22 Stellar Remnant/HR Diagram
... We can now get the temperature (within a few 10’s of a degree) Find a MS star at that Temp Find the Luminosity/absolute magnitude Gives a distance! ...
... We can now get the temperature (within a few 10’s of a degree) Find a MS star at that Temp Find the Luminosity/absolute magnitude Gives a distance! ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... medium aperture scope. The best thing is that it so easy to locate. NGC 869 & 884, popularly known as the Double Cluster, are a pair of open star clusters situated about 7,300 light years away. With visual magnitudes of 5.3 and 6.1 respectively, the pair was labeled as Caldwell 14 by Sir Patrick Moo ...
... medium aperture scope. The best thing is that it so easy to locate. NGC 869 & 884, popularly known as the Double Cluster, are a pair of open star clusters situated about 7,300 light years away. With visual magnitudes of 5.3 and 6.1 respectively, the pair was labeled as Caldwell 14 by Sir Patrick Moo ...
J tieutifit meti(au.
... North of Andromeda the eye is caught by a zigzag October 7th. but suddenly it was found electricity was destined to rowof stars resembling the letter" W;"these mark the ...
... North of Andromeda the eye is caught by a zigzag October 7th. but suddenly it was found electricity was destined to rowof stars resembling the letter" W;"these mark the ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... Our Sun- single star system, which is the closest star to Earth Constellations- groups of stars in which people at one time thought they saw imaginary figures of animals and people: ex Ursa Minor (Little Bear)- containing the Polaris (North Star) Orion (Hunter)- containing the bright supergiant star ...
... Our Sun- single star system, which is the closest star to Earth Constellations- groups of stars in which people at one time thought they saw imaginary figures of animals and people: ex Ursa Minor (Little Bear)- containing the Polaris (North Star) Orion (Hunter)- containing the bright supergiant star ...
Everything Under and Over The Stars
... If the sun went nova, what would happen to the solar system? There was a recent supernova called SN1993J in a star system, which is not mentioned. The powerful shockwave traveled at 44 million mph, but 5 years later it slowed down because of drag caused by particles. There has been a supernova in t ...
... If the sun went nova, what would happen to the solar system? There was a recent supernova called SN1993J in a star system, which is not mentioned. The powerful shockwave traveled at 44 million mph, but 5 years later it slowed down because of drag caused by particles. There has been a supernova in t ...
Characteristics of Stars
... 1. How long would it take to travel to the Sun at light speed? How long would it take to travel to the nearest star if you could travel at light speed? What is a galaxy? What is the name of the galaxy we live in? How many stars are in a galaxy? How long would it take to travel to the center of our g ...
... 1. How long would it take to travel to the Sun at light speed? How long would it take to travel to the nearest star if you could travel at light speed? What is a galaxy? What is the name of the galaxy we live in? How many stars are in a galaxy? How long would it take to travel to the center of our g ...
Chapter 21 Study Guide
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
... 12. A building that contains one or more telescopes is called an _____________________________. 13. Name one reason why astronomers have built large telescopes on the tops of mountains. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. The Hubble Space Telesco ...
solution
... The gravitational energy causes Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction, which increases the pressure, density and temperature of the central region of a protostar. Once the temperature exceeds a few million K, H begins to fuse into He (via the p-p chain in a Sun-sized protostar, or the CNO cycle in a larger o ...
... The gravitational energy causes Kelvin-Helmholtz contraction, which increases the pressure, density and temperature of the central region of a protostar. Once the temperature exceeds a few million K, H begins to fuse into He (via the p-p chain in a Sun-sized protostar, or the CNO cycle in a larger o ...
1 au d p = 1 au d
... Starting from the observed luminosity function, possible to derive an estimate for the Initial Mass Function (IMF). To define the IMF, imagine that we form a large number of stars. Then: the number of stars that have been x (M)DM = born with initial masses between M and M+DM (careful not to confuse ...
... Starting from the observed luminosity function, possible to derive an estimate for the Initial Mass Function (IMF). To define the IMF, imagine that we form a large number of stars. Then: the number of stars that have been x (M)DM = born with initial masses between M and M+DM (careful not to confuse ...
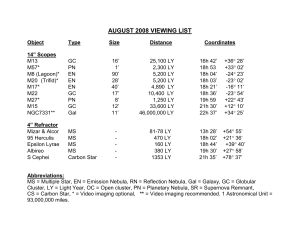
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
HW #5 Answers (Due 9/29)
... stars that are just leaving the main sequence. Explain how this turn-off mass gives us the age of the cluster. As we found out in class, the more massive a star is the faster it uses up its fuel supply. For very massive stars, the fuel is used up in a matter of a couple million years. For less massi ...
... stars that are just leaving the main sequence. Explain how this turn-off mass gives us the age of the cluster. As we found out in class, the more massive a star is the faster it uses up its fuel supply. For very massive stars, the fuel is used up in a matter of a couple million years. For less massi ...
THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF
... serious students of astrology. Opening page of Tetrabiblos, published in 1484. ...
... serious students of astrology. Opening page of Tetrabiblos, published in 1484. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell used spectral class against absolute magnitude. Their resultant plots showed that the relationship between temperature and luminosity of a star was not random but instead appeared t ...
... against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell used spectral class against absolute magnitude. Their resultant plots showed that the relationship between temperature and luminosity of a star was not random but instead appeared t ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.