Unit 11 Vocabulary
... 4. main sequence star - stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. Most of the stars in the universe are main sequence stars – they are the stars that “twinkle.” 5. red giant star - a star that has exhausted the primary supply of hydrogen fuel, and is in the last stage ...
... 4. main sequence star - stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. Most of the stars in the universe are main sequence stars – they are the stars that “twinkle.” 5. red giant star - a star that has exhausted the primary supply of hydrogen fuel, and is in the last stage ...
Stellar Evolution: After the Main Sequence
... • When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core • This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
... • When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core • This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
Objects Beyond our Solar System
... India in 1054 where the explosion could be seen during the daytime and it lasted for around 21 months. ...
... India in 1054 where the explosion could be seen during the daytime and it lasted for around 21 months. ...
galaxies and stars - Valhalla High School
... faster it is moving. • It takes 2 million years for light from the Andromeda galaxy to reach earth. • Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. ...
... faster it is moving. • It takes 2 million years for light from the Andromeda galaxy to reach earth. • Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical
... From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical Societies, this is IT'S OVER YOUR HEAD for the week beginning July 17th, a look at what's up in the sky over Puget Sound. The glory of the summer sky is highlighted by the Milky Way, a giant spiral galaxy, which stretches from the northern horizon in Perseus ...
... From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical Societies, this is IT'S OVER YOUR HEAD for the week beginning July 17th, a look at what's up in the sky over Puget Sound. The glory of the summer sky is highlighted by the Milky Way, a giant spiral galaxy, which stretches from the northern horizon in Perseus ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... with parallax**** • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the ma ...
... with parallax**** • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the ma ...
Star Life Cycle Computer Lab
... 12. What is the 3rd fuel that stars can use after Hydrogen and Helium? The Beginning of the End 13. When a star is fusing helium, what stage of its life is it considered? What type of star is this? 14. Do the helium lab and Star Quiz 2. End of a Star 15. What are the 3 possible deaths of a star? 16. ...
... 12. What is the 3rd fuel that stars can use after Hydrogen and Helium? The Beginning of the End 13. When a star is fusing helium, what stage of its life is it considered? What type of star is this? 14. Do the helium lab and Star Quiz 2. End of a Star 15. What are the 3 possible deaths of a star? 16. ...
Science Assessment Stage H--Performance Standard 12F-H
... • Interpret and represent analysis of astronomical data about constellation members. • Analyze research and data for supporting or refuting the selected hypotheses. • Report, display and defend the data analysis of constellation members and other star groupings. • Generate further questions for star ...
... • Interpret and represent analysis of astronomical data about constellation members. • Analyze research and data for supporting or refuting the selected hypotheses. • Report, display and defend the data analysis of constellation members and other star groupings. • Generate further questions for star ...
Life and Death Of A Star - EarthSpaceScience
... appear at the top of the chart as Giants or Super Giants. • Main sources stars that have collapsed in on them self become low luminosity White Dwarfs ...
... appear at the top of the chart as Giants or Super Giants. • Main sources stars that have collapsed in on them self become low luminosity White Dwarfs ...
Chapter 1 Daily Note Sheets Completed Power Point
... • Bayer Name: Name given to star going from the brightest to the dimmest. Use the Greek alphabet α alpha is the brightest, β Beta is next brightest, γ gamma is next etc….. Then use the Latin Possessive. • Example alpha Ursa Minoris ( brightest star in Ursa Major) Polaris, alpha Canis Majoris ( brigh ...
... • Bayer Name: Name given to star going from the brightest to the dimmest. Use the Greek alphabet α alpha is the brightest, β Beta is next brightest, γ gamma is next etc….. Then use the Latin Possessive. • Example alpha Ursa Minoris ( brightest star in Ursa Major) Polaris, alpha Canis Majoris ( brigh ...
Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Only 6 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky are closer to us than 10pc 14 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky must have absolute magnitude of at least 1.5 (20 times brighter than the Sun) Out of the 6000 stars visible, only 50 are dimmer than the Sun in absolute magnitude. Question: Is the Sun be ...
... Only 6 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky are closer to us than 10pc 14 of the 20 brightest stars in the sky must have absolute magnitude of at least 1.5 (20 times brighter than the Sun) Out of the 6000 stars visible, only 50 are dimmer than the Sun in absolute magnitude. Question: Is the Sun be ...
Stars and Galaxies – Notes
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are doublestar systems in which two stars revolve around each ...
Size Color and Temperature
... than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars in the sky, even though it is 522 light-y ...
... than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars in the sky, even though it is 522 light-y ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... M41 (also known as the Little Beehive) is a fine open cluster lying about 2,000 lightyears from the back of your eyeball. It has about 25 bright stars spattered across a field about the size of a full moon; in reality, they're spread over an area 20 lightyears in width. Bright enough to be sometimes ...
... M41 (also known as the Little Beehive) is a fine open cluster lying about 2,000 lightyears from the back of your eyeball. It has about 25 bright stars spattered across a field about the size of a full moon; in reality, they're spread over an area 20 lightyears in width. Bright enough to be sometimes ...
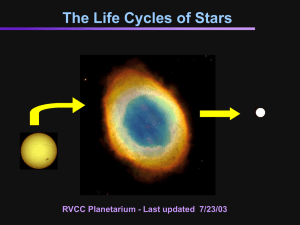
the life cycle of stars
... • When shrinks – atmosphere grows large and cools to a red giant or red supergiant • In 5 billion years the sun will become a red giant ...
... • When shrinks – atmosphere grows large and cools to a red giant or red supergiant • In 5 billion years the sun will become a red giant ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.