeters is usually the size range in an adult’s pupil charged couple device (CCD) are more sensitive than film Messier 13 (M13): ~ great globular cluster ~ 25, 100 light years away ...
... 7 milimeters is usually the size range in an adult’s pupil charged couple device (CCD) are more sensitive than film Messier 13 (M13): ~ great globular cluster ~ 25, 100 light years away ...
The night sky in October and November
... constellation Pisces as two fish. No bright stars, but on a clear night, should be able to see the “vee” that is the cord and two fish. If born under the sign of Pisces, the sun was in front of the constellation Pisces, but 2,000 years ago. Now, on the same date, the sun is in the constellation Aqua ...
... constellation Pisces as two fish. No bright stars, but on a clear night, should be able to see the “vee” that is the cord and two fish. If born under the sign of Pisces, the sun was in front of the constellation Pisces, but 2,000 years ago. Now, on the same date, the sun is in the constellation Aqua ...
CYGNUS CONSTELLATION, the Swan Cygnus is
... Alpha Cygni, called Deneb, is the brightest star in Cygnus. It is a white supergiant star of spectral type A2Iae that varies between magnitudes 1.21 and 1.29, one of the largest and most luminous A-class stars known. It is located about 3200 light-years away (an A-type star is a main-sequence (hydro ...
... Alpha Cygni, called Deneb, is the brightest star in Cygnus. It is a white supergiant star of spectral type A2Iae that varies between magnitudes 1.21 and 1.29, one of the largest and most luminous A-class stars known. It is located about 3200 light-years away (an A-type star is a main-sequence (hydro ...
HOMEWORK #1
... You may assume the planet moves in a circular orbit and transits across the star’s diameter as seen from Earth. Show all your work even though you may not be satisfied with your final answer. We will discuss the details afterwards and learn an important lesson about assumptions and errors. ...
... You may assume the planet moves in a circular orbit and transits across the star’s diameter as seen from Earth. Show all your work even though you may not be satisfied with your final answer. We will discuss the details afterwards and learn an important lesson about assumptions and errors. ...
HOMEWORK #1
... You may assume the planet moves in a circular orbit and transits across the star’s diameter as seen from Earth. Show all your work even though you may not be satisfied with your final answer. We will discuss the details afterwards and learn an important lesson about assumptions and errors. ...
... You may assume the planet moves in a circular orbit and transits across the star’s diameter as seen from Earth. Show all your work even though you may not be satisfied with your final answer. We will discuss the details afterwards and learn an important lesson about assumptions and errors. ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.