Aspire: Star Life Cycle - Easy Peasy All-in
... 20. Choose a hypothesis and then continue. 21. Where would you expect to find other main sequence stars of the same size on this diagram? (2 Points) 22. Which description of the relationship is correct? (2 Points) 23. Write down the hypothesis that is correct. (2 Points) 24. Determine if the followi ...
... 20. Choose a hypothesis and then continue. 21. Where would you expect to find other main sequence stars of the same size on this diagram? (2 Points) 22. Which description of the relationship is correct? (2 Points) 23. Write down the hypothesis that is correct. (2 Points) 24. Determine if the followi ...
File
... Once born, stars are self-illuminating…they ____________________________________________! Main sequence = ______________ yellow stars (like our sun!) + ______________ blue stars As a star runs out of energy, it ______________ into a red ______________ or a red ______________________ After stars die, ...
... Once born, stars are self-illuminating…they ____________________________________________! Main sequence = ______________ yellow stars (like our sun!) + ______________ blue stars As a star runs out of energy, it ______________ into a red ______________ or a red ______________________ After stars die, ...
Project Packet - Montville.net
... Constellations, especially signs of the Zodiac, have influenced human culture and folklore since the time of the Babylonians, although most of the constellations we know today are of Greek and Roman names. Most people have looked up their horoscope once or twice to see what the stars say their day i ...
... Constellations, especially signs of the Zodiac, have influenced human culture and folklore since the time of the Babylonians, although most of the constellations we know today are of Greek and Roman names. Most people have looked up their horoscope once or twice to see what the stars say their day i ...
Exercise 7
... declination (think of this as a space latitude). The declination runs from -90° (celestial south pole) to +90° (celestial north pole). Both of these coordinates are laminated to the metal pole bases. In addition, the stars have been colored according to their spectral classes; blue balls represent O ...
... declination (think of this as a space latitude). The declination runs from -90° (celestial south pole) to +90° (celestial north pole). Both of these coordinates are laminated to the metal pole bases. In addition, the stars have been colored according to their spectral classes; blue balls represent O ...
Stars Notes
... 4.b – Students know that the Sun is one of many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and that stars may differ in size, temperature and color 4.d – Students know that stars are the source of light for all bright objects in outer space and that the Moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight, not by thei ...
... 4.b – Students know that the Sun is one of many stars in the Milky Way galaxy and that stars may differ in size, temperature and color 4.d – Students know that stars are the source of light for all bright objects in outer space and that the Moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight, not by thei ...
10.5 The Hertzsprung
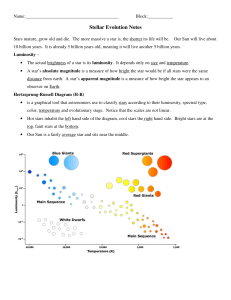
... The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
... The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
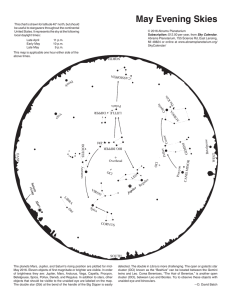
The Night Sky
... The biggest problem in navigating using the stars was in determining one’s longitude. Explain why this is so difficult? ...
... The biggest problem in navigating using the stars was in determining one’s longitude. Explain why this is so difficult? ...
The Stars
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
Stellar Spectral Classes
... For which two spectral classes are these lines the prominent feature? ...
... For which two spectral classes are these lines the prominent feature? ...
common constellations
... Hunter Orion is no exception. Orion has two dogs as companions, Canis Major (the Great Dog) and Canis Minor (the lesser dog). Both of these faithful companions sit at the feet of Orion waiting for their next expedition. In addition to being one of the companions of Orion, Canis Major is also the ste ...
... Hunter Orion is no exception. Orion has two dogs as companions, Canis Major (the Great Dog) and Canis Minor (the lesser dog). Both of these faithful companions sit at the feet of Orion waiting for their next expedition. In addition to being one of the companions of Orion, Canis Major is also the ste ...
10 September: Faint Stars and Bright Stars
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of an object as it appears to you • System due to Hipparchos (2nd century BC) • Nowadays system made more precise • Magnitude changes are “logarithmic”, each magnitude means factor of 2.512 in brightness • See Table 16.2 (p382) ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of an object as it appears to you • System due to Hipparchos (2nd century BC) • Nowadays system made more precise • Magnitude changes are “logarithmic”, each magnitude means factor of 2.512 in brightness • See Table 16.2 (p382) ...
