File - Mr. Goodyear Astronomy
... Stage 6 Planetary Nebula / Nova - star uses up most of He and moves back toward main sequence area of H-R diagram. - Star fluctuates on and off main sequence. Gravity tries to contact star creating other elements in star increasing fusion process. - This increase energy causes an explosion-like occ ...
... Stage 6 Planetary Nebula / Nova - star uses up most of He and moves back toward main sequence area of H-R diagram. - Star fluctuates on and off main sequence. Gravity tries to contact star creating other elements in star increasing fusion process. - This increase energy causes an explosion-like occ ...
September Evening Skies
... of the "Teapot," is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... of the "Teapot," is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
star brightness
... it would appear over 38 our in times fainter than uld be daytime sky! In fact, it wo in night sky, which is the ma the in n cyo Pro as t as fain g) Do all Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not singl ...
... it would appear over 38 our in times fainter than uld be daytime sky! In fact, it wo in night sky, which is the ma the in n cyo Pro as t as fain g) Do all Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not singl ...
8hrdiagram1s
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
Document
... g. Which star is the closest (find m-M)? h. Which star has the smallest parallax angle? i. ...
... g. Which star is the closest (find m-M)? h. Which star has the smallest parallax angle? i. ...
The IC 348 surface density in the Perseus molecular cloud L. Cambrésy Observatoire de Strasbourg, France
... IC 348 surface density of unknown members ...
... IC 348 surface density of unknown members ...
Read
... Here are some important definitions for terms used in the lab: Apparent magnitude – The measure of the brightness of a star as seen from Earth. Absolute magnitude – The measure of the brightness of a star as it would be seen from the standard distance of 10 parsecs. A parsec (pc) is a unit of distan ...
... Here are some important definitions for terms used in the lab: Apparent magnitude – The measure of the brightness of a star as seen from Earth. Absolute magnitude – The measure of the brightness of a star as it would be seen from the standard distance of 10 parsecs. A parsec (pc) is a unit of distan ...
Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics
... called its _apparent magnitude__ or brightness. •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have ...
... called its _apparent magnitude__ or brightness. •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have ...
Document
... Aside from temperature (color) and luminosity (absolute magnitude), what other physical parameters are needed to characterize a star? • Chemical composition • Mass • Radius • Age These parameters can be measured directly using: • nearby/bright stars, (spectrum = composition) • binary stars, (binary ...
... Aside from temperature (color) and luminosity (absolute magnitude), what other physical parameters are needed to characterize a star? • Chemical composition • Mass • Radius • Age These parameters can be measured directly using: • nearby/bright stars, (spectrum = composition) • binary stars, (binary ...
STARS - AN INTRODUCTION
... They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
... They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System
... calculate—its mass. • The word constellation is used to designate an area of the sky that contains a specific pattern of stars. • Two stars that orbit each other, pulled toward each other by gravity, are called binary stars. ...
... calculate—its mass. • The word constellation is used to designate an area of the sky that contains a specific pattern of stars. • Two stars that orbit each other, pulled toward each other by gravity, are called binary stars. ...
ASTRONOMY
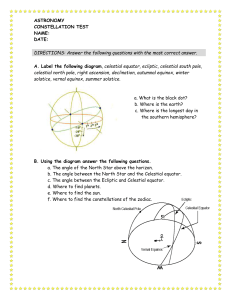
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
The Life of a Star
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... Usually neglected since speed of light is VERY large Becomes significant in very bright objects – e.g. Lasers, Hot Stars Question is: How big is this force vs. gravity? For the Sun, Mass lost over lifetime ~ 0.01% For hot stars (M = 10 - 50 M) mass can be reduced by ½! ...
... Usually neglected since speed of light is VERY large Becomes significant in very bright objects – e.g. Lasers, Hot Stars Question is: How big is this force vs. gravity? For the Sun, Mass lost over lifetime ~ 0.01% For hot stars (M = 10 - 50 M) mass can be reduced by ½! ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
Star Sizes
... Sirius is the brightest star in our night sky. The reason for this is that it is relatively close at only 8.6 light years away. Remember the next nearest star is 4.3 light years away. Sirius is about twice as massive as the Sun but it is 25 times as luminous. It can be found in the constellation Ca ...
... Sirius is the brightest star in our night sky. The reason for this is that it is relatively close at only 8.6 light years away. Remember the next nearest star is 4.3 light years away. Sirius is about twice as massive as the Sun but it is 25 times as luminous. It can be found in the constellation Ca ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... The force of the Sun’s gravity is proportional to the mass of the Sun, and so the speeds of the planets as they orbit the Sun depend on the mass of the Sun. Newton’s generalization of Kepler’s 3rd law says: P 2 = a3 / M where P is the time to orbit, measured in years, a is the size of the orbit, mea ...
... The force of the Sun’s gravity is proportional to the mass of the Sun, and so the speeds of the planets as they orbit the Sun depend on the mass of the Sun. Newton’s generalization of Kepler’s 3rd law says: P 2 = a3 / M where P is the time to orbit, measured in years, a is the size of the orbit, mea ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.