
solution
... apparent magnitude of 13.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Explain your answer. Zubenelgenubi appears to be brighter, since it has a lower apparent magnitude (remember that a negative apparent magnitude is very ...
... apparent magnitude of 13.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Explain your answer. Zubenelgenubi appears to be brighter, since it has a lower apparent magnitude (remember that a negative apparent magnitude is very ...
PHY299B Poster-Justin Hudson-v2
... • Using the UMD Observatory 6 and 7inch telescopes, with CCD cameras to gather images we must first cool the CCD cameras for at least 2 hours. • Following cooling, taking flat images of the sky slowly getting darker as day turns to night to help clean up our images that could be altered by dust or o ...
... • Using the UMD Observatory 6 and 7inch telescopes, with CCD cameras to gather images we must first cool the CCD cameras for at least 2 hours. • Following cooling, taking flat images of the sky slowly getting darker as day turns to night to help clean up our images that could be altered by dust or o ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... 4) What does the brightness of a star depend on? A) Define brightness as the watts/m2 received from a star. B) Brightness follows an inverse square relation B=L/(4πR2). Draw the picture (see figure 54.2 C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightn ...
... 4) What does the brightness of a star depend on? A) Define brightness as the watts/m2 received from a star. B) Brightness follows an inverse square relation B=L/(4πR2). Draw the picture (see figure 54.2 C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightn ...
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... What are the four important things to note about the HR Diagram? Most of the stars in the solar neighborhood fall on a well defined “Main Sequence”; there are very few “red giants”; there are very few “blue supergiants”; and there are a few faints stars near the bottom left of the diagram, which are ...
... What are the four important things to note about the HR Diagram? Most of the stars in the solar neighborhood fall on a well defined “Main Sequence”; there are very few “red giants”; there are very few “blue supergiants”; and there are a few faints stars near the bottom left of the diagram, which are ...
Test#3
... 1. A measurement of the parallax of a star allows us directly to determine the star's a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 2. How much brighter would a star be if an observer moved from 3 to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 3. The difference b ...
... 1. A measurement of the parallax of a star allows us directly to determine the star's a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 2. How much brighter would a star be if an observer moved from 3 to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 3. The difference b ...
Pretest
... the entire galaxy. The most recent evidence suggests that the Milky Way is a barred-spiral galaxy, that is, a spiral galaxy with a large bar-shaped region of stars and gas passing through its center. S 8.4.a ...
... the entire galaxy. The most recent evidence suggests that the Milky Way is a barred-spiral galaxy, that is, a spiral galaxy with a large bar-shaped region of stars and gas passing through its center. S 8.4.a ...
ASTR101 Unit 10 Assessment Answer Key 1. Mass, luminosity, size
... from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3,000 K, and in age, from about 13 billion years to stars that are just now being born. ...
... from about 60 solar masses to about 1/12 solar mass, in luminosity from about 1,000,000 to 1/10,000 solar luminosities, in radius from about 1,000 to 1/10 solar radii, in surface temperature from about 35,000 to 3,000 K, and in age, from about 13 billion years to stars that are just now being born. ...
Spectra of stars
... (c) the chemical composition of the star can be determined by looking at the absorption lines in the spectrum. These lines correspond to the emission lines of particular elements in the star. Spectral classification The spectra of stars are classified into a number of types first proposed by a group ...
... (c) the chemical composition of the star can be determined by looking at the absorption lines in the spectrum. These lines correspond to the emission lines of particular elements in the star. Spectral classification The spectra of stars are classified into a number of types first proposed by a group ...
Measuring stars Part I
... Deneb has an Absolute visual magnitude of -8.73 (this is about the same brightness as the quarter moon---but at 32.6 light years away!) Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolu ...
... Deneb has an Absolute visual magnitude of -8.73 (this is about the same brightness as the quarter moon---but at 32.6 light years away!) Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolu ...
Lecture 5: Light as a tool
... 1) Why does our sky appear to be mostly blue, and not violet, at mid-day? 2) What color would our sky be if atmospheric particles were slightly larger? 3) Why is the sky black on the moon? ...
... 1) Why does our sky appear to be mostly blue, and not violet, at mid-day? 2) What color would our sky be if atmospheric particles were slightly larger? 3) Why is the sky black on the moon? ...
