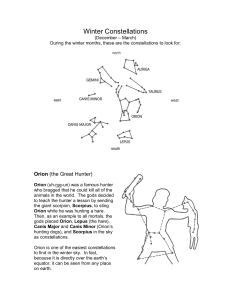
seven winter constellations
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
Stellar Evolution
... Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, followed by collapse to white dwarf by blowing out their outer layer, and eventually light up planetary nebulae Mass ...
... Low Mass Stars – consume fuel at a slow rate, may remain on main-sequence for up to 100 billion years, end up collapsing into white dwarfs Medium Mass Stars – go into red-giant stage, followed by collapse to white dwarf by blowing out their outer layer, and eventually light up planetary nebulae Mass ...
Calculating Main Sequence Lifetimes
... stars having larger magnitudes. Don’t confuse the relative magnitude with absolute magnitude. The relative magnitude measures the brightness of a star as it appears in the sky and it depends on the brightness and on the distance; if we put a star at the distance of 10 Parsec (33 year light), its mag ...
... stars having larger magnitudes. Don’t confuse the relative magnitude with absolute magnitude. The relative magnitude measures the brightness of a star as it appears in the sky and it depends on the brightness and on the distance; if we put a star at the distance of 10 Parsec (33 year light), its mag ...
OUSNMAR05 - The Open University
... orientation of the map may differ from that of the observed image of the Moon depending on the type of telescope used. If you find the Moon too bright use a filter to reduce the glare. At times features along different parts of the limb are better presented due the effect of libration – an apparent ...
... orientation of the map may differ from that of the observed image of the Moon depending on the type of telescope used. If you find the Moon too bright use a filter to reduce the glare. At times features along different parts of the limb are better presented due the effect of libration – an apparent ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... stars ? If an astronomer were observing from the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa, by how much would Vega shift during the Jovian year ? (Hint: Jupiter is 5.2 AU from the sun.) A parallax of 0.129 means that when the observer moves 1 AU, the star shifts 0.129 arcsec. Since the diameter of the Earth’ ...
... stars ? If an astronomer were observing from the surface of Jupiter’s moon Europa, by how much would Vega shift during the Jovian year ? (Hint: Jupiter is 5.2 AU from the sun.) A parallax of 0.129 means that when the observer moves 1 AU, the star shifts 0.129 arcsec. Since the diameter of the Earth’ ...
City Built Over Caves To be Explored in Mexico
... in his foot, about an equal distance to the south. Below him is one of his dogs, Canis Major, markedby brilliant Sirius, brightest star of the sky. About as high above the horizon, almost directly east, is the other dog, Canis Minor, with Procyon.Higher, and still farthernorth, are the twins, Gemini ...
... in his foot, about an equal distance to the south. Below him is one of his dogs, Canis Major, markedby brilliant Sirius, brightest star of the sky. About as high above the horizon, almost directly east, is the other dog, Canis Minor, with Procyon.Higher, and still farthernorth, are the twins, Gemini ...
Sample exam 2
... 12. What are the conditions necessary to initiate star formation? Give at least three different characteristics, and how each leads to (or is needed for) star formation. 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You ...
... 12. What are the conditions necessary to initiate star formation? Give at least three different characteristics, and how each leads to (or is needed for) star formation. 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You ...
Astronomy
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
Scientists classify stars by
... (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from u ...
... (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from u ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will cover: Brief review
... Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “RR..RZ...SS...SZ...ZZ”, and then “AA...A ...
... Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “RR..RZ...SS...SZ...ZZ”, and then “AA...A ...
Bright stars and faint stars: the stellar magnitude system Magnitudes
... Absolute Magnitude: a measure of the intrinsic brilliance of a star • Pick a star (any star) • Imagine moving it to a distance of 10 parsecs • The apparent magnitude it would have is its absolute magnitude • The absolute magnitude is a distanceindependent quantity • Look at Appendix 12 and Appendix ...
... Absolute Magnitude: a measure of the intrinsic brilliance of a star • Pick a star (any star) • Imagine moving it to a distance of 10 parsecs • The apparent magnitude it would have is its absolute magnitude • The absolute magnitude is a distanceindependent quantity • Look at Appendix 12 and Appendix ...
Morning Announcements
... Part 2: Stellar Sizes: Once we know a star’s temperature and its total luminosity we can also deduce its size. The reason is that there is a connection between temperature and total energy output, which is described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. There are two important aspects to remember: • The tota ...
... Part 2: Stellar Sizes: Once we know a star’s temperature and its total luminosity we can also deduce its size. The reason is that there is a connection between temperature and total energy output, which is described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. There are two important aspects to remember: • The tota ...
22 October: The Formation of Stars
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
Stars
... light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars - ...
... light the planets in a system • A star is a ball of plasma held together by its own gravity – Nuclear reactions occur in stars - ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Types of Stars • Stars that fit the expected pattern – cool and dim; hot and bright – are called main sequence stars – Most stars fall in the region called main sequence. ...
... Types of Stars • Stars that fit the expected pattern – cool and dim; hot and bright – are called main sequence stars – Most stars fall in the region called main sequence. ...
Light as a Wave (1) Distances to Stars
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): ...
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): ...
Which property of a star would not change if we could observe it
... – Mnemonics: “Oh, Be A Fine Girl/Guy, ...
... – Mnemonics: “Oh, Be A Fine Girl/Guy, ...
Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The
... Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The classification of stars by surface temperature and spectral pattern is a painstaking process requiring the efforts of many scientists from hundreds of observatories around the world. To make it easier to refer to the different types of main sequen ...
... Astronomy – Interpreting Main Sequence Star Data The classification of stars by surface temperature and spectral pattern is a painstaking process requiring the efforts of many scientists from hundreds of observatories around the world. To make it easier to refer to the different types of main sequen ...
Nebula - NICADD
... • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. ...
... • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.