PSC100 Transparant Replacement for Chapter 8 Measurement of
... * Calculate distance as speed of light x time of travel. Stellar Parallax * Measure angle to star at two different times. * Use largest base line possible, the diameter of Earth’s orbit around the Sun * This means data readings must be taken 6 months apart. * Calculate distance using triangulation. ...
... * Calculate distance as speed of light x time of travel. Stellar Parallax * Measure angle to star at two different times. * Use largest base line possible, the diameter of Earth’s orbit around the Sun * This means data readings must be taken 6 months apart. * Calculate distance using triangulation. ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
... 47. The most basic way to measure the distance to a star is ____________________. 48. A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. 49. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ____________________ as it appears from ____________________. 50. Some stars, called _________________ ...
29.2 Measuring the Stars - Mr. Tobin`s Earth Science Class
... Sequence: Contains 90% of stars including Sun (which is at the center because it has an average temperature and luminosity.) • Stars here fuse hydrogen. • As hydrogen runs out stars fuse helium ...
... Sequence: Contains 90% of stars including Sun (which is at the center because it has an average temperature and luminosity.) • Stars here fuse hydrogen. • As hydrogen runs out stars fuse helium ...
Measuring stars Part I
... Deneb has an Absolute visual magnitude of -8.73 (this is about the same brightness as the quarter moon---but at 32.6 light years away!) Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolu ...
... Deneb has an Absolute visual magnitude of -8.73 (this is about the same brightness as the quarter moon---but at 32.6 light years away!) Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolu ...
Diapositiva 1
... Halo of the Cat's Eye Machine with which the photo has been taken: Nordic Optical Telescope. Explanation: The Cat’s Eye Nebula (NGC 6543) is one of the best known planetary nebulae in the sky. Its haunting symmetries are seen in the very central region of this stunning false-color picture, processe ...
... Halo of the Cat's Eye Machine with which the photo has been taken: Nordic Optical Telescope. Explanation: The Cat’s Eye Nebula (NGC 6543) is one of the best known planetary nebulae in the sky. Its haunting symmetries are seen in the very central region of this stunning false-color picture, processe ...
Stellar Properties
... what would be the distance to the star? A)1/5, b)1. c)5, d)25 pc 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. A ...
... what would be the distance to the star? A)1/5, b)1. c)5, d)25 pc 2. Star A and B have same luminosity. If star A is 4 times closer to Earth then star B, then _____ to earthly viewer.: a=A is 4 x brighter, b=B is 4x brighter, c=A is 16 times brighter d=B is 16 times brighter, e=A is 64x brighter 3. A ...
Life cycle of a star
... When the helium core runs out, and the outer layers drift of away from the core as a gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a ...
... When the helium core runs out, and the outer layers drift of away from the core as a gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a ...
W > 1 - The Open University
... Use the guide above for Coma to locate M99. Then move 2o southeast to reach NGC4374 (M84) (9.3) eg and NGC4406 (M86) (9.2) eg easily visible in the same field of view. Scan this field carefully to locate other non-Messier galaxies. Note their positions and sketch the field, then use a suitable star ...
... Use the guide above for Coma to locate M99. Then move 2o southeast to reach NGC4374 (M84) (9.3) eg and NGC4406 (M86) (9.2) eg easily visible in the same field of view. Scan this field carefully to locate other non-Messier galaxies. Note their positions and sketch the field, then use a suitable star ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... together by gravity and is composed of gas and emits light. • A star is born when the gases inside a nebula contract together. Inside the nebula you will find new starts. ...
... together by gravity and is composed of gas and emits light. • A star is born when the gases inside a nebula contract together. Inside the nebula you will find new starts. ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... The key is that all stars were not born at the same time. the stars which we see today are at different stages in their ...
... The key is that all stars were not born at the same time. the stars which we see today are at different stages in their ...
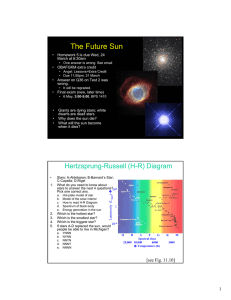
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... Giants are dying stars; white dwarfs are dead stars • Evidence on giants from star clusters • Compare members of a population. (Twin study) ...
... Giants are dying stars; white dwarfs are dead stars • Evidence on giants from star clusters • Compare members of a population. (Twin study) ...
Interactive Vocabulary Review for Outer Space Indicator
... A natural, luminous, celestial body is better known as a STAR! ...
... A natural, luminous, celestial body is better known as a STAR! ...
Sky Notes - February 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... surface temperature of around 10,000 degrees Celcius - about twice as hot as our Sun. In fact, it’s name is derived from the Greek ‘Seirios’ meaning ‘glowing’ or ‘scorcher’ - very appropriate. In addition, the star is somewhat larger than the Sun, more than twice as massive and around 25 times as lu ...
... surface temperature of around 10,000 degrees Celcius - about twice as hot as our Sun. In fact, it’s name is derived from the Greek ‘Seirios’ meaning ‘glowing’ or ‘scorcher’ - very appropriate. In addition, the star is somewhat larger than the Sun, more than twice as massive and around 25 times as lu ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... ii) In the solar neighborhood 1 parsec is about the average distance between stars iii) 1 parsec = 3.26 ly = 3.09x1013 km = 206,137 AU (1) Analogy: if an AU was a foot, a parsec would be 39 miles (2) Analogy: if an Au was a foot, the Solar System would fit in a 40-foot circle (i.e. within the confin ...
... ii) In the solar neighborhood 1 parsec is about the average distance between stars iii) 1 parsec = 3.26 ly = 3.09x1013 km = 206,137 AU (1) Analogy: if an AU was a foot, a parsec would be 39 miles (2) Analogy: if an Au was a foot, the Solar System would fit in a 40-foot circle (i.e. within the confin ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same apparent brightness __________ ...
... Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same apparent brightness __________ ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.