Lives of stars
... 6. Which letter is most similar to the current sun’s location n the diagram? 7. When the sun starts to die, the sun will start to expand. The sun will be larger, hence brighter, but it till be lower temperature. Which letter represents this state of the sun? What do call this type of star? 8. After ...
... 6. Which letter is most similar to the current sun’s location n the diagram? 7. When the sun starts to die, the sun will start to expand. The sun will be larger, hence brighter, but it till be lower temperature. Which letter represents this state of the sun? What do call this type of star? 8. After ...
Stars-Chapter 18
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Their main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Distance and Luminosity (new 2012)
... A cool (red) giant star is more luminous than the Sun because, even though it is cooler, it is much larger than the Sun. ...
... A cool (red) giant star is more luminous than the Sun because, even though it is cooler, it is much larger than the Sun. ...
Stars
... Greek and Middle Eastern astronomers named the constellations after characters from mythology. The formations appear at different times of the year. Each season earth can view a different sets of constellations. Also the earth views a different set of constellations on the northern and southern hemi ...
... Greek and Middle Eastern astronomers named the constellations after characters from mythology. The formations appear at different times of the year. Each season earth can view a different sets of constellations. Also the earth views a different set of constellations on the northern and southern hemi ...
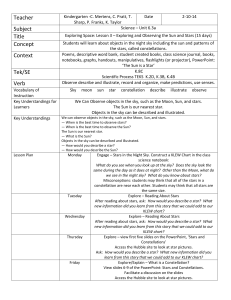
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... Poems, descriptive word bank, student created books, class science journal, books, notebooks, graphs, handouts, manipulatives, flashlights (or projector), PowerPoint: ‘The Sun is a Star’ K.8C Scientific Process TEKS K.2D, K.3B, K.4B Observe describe and illustrate, record and organize, make predicti ...
... Poems, descriptive word bank, student created books, class science journal, books, notebooks, graphs, handouts, manipulatives, flashlights (or projector), PowerPoint: ‘The Sun is a Star’ K.8C Scientific Process TEKS K.2D, K.3B, K.4B Observe describe and illustrate, record and organize, make predicti ...
Lesson #5: Constellations - Center for Learning in Action
... 12) Recognize that the universe contains many billions of galaxies, and that each galaxy contains many billions of stars. 13) Recognize that the earth is part of a system called the “solar system” that includes the sun (a star), planets, and many moons. The earth is the third planet from the sun in ...
... 12) Recognize that the universe contains many billions of galaxies, and that each galaxy contains many billions of stars. 13) Recognize that the earth is part of a system called the “solar system” that includes the sun (a star), planets, and many moons. The earth is the third planet from the sun in ...
of a Star
... • Mission – Map 100000 nearest stars to 2 milliseconds of arc • Map another 1000000 stars to 10 milliseconds of arc along with color information. • Exceeded goals. 120000 stars to 1milliseconds ...
... • Mission – Map 100000 nearest stars to 2 milliseconds of arc • Map another 1000000 stars to 10 milliseconds of arc along with color information. • Exceeded goals. 120000 stars to 1milliseconds ...
1. Star A has a distance of 3 parsecs. What is its parallax angle? 1a
... Which has a greater luminosity, a star with absolute magnitude -4 or a star with absolute magnitude +6? By how much? The -4 magntude star has a greater luminosity by a factor 2.51210 . Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the follow ...
... Which has a greater luminosity, a star with absolute magnitude -4 or a star with absolute magnitude +6? By how much? The -4 magntude star has a greater luminosity by a factor 2.51210 . Star I is of spectral type O2 and star II is of spectral type O3. Which star is hotter? Star I. Which of the follow ...
Spring Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... • If you really want to challenge yourself, use binoculars and go straight out from the nose of the lion. You should run into the “Beehive Cluster”. ...
... • If you really want to challenge yourself, use binoculars and go straight out from the nose of the lion. You should run into the “Beehive Cluster”. ...
Lesson 10 Red Shift
... "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, violet and red each have a characteristic range of wavelengths. In the visible spectrum, violet has the shortest wavelengths and red as the longest. Normally when we look at white light, such as from the Sun ...
... "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, violet and red each have a characteristic range of wavelengths. In the visible spectrum, violet has the shortest wavelengths and red as the longest. Normally when we look at white light, such as from the Sun ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
constellations[1]
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...





















![constellations[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081352_2-f872c73597ccdde4cfed49c9b322d3b2-300x300.png)
