May 2009 Tz 2
... (d) Alnitak is a main sequence star with a luminosity similar to that of Antares. Use the value quoted in (c)(ii) to deduce that the mass of Alnitak is in the range 16 MS to 40 MS, where MS is the mass of the Sun. ...
... (d) Alnitak is a main sequence star with a luminosity similar to that of Antares. Use the value quoted in (c)(ii) to deduce that the mass of Alnitak is in the range 16 MS to 40 MS, where MS is the mass of the Sun. ...
Russell Diagram
... • Supergiants -- cool, bright, red, large stars • Giants -- cool, bright red, less large stars • Main Sequence -- spans range from hot, bright stars to cool, dim stars. • White dwarfs -- hot, small, dim stars. ...
... • Supergiants -- cool, bright, red, large stars • Giants -- cool, bright red, less large stars • Main Sequence -- spans range from hot, bright stars to cool, dim stars. • White dwarfs -- hot, small, dim stars. ...
Why does Sirius twinkle?
... white dwarf star. As seen with the naked eye, Sirius can be seen to twinkle many different colors other stars for some very simple reasons. It is very bright, which can amplify atmospheric effects and it low in the winter evening sky. is also very low down in the atmosphere for those in the northern ...
... white dwarf star. As seen with the naked eye, Sirius can be seen to twinkle many different colors other stars for some very simple reasons. It is very bright, which can amplify atmospheric effects and it low in the winter evening sky. is also very low down in the atmosphere for those in the northern ...
lecture12
... temperatures of stars on a scale defined by spectral types, called O B A F G K M, ranging from the hottest (type O) to the coolest (type M) stars. ...
... temperatures of stars on a scale defined by spectral types, called O B A F G K M, ranging from the hottest (type O) to the coolest (type M) stars. ...
File
... Answer the following questions in your notebook. Write the complete question and write your answer in complete sentences. 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of t ...
... Answer the following questions in your notebook. Write the complete question and write your answer in complete sentences. 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of t ...
The Brightness of Stars
... – Don’t worry, you won’t have to calculate the summed brightness of multiple stars, but you do have to know that you can’t just add magnitudes – And you must realize that smaller numbers, even negative numbers, mean brighter objects ...
... – Don’t worry, you won’t have to calculate the summed brightness of multiple stars, but you do have to know that you can’t just add magnitudes – And you must realize that smaller numbers, even negative numbers, mean brighter objects ...
A star by any other name - Baruch Sterman
... doesn’t look particularly impressive. Why would this relatively insignificant star be given the distinction of having such an auspicious name - The Star? The answer has to do with a phenomenon called the Precession of the Equinoxes. Our earth spins around its axis completing one revolution every day ...
... doesn’t look particularly impressive. Why would this relatively insignificant star be given the distinction of having such an auspicious name - The Star? The answer has to do with a phenomenon called the Precession of the Equinoxes. Our earth spins around its axis completing one revolution every day ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... lord Rosse and others using the 72" at Birr Castle in the 19th century observed three dark rifts radiating from the centre. later visual observers confirmed these. However with the advent of photography the rifts disappeared. In the 1950's the late Walter Scott Houston in his "Sky and Telescope" col ...
... lord Rosse and others using the 72" at Birr Castle in the 19th century observed three dark rifts radiating from the centre. later visual observers confirmed these. However with the advent of photography the rifts disappeared. In the 1950's the late Walter Scott Houston in his "Sky and Telescope" col ...
Stars and constellations
... Sometimes the nuclear furnace that powers a star gets out of control. When this happens the star blows up. Now a star is a huge thing and so when it blows up you get a huge explosion. In fact it makes the star so bright that you can sometimes see it in daylight. This is what happened in 1054 when th ...
... Sometimes the nuclear furnace that powers a star gets out of control. When this happens the star blows up. Now a star is a huge thing and so when it blows up you get a huge explosion. In fact it makes the star so bright that you can sometimes see it in daylight. This is what happened in 1054 when th ...
STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... - Last star in the Little Dipper handle - Pole star- called Polaris - Known to the Vikings as the Jewel Nailhead, to the Mongols as the Golden Peg, to the Chinese as the Emperor of Heavens, and to the American Indians as the Chief Star. The American Indians made and used star charts. - Polaris is a ...
... - Last star in the Little Dipper handle - Pole star- called Polaris - Known to the Vikings as the Jewel Nailhead, to the Mongols as the Golden Peg, to the Chinese as the Emperor of Heavens, and to the American Indians as the Chief Star. The American Indians made and used star charts. - Polaris is a ...
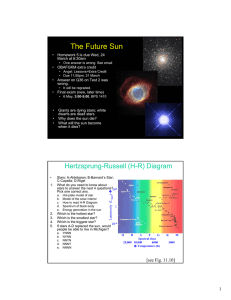
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... In what ways are HR diagrams of H+χ Perseus, Pleiades, Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Hottest stars in Perseus are hotter than hottest stars in Pleiades. b. Most stars are on the main sequence. c. NGC188 has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
... In what ways are HR diagrams of H+χ Perseus, Pleiades, Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Hottest stars in Perseus are hotter than hottest stars in Pleiades. b. Most stars are on the main sequence. c. NGC188 has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
Star Classification Lab
... In bold letters, label the following regions of your Hertzsprung-Russell diagram: White Dwarfs, Red Dwarfs, Red Giants, Main Sequence Stars, and Blue Supergiants. ...