Bright stars and faint stars: the stellar magnitude system Magnitudes
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of an object as it appears to you • System due to Hipparchos (2nd century BC) • Nowadays system made more precise • Magnitude changes are “logarithmic”, each magnitude means factor of 2.512 in brightness • See Table 16.2 (p382) ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of an object as it appears to you • System due to Hipparchos (2nd century BC) • Nowadays system made more precise • Magnitude changes are “logarithmic”, each magnitude means factor of 2.512 in brightness • See Table 16.2 (p382) ...
Lecture 13: The Stars –
... squarely in its star’s habitable zone, where the conditions are right for liquid water. The new planet is about three times the mass of Earth, which indicates it is probably rocky and has enough surface gravity to sustain a stable atmosphere. ...
... squarely in its star’s habitable zone, where the conditions are right for liquid water. The new planet is about three times the mass of Earth, which indicates it is probably rocky and has enough surface gravity to sustain a stable atmosphere. ...
Foundations III The Stars
... squarely in its star’s habitable zone, where the conditions are right for liquid water. The new planet is about three times the mass of Earth, which indicates it is probably rocky and has enough surface gravity to sustain a stable atmosphere. ...
... squarely in its star’s habitable zone, where the conditions are right for liquid water. The new planet is about three times the mass of Earth, which indicates it is probably rocky and has enough surface gravity to sustain a stable atmosphere. ...
HERE
... lifespan,burn-rate, size: Spectral class O, B stars (rare, but very interesting): Giant, hot, bright, blue stars burn up quickly and die violently. Lifetime is only 1-10 million years. Spectral class A,F,G,K stars (like the Sun): Middle of the road habits. Orange, yellow or white in color. Typic ...
... lifespan,burn-rate, size: Spectral class O, B stars (rare, but very interesting): Giant, hot, bright, blue stars burn up quickly and die violently. Lifetime is only 1-10 million years. Spectral class A,F,G,K stars (like the Sun): Middle of the road habits. Orange, yellow or white in color. Typic ...
Astronomy of the Northern Sky—
... The Cat’s Eye Nebulae, NGC 6543, in Draco is among the brightest anywhere, magnitude 8.1 (17:59 +66º 38’). On the way from β to γ Ursa Majoris (and slightly outside this line which makes the bottom of the Big Dipper’s Bowl), near the point of a thin north-pointing triangle, is the Owl Nebula, M97, a ...
... The Cat’s Eye Nebulae, NGC 6543, in Draco is among the brightest anywhere, magnitude 8.1 (17:59 +66º 38’). On the way from β to γ Ursa Majoris (and slightly outside this line which makes the bottom of the Big Dipper’s Bowl), near the point of a thin north-pointing triangle, is the Owl Nebula, M97, a ...
LAB: Star Classification
... Table 3 - Spectral Class and Temperature Spectral Class O B A F G K M ...
... Table 3 - Spectral Class and Temperature Spectral Class O B A F G K M ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
Star Life Cycle
... When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming wh ...
... When a star has burned between 10% and 20% of its hydrogen, its core will to run out of fuel. At this stage, the star is entering the end of its life. The diameter of the star can increase by a factor of 200, while its cooling is translated into a reddening of its radiation : the star is becoming wh ...
Earth Science, 10th edition Chapter 23: Beyond Our Solar System I
... I. Properties of stars A. Distance 1. Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult 2. Stellar parallax a. Used for measuring distance to a star b. Apparent shift in a star's position due to the orbital motion of Earth c. Measured as an angle d. Near stars have the largest parallax e. Largest pa ...
... I. Properties of stars A. Distance 1. Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult 2. Stellar parallax a. Used for measuring distance to a star b. Apparent shift in a star's position due to the orbital motion of Earth c. Measured as an angle d. Near stars have the largest parallax e. Largest pa ...
Activity: Star Classification - d
... Part 1: Exploring with Classification Each group will receive 1 set of 27 stars. Every star has: a color, name, temperature, size, & luminosity value o The luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity. If a star has a luminosity value of 5, then it is 5 times brighter than our sun. If a star h ...
... Part 1: Exploring with Classification Each group will receive 1 set of 27 stars. Every star has: a color, name, temperature, size, & luminosity value o The luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity. If a star has a luminosity value of 5, then it is 5 times brighter than our sun. If a star h ...