File
... What is the Zodiac? Earth orbits our Sun once each year. Viewed from Earth, our Sun appears to trace a circular path. This path defines a plane called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. ...
... What is the Zodiac? Earth orbits our Sun once each year. Viewed from Earth, our Sun appears to trace a circular path. This path defines a plane called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. ...
Main Sequence stars
... The star Rigel is about 100,000 times brighter than the Sun and belongs to spectral type B8. The star Sirius B is about 3000 times dimmer than the Sun and also belongs to spectral type B8. Which star has the greatest surface temperature? 1. Rigel 2. Sirius B 3. They have the same temperature. 4. Th ...
... The star Rigel is about 100,000 times brighter than the Sun and belongs to spectral type B8. The star Sirius B is about 3000 times dimmer than the Sun and also belongs to spectral type B8. Which star has the greatest surface temperature? 1. Rigel 2. Sirius B 3. They have the same temperature. 4. Th ...
Astronomy Day 2006: A short presentation on eclipsing binary stars
... Just what are they? Why do we care? It is recognized as fact by astronomers that well over half of the stars in the universe belong to multiple systems. You might think of our Sun as being an exceptional system that involves only one star and you would be right. ...
... Just what are they? Why do we care? It is recognized as fact by astronomers that well over half of the stars in the universe belong to multiple systems. You might think of our Sun as being an exceptional system that involves only one star and you would be right. ...
Quantum Well Electron Gain Structures and Infrared
... star is dominant source of ionizing radiation • Thus, even if it is a binary, probable q>1 and mass limit >> 75 M0 • (And … something BIGGER made a neutron star ...
... star is dominant source of ionizing radiation • Thus, even if it is a binary, probable q>1 and mass limit >> 75 M0 • (And … something BIGGER made a neutron star ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... m = constant – 2.5 log10F , choosing constant to make scale consistent with Hipparchus. Absolute magnitude M is defined as the apparent magnitude a star ...
... m = constant – 2.5 log10F , choosing constant to make scale consistent with Hipparchus. Absolute magnitude M is defined as the apparent magnitude a star ...
luminosity1
... • To figure out the total luminosity being emitted by the box, we would need to multiply the luminosity of one side by 6. This is because there are six sides of the cube for the energy to escape from. ...
... • To figure out the total luminosity being emitted by the box, we would need to multiply the luminosity of one side by 6. This is because there are six sides of the cube for the energy to escape from. ...
A little bit more to do. Stefan
... • To figure out the total luminosity being emitted by the box, we would need to multiply the luminosity of one side by 6. This is because there are six sides of the cube for the energy to escape from. ...
... • To figure out the total luminosity being emitted by the box, we would need to multiply the luminosity of one side by 6. This is because there are six sides of the cube for the energy to escape from. ...
REACH FOR THE STARS MLK 2009
... Answer the following questions. If the Absolute magnitude and Apparent magnitude are equal, what do you know about the distance of the star? _____________________________________________ How many AU does light travel in one year? _____________ What are Hayashi tracks? _______________________________ ...
... Answer the following questions. If the Absolute magnitude and Apparent magnitude are equal, what do you know about the distance of the star? _____________________________________________ How many AU does light travel in one year? _____________ What are Hayashi tracks? _______________________________ ...
Name _________ Date _____________ Period ______ Skills
... _____ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. _____ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in the sky ______________________ stars. 21. What type o ...
... _____ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. _____ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in the sky ______________________ stars. 21. What type o ...
HW #4 (due March 27)
... their Hα lines. If you can't rank them all easily, try coloring in the area between the line connecting the triangle centers and the actual spectrum. The bigger the colored area, the greater the line strength. Originally, astronomers classified those stars with the strongest hydrogen lines as 'A' st ...
... their Hα lines. If you can't rank them all easily, try coloring in the area between the line connecting the triangle centers and the actual spectrum. The bigger the colored area, the greater the line strength. Originally, astronomers classified those stars with the strongest hydrogen lines as 'A' st ...
TYPES OF STARS
... their Hα lines. If you can't rank them all easily, try coloring in the area between the line connecting the triangle centers and the actual spectrum. The bigger the colored area, the greater the line strength. Originally, astronomers classified those stars with the strongest hydrogen lines as 'A' st ...
... their Hα lines. If you can't rank them all easily, try coloring in the area between the line connecting the triangle centers and the actual spectrum. The bigger the colored area, the greater the line strength. Originally, astronomers classified those stars with the strongest hydrogen lines as 'A' st ...
Slide 1 - Beverley High School
... sequence depends entirely on its mass. Low mass stars are found at the left and high mass stars at the right. • The mass of a star controls its radius, its temperature, its life expectancy and its eventual fate. ...