... In bold letters, label the following regions of your Hertzsprung-Russell diagram: White Dwarfs, Red Dwarfs, Red Giants, Main Sequence Stars, and Blue Supergiants. ...
For stars
... Noon, over a period of 15 minutes what direction would it appear to move? A. west (to the left) B. east (to the right) C. South (out of the page) D. away from the horizon (up) E. toward the horizon (down) & east ...
... Noon, over a period of 15 minutes what direction would it appear to move? A. west (to the left) B. east (to the right) C. South (out of the page) D. away from the horizon (up) E. toward the horizon (down) & east ...
FRAC TRIVIA I QUIZ - Flint River Astronomy Club
... 14. ( 1 pt.) True or False: If you were standing on the floor at the center of the lunar crater Clavius, you could not see its 16,100-ft. walls in any direction. 15. (1 pt.) What is the largest of the 20 brightest stars in actual size? 16. (1 pt.) Which constellation contains the most naked-eye star ...
... 14. ( 1 pt.) True or False: If you were standing on the floor at the center of the lunar crater Clavius, you could not see its 16,100-ft. walls in any direction. 15. (1 pt.) What is the largest of the 20 brightest stars in actual size? 16. (1 pt.) Which constellation contains the most naked-eye star ...
First Ever STEREO Images of the Entire Sun NASA Deputy
... Follow a line from Sirius to the tip of Canis Major's nose (Theta Canis Majoris), continue nearly as far exactly straight onward, and there you are. M50 is magnitude 5.9, quite a bit fainter than M41's magnitude 4.5. In the same field with M50 is another, the fainter cluster: NGC 2343, a tougher cat ...
... Follow a line from Sirius to the tip of Canis Major's nose (Theta Canis Majoris), continue nearly as far exactly straight onward, and there you are. M50 is magnitude 5.9, quite a bit fainter than M41's magnitude 4.5. In the same field with M50 is another, the fainter cluster: NGC 2343, a tougher cat ...
Sun, Stars, HR Diagram
... Base your answers to questions 18through 20 on the diagram below, which shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space. ...
... Base your answers to questions 18through 20 on the diagram below, which shows two possible sequences in the life cycle of stars, beginning with their formation from nebular gas clouds in space. ...
The H-R Diagram
... The Herzsprung Russel Diagram (HRD) is a systematic way of arranging stellar data. It plots the Absolute Magnitude (MV) or Luminosity (L/L¤) versus the Spectral Type, Surface Temperature or Color. The brightest stars are at the top and the hottest stars at the left. The radius increases diagonally t ...
... The Herzsprung Russel Diagram (HRD) is a systematic way of arranging stellar data. It plots the Absolute Magnitude (MV) or Luminosity (L/L¤) versus the Spectral Type, Surface Temperature or Color. The brightest stars are at the top and the hottest stars at the left. The radius increases diagonally t ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... Just rising over the northeastern horizon is the constellation Perseus. Between Perseus and Cassiopeia is found one the most interesting objects to be seen through a small to medium aperture scope. The best thing is that it so easy to locate. NGC 869 & 884, popularly known as the Double Cluster, are ...
... Just rising over the northeastern horizon is the constellation Perseus. Between Perseus and Cassiopeia is found one the most interesting objects to be seen through a small to medium aperture scope. The best thing is that it so easy to locate. NGC 869 & 884, popularly known as the Double Cluster, are ...
Astronomy 20 Homework # 2
... Å wide. How many counts per resolution element are detected from the galaxy alone in a 1-hour exposure? From the foreground sky? If a blank piece of sky is measured at the same time in order to subtract the sky spectrum from the total, what is the signal-to-noise ratio per resolution element in the ...
... Å wide. How many counts per resolution element are detected from the galaxy alone in a 1-hour exposure? From the foreground sky? If a blank piece of sky is measured at the same time in order to subtract the sky spectrum from the total, what is the signal-to-noise ratio per resolution element in the ...
Star Classification
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
... Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to ...
Stars
... • Can order the stars we see by the property of temperature and luminosity (or absolute magnitude). Prominent stars Nearby Stars Brightest Stars 1000 pc Stars ...
... • Can order the stars we see by the property of temperature and luminosity (or absolute magnitude). Prominent stars Nearby Stars Brightest Stars 1000 pc Stars ...
Lucas - WordPress.com
... Auriga is located north of the celestial equator. Its name is the Latin word for "charioteer", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent in the northern Hemisphere winter sky, along with the five other constellations that have ...
... Auriga is located north of the celestial equator. Its name is the Latin word for "charioteer", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent in the northern Hemisphere winter sky, along with the five other constellations that have ...
Stars
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
Stars
... The Blue Supergiants will begin to burn up all of the hydrogen that they have after a few million years. When this happens, the outer shell of the star begins to expand. It grows to about triple the size that it currently is. The Blue Supergiant now becomes a Supergiant. Supergiants are orange/yello ...
... The Blue Supergiants will begin to burn up all of the hydrogen that they have after a few million years. When this happens, the outer shell of the star begins to expand. It grows to about triple the size that it currently is. The Blue Supergiant now becomes a Supergiant. Supergiants are orange/yello ...