Stars
... star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
... star really is. If all stars were the same distance from us, how bright would it look compared to the other stars? ...
Part 2 Answer Key
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
April
... shape with uneven brightness and texture. This is as a result of an unusual characteristic: the central portion of the galaxy rotates in one direction out to approximately 3,000 light years, but the outer portion of the galaxy rotates in the opposite direction! Where the two countra-rotating section ...
... shape with uneven brightness and texture. This is as a result of an unusual characteristic: the central portion of the galaxy rotates in one direction out to approximately 3,000 light years, but the outer portion of the galaxy rotates in the opposite direction! Where the two countra-rotating section ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature? - d
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500oC are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000oC to 3500oC a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000o C are orange-red, up to 6000oC yellow-white, up to 7500oC blue-white, and up to 40,000oC blue. 5. Look for patterns in your grap ...
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500oC are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000oC to 3500oC a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000o C are orange-red, up to 6000oC yellow-white, up to 7500oC blue-white, and up to 40,000oC blue. 5. Look for patterns in your grap ...
Stars: Other Suns
... • New optical techniques work on some stars (more to come!) • Angular diameter + distance => physical diameter ...
... • New optical techniques work on some stars (more to come!) • Angular diameter + distance => physical diameter ...
09astrophysics_2007Nov
... Formula: Distance (pc)=1/parallax Limiting Optical resolution of telescope (due to wave nature of light) limits smallest parallax we can measure ...
... Formula: Distance (pc)=1/parallax Limiting Optical resolution of telescope (due to wave nature of light) limits smallest parallax we can measure ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... Based on apparent magnitude, the Sun is the brightest star (-26.40) and Deneb is the dimmest star (1.25). Absolute magnitude shows Rigel to be the brightest star (-8.61) and the Sun to be the dimmest star (4.80). Brightness of stars is traditionally expressed as magnitude. The more negative the valu ...
... Based on apparent magnitude, the Sun is the brightest star (-26.40) and Deneb is the dimmest star (1.25). Absolute magnitude shows Rigel to be the brightest star (-8.61) and the Sun to be the dimmest star (4.80). Brightness of stars is traditionally expressed as magnitude. The more negative the valu ...
of a Star
... NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Launched in February, SDO is the most advanced spacecraft ever designed to study the sun. ...
... NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Launched in February, SDO is the most advanced spacecraft ever designed to study the sun. ...
Scientists classify stars by
... (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from u ...
... (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from u ...
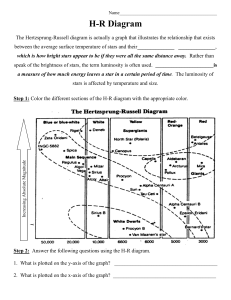
H-R Diagram Student
... H-R Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of ...
... H-R Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of ...
Place in Space
... distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So, this distance is 1 lightyear. ...
... distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So, this distance is 1 lightyear. ...
What are stars? - Manhasset Schools
... nothing can escape its gravity • Usually results from the supernova of a very massive star ...
... nothing can escape its gravity • Usually results from the supernova of a very massive star ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
Day-6
... Very low-mass stars (< 0.08 M) never start hydrogen fusion. These are called brown dwarfs. ...
... Very low-mass stars (< 0.08 M) never start hydrogen fusion. These are called brown dwarfs. ...
Lecture 5: Light as a tool
... The Absolute Magnitude A star’s absolute magnitude Mv is the apparent magnitude it ...
... The Absolute Magnitude A star’s absolute magnitude Mv is the apparent magnitude it ...
Star Formation
... • Interstellar gas, like the sun, is 74% hydrogen and 25% helium. • Interstellar dust, like clouds in the gas giants, are molecular carbon monoxide, ammonia, and water. • Traces of all other elements are present. ...
... • Interstellar gas, like the sun, is 74% hydrogen and 25% helium. • Interstellar dust, like clouds in the gas giants, are molecular carbon monoxide, ammonia, and water. • Traces of all other elements are present. ...
Review 2
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? A star when observed through ...
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? A star when observed through ...
Space Science Unit
... • This chart uses surface temperature of the star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). Th ...
... • This chart uses surface temperature of the star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). Th ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale in the 1st century B.C.. ASTERISMS - An asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. C ...
... night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale in the 1st century B.C.. ASTERISMS - An asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. C ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.