... sequence depends entirely on its mass. Low mass stars are found at the left and high mass stars at the right. • The mass of a star controls its radius, its temperature, its life expectancy and its eventual fate. ...
Lecture 6
... Brightness is a function of the inverse square of distance, so if distance was cut by half it would get brighter by 4x=1/(.5)2 ...
... Brightness is a function of the inverse square of distance, so if distance was cut by half it would get brighter by 4x=1/(.5)2 ...
Measuring Distance with Spectroscopic Parallax
... 1. Print out the HR diagram. 2. Using a pen or pencil, draw a smooth best-fit curve that runs through the middle of all of your main sequence stars. Just ignore the red giants and white dwarfs for this activity. Note that this will not be a straight line; it will curve slightly. And, it will not go ...
... 1. Print out the HR diagram. 2. Using a pen or pencil, draw a smooth best-fit curve that runs through the middle of all of your main sequence stars. Just ignore the red giants and white dwarfs for this activity. Note that this will not be a straight line; it will curve slightly. And, it will not go ...
Galaxy Powerpoint
... • A. Different constellations can be seen at different times of the year.. • i. Due to the Earth’s revolution around the Sun. • Ii. Ex. Orion can be seen in the winter and spring . Pegasus can only be seen in summer and fall. ...
... • A. Different constellations can be seen at different times of the year.. • i. Due to the Earth’s revolution around the Sun. • Ii. Ex. Orion can be seen in the winter and spring . Pegasus can only be seen in summer and fall. ...
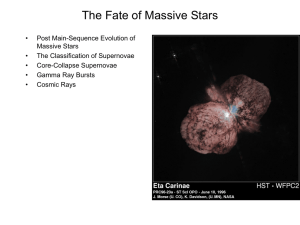
The Fate of Massive Stars
... increased opacity due to presence of various Ions (including Fe) in stellar atmosphere Diagonal upper-luminosity cutoff that is temperature dependent Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM ...
... increased opacity due to presence of various Ions (including Fe) in stellar atmosphere Diagonal upper-luminosity cutoff that is temperature dependent Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM ...
Astronomy Teaching that Focuses on Learning Subtitled
... constructed? (aka, When can I lecture?) • Seasons are caused by changing distance from the Sun • The North Star is the brightest star in the sky • Astronauts on the Space Shuttle float because there is no gravity in space • The Space Shuttle goes to the Moon every week • Black holes fly around and v ...
... constructed? (aka, When can I lecture?) • Seasons are caused by changing distance from the Sun • The North Star is the brightest star in the sky • Astronauts on the Space Shuttle float because there is no gravity in space • The Space Shuttle goes to the Moon every week • Black holes fly around and v ...
proposed october viewing list
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
Star Jeopardy "Review #1
... 1.4 to 3 solar masses becomes a neutron star from a Type II supernova explosion. Above 3 solar masses becomes a black hole ...
... 1.4 to 3 solar masses becomes a neutron star from a Type II supernova explosion. Above 3 solar masses becomes a black hole ...
HR Diagram
... luminous it is. If you observe the H-R diagram on the cover of the lab, it is clear that there are fewer luminous stars as compared to the less luminous ones. In terms of the diagram, there are more stars on the lower end than the higher end of the main sequence on the absolute magnitude axis (which ...
... luminous it is. If you observe the H-R diagram on the cover of the lab, it is clear that there are fewer luminous stars as compared to the less luminous ones. In terms of the diagram, there are more stars on the lower end than the higher end of the main sequence on the absolute magnitude axis (which ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Luminosity • Luminosity – how bright a star is • Apparent magnitude – how bright a star appears to an observer on Earth – Stars can appear to be the same brightness to us on Earth even though they may not be (one may be farther away from us than the other) ...
... Luminosity • Luminosity – how bright a star is • Apparent magnitude – how bright a star appears to an observer on Earth – Stars can appear to be the same brightness to us on Earth even though they may not be (one may be farther away from us than the other) ...
Aspire: Star Life Cycle - Easy Peasy All-in
... 20. Choose a hypothesis and then continue. 21. Where would you expect to find other main sequence stars of the same size on this diagram? (2 Points) 22. Which description of the relationship is correct? (2 Points) 23. Write down the hypothesis that is correct. (2 Points) 24. Determine if the followi ...
... 20. Choose a hypothesis and then continue. 21. Where would you expect to find other main sequence stars of the same size on this diagram? (2 Points) 22. Which description of the relationship is correct? (2 Points) 23. Write down the hypothesis that is correct. (2 Points) 24. Determine if the followi ...