Stellar Evolution Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Hertzsprung
... some go through nova/supernova stage most become black dwarfs and disappear ...
... some go through nova/supernova stage most become black dwarfs and disappear ...
Constellations, Star Names, and Magnitudes
... Astronomers consider the names designated by the International Astronomical Union official, but the IAU has no true legal authority to name stars (or demote planets, for that matter). Companies that sell star names as gifts are a SCAM! ...
... Astronomers consider the names designated by the International Astronomical Union official, but the IAU has no true legal authority to name stars (or demote planets, for that matter). Companies that sell star names as gifts are a SCAM! ...
NAME:______ANSWER KEY_______________________Period
... 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in sta ...
... 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in sta ...
GIZMO H-RDiagramSE
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
Astronomical Ideas Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1. Two stars
... massive stars that still burn H on the main sequence is a clock, because we know that the cluster needs to be old enough so that all of the more massive stars have already burned up all of their Hydrogen and left the main sequence. ...
... massive stars that still burn H on the main sequence is a clock, because we know that the cluster needs to be old enough so that all of the more massive stars have already burned up all of their Hydrogen and left the main sequence. ...
Here - Thanet Astronomy Group
... Constellation (Orion), Nebula (M42) This guide is for 7pm 24th February 2014. Last month I featured the star Sirius, the constellation Orion and 5 of its main stars. This month three more stars and a nebula. I'm hoping you all found Jupiter and Orion last month and have been looking at them since. A ...
... Constellation (Orion), Nebula (M42) This guide is for 7pm 24th February 2014. Last month I featured the star Sirius, the constellation Orion and 5 of its main stars. This month three more stars and a nebula. I'm hoping you all found Jupiter and Orion last month and have been looking at them since. A ...
Star names and magnitudes
... developed the first system for unambiguously identifying celestial sources. Now, we use co-ordinate systems based on angular distance scales. Astronomical co-ordinates ...
... developed the first system for unambiguously identifying celestial sources. Now, we use co-ordinate systems based on angular distance scales. Astronomical co-ordinates ...
16. Properties of Stars
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
constellations are not real!
... per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial sphere - the extensions of the north pole (NP) and south pole (SP) of the Earth intersect with the north celestial pole (NCP) and the south celes ...
... per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial sphere - the extensions of the north pole (NP) and south pole (SP) of the Earth intersect with the north celestial pole (NCP) and the south celes ...
Thought Question
... The only direct way to measure the distance to a star is from the parallax By definition, a star with a parallax of 1 arcsecond (arcsec) is at a distance of 1 parsec (pc). 1 arcsec = 1/3,600 degree. ...
... The only direct way to measure the distance to a star is from the parallax By definition, a star with a parallax of 1 arcsecond (arcsec) is at a distance of 1 parsec (pc). 1 arcsec = 1/3,600 degree. ...
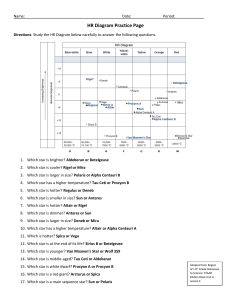
HR Diagram Practice Page
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
... 1. Which star is brighter? Aldeberan or Betelgeuse 2. Which star is cooler? Rigel or Mira 3. Which star is larger in size? Polaris or Alpha Centauri B 4. Which star has a higher temperature? Tau Ceti or Procyon B 5. Which star is hotter? Regulus or Deneb 6. Which star is smaller in size? Sun or Anta ...
Spectral Variations of Several RV Tauri Type Stars Patrick Durant
... Light curve fits by Nesmith and Cash (adjacent poster, this conference) were used to convert the Julian Dates of our spectral observations to the appropriate phase of the ...
... Light curve fits by Nesmith and Cash (adjacent poster, this conference) were used to convert the Julian Dates of our spectral observations to the appropriate phase of the ...
Stellar evolution, II
... The faster the nuclear reactions run, the more luminosity the star has. This explains why more massive stars have greater luminosity, and why more massive stars use up their core hydrogen at a much faster rate. ...
... The faster the nuclear reactions run, the more luminosity the star has. This explains why more massive stars have greater luminosity, and why more massive stars use up their core hydrogen at a much faster rate. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... but the letters were rearranged. In order of decreasing temperatures, the stellar classification is now: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. Or an easy way to ...
... but the letters were rearranged. In order of decreasing temperatures, the stellar classification is now: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. Or an easy way to ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... • Astronomers use spectrographs to find out what elements are in a star. A spectrograph is a device that breaks light into colors (like a prism). Scientists compare a star’s light with the light produced by different elements to find out what elements are in a star. ...
... • Astronomers use spectrographs to find out what elements are in a star. A spectrograph is a device that breaks light into colors (like a prism). Scientists compare a star’s light with the light produced by different elements to find out what elements are in a star. ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... reduction. He paid them 50 cents to the dollar, but he paid them. ...
... reduction. He paid them 50 cents to the dollar, but he paid them. ...
Starry Lives, Starry Skies
... 4. Crisis when a star swells up into a red giant and loses some of its mass Betelgeuse Antares Aldebaran 5. Old Age lowmass stars produce a planetary nebula, and highmass stars make heavier elements using nuclear fusion The Ring Nebula (planetary nebula M57) The Helix Nebula (planetar ...
... 4. Crisis when a star swells up into a red giant and loses some of its mass Betelgeuse Antares Aldebaran 5. Old Age lowmass stars produce a planetary nebula, and highmass stars make heavier elements using nuclear fusion The Ring Nebula (planetary nebula M57) The Helix Nebula (planetar ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
... moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster A stellar association is a group of newborn stars that are moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
Stellar Spectra
... spectrum with “absorption” lines. • Some stars show “emission” lines. – All stars do not have the same spectrum! • Interstellar clouds show a continuum with emission lines ...
... spectrum with “absorption” lines. • Some stars show “emission” lines. – All stars do not have the same spectrum! • Interstellar clouds show a continuum with emission lines ...
StarType
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
... When you look at the stars you’ll notice that some are white, some are yellow, and some are red. Stars are classified according to their colors, ranging from electric blue for the hottest stars to dull red for the coolest stars. Early spectrometers identified emission lines in the stars’ spectrum fo ...
The Inverse Square Law and Surface Area
... • There are several classes of stars with known power output. • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with mo ...
... • There are several classes of stars with known power output. • Stars which have the same surface temperature ( and spectral characteristics) as the sun all have the same power output • We can readily calculate the power output of nearby stars and classify their power output and compare them with mo ...
Characteristics of Stars ppt.
... Some stars that appear as a single star from Earth are actually binary stars, which are two stars that rotate around a common center of mass. ...
... Some stars that appear as a single star from Earth are actually binary stars, which are two stars that rotate around a common center of mass. ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
... 4) Which of the following statements about the sunspot cycle is not true? A) The number of solar flares peaks about every 11 years. B) The rate of nuclear fusion in the Sun peaks about every 11 years. C) With each subsequent peak in the number of sunspots, the magnetic polarity of the Sun is the rev ...
The Stars - University of Redlands
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...