Grade Nine Planetarium script
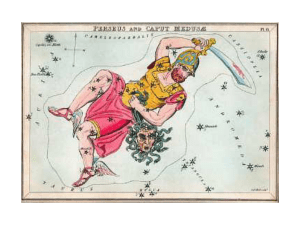
... the bright star near the foot of Perseus' forward leg (the one towards Andromeda) consists of a pair of stars - one much dimmer than the other every 2 days and 21 hours the dimmer star passes right between us and the brighter star over a four-hour period, you can see Algol dim to about a tenth its n ...
... the bright star near the foot of Perseus' forward leg (the one towards Andromeda) consists of a pair of stars - one much dimmer than the other every 2 days and 21 hours the dimmer star passes right between us and the brighter star over a four-hour period, you can see Algol dim to about a tenth its n ...
THE STARS G. Iafrate(a), M. Ramella(a) and V. Bologna(b) (a) INAF
... completely into helium. The star now burns helium in the nucleus and hydrogen in a shell surrounding it. The star starts to expand and becomes a red giant. Giant stars are very big and relatively cool, they radiate a large amount of energy and appear very luminous. When the star finishes all kinds o ...
... completely into helium. The star now burns helium in the nucleus and hydrogen in a shell surrounding it. The star starts to expand and becomes a red giant. Giant stars are very big and relatively cool, they radiate a large amount of energy and appear very luminous. When the star finishes all kinds o ...
the stars - Uni Heidelberg
... completely into helium. The star now burns helium in the nucleus and hydrogen in a shell surrounding it. The star starts to expand and becomes a red giant. Giant stars are very big and relatively cool, they radiate a large amount of energy and appear very luminous. When the star finishes all kinds o ...
... completely into helium. The star now burns helium in the nucleus and hydrogen in a shell surrounding it. The star starts to expand and becomes a red giant. Giant stars are very big and relatively cool, they radiate a large amount of energy and appear very luminous. When the star finishes all kinds o ...
Chapter 9 “The Family of Stars “
... compared to Earth. We would be able to determine the distance to nearby stars more accurately and determine the distance to stars that are currently too far to be measured using parallax from Earth. ...
... compared to Earth. We would be able to determine the distance to nearby stars more accurately and determine the distance to stars that are currently too far to be measured using parallax from Earth. ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... home to one of the loveliest open clusters in the sky, Praesepe, now more commonly known as the Beehive Cluster or M44. This lovely group of stars is just visible to the naked-eye even from Bristol, and a stunning sight in binoculars To the southeast of Leo lies the large faint constellation of Virg ...
... home to one of the loveliest open clusters in the sky, Praesepe, now more commonly known as the Beehive Cluster or M44. This lovely group of stars is just visible to the naked-eye even from Bristol, and a stunning sight in binoculars To the southeast of Leo lies the large faint constellation of Virg ...
Week 6
... The bright star in the top left corner of Orion, Betelgeuse, has a radius 936 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What is the luminosity of this star? If Betelgeuse is 640 ly from Earth, what is the brightness of the light from Betelgeuse that reaches Earth? ...
... The bright star in the top left corner of Orion, Betelgeuse, has a radius 936 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What is the luminosity of this star? If Betelgeuse is 640 ly from Earth, what is the brightness of the light from Betelgeuse that reaches Earth? ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... (Algieba), this is a great double for small telescopes. The primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow Gclass star. The pair are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. Just to the west of Leo lies the faint constellation of Cancer, which is home to one o ...
... (Algieba), this is a great double for small telescopes. The primary is a magnitude +2.2 K-class yellow-orange giant, it’s companion is a magnitude +2.5 yellow Gclass star. The pair are separated by 4.4 arcseconds. Just to the west of Leo lies the faint constellation of Cancer, which is home to one o ...
Lesson 6 - Magnitudes of Stars
... Magnitudes are a way of assigning a number to a star so we know how bright it is Similar to how the Richter scale assigns a number to the strength of an earthquake Betelgeuse and Rigel, stars in Orion with apparent magnitudes 0.3 and 0.9 ...
... Magnitudes are a way of assigning a number to a star so we know how bright it is Similar to how the Richter scale assigns a number to the strength of an earthquake Betelgeuse and Rigel, stars in Orion with apparent magnitudes 0.3 and 0.9 ...
Test 2, November 14, 2016 - Physics@Brock
... 12. Which of the following features determines the resolving power of a telescope? (a) the focal length of the objective. (b) the focal length of the eyepiece. (c) the diameter of the objective. (d) the diameter of the eyepiece. 13. If the focal length of the objective of a telescope is 120 cm and t ...
... 12. Which of the following features determines the resolving power of a telescope? (a) the focal length of the objective. (b) the focal length of the eyepiece. (c) the diameter of the objective. (d) the diameter of the eyepiece. 13. If the focal length of the objective of a telescope is 120 cm and t ...
stars_2nd_edit
... years for massive stars to billions for smaller stars. Our Sun, which is of average mass, is predicted to live for about 10 billion years. By knowing the distance, mass, magnitude, and chemical composition of a star, we can determine approximately how old it is, when it was born, and when it will di ...
... years for massive stars to billions for smaller stars. Our Sun, which is of average mass, is predicted to live for about 10 billion years. By knowing the distance, mass, magnitude, and chemical composition of a star, we can determine approximately how old it is, when it was born, and when it will di ...
COM 2014 January
... The Alpha Persei Cluster, also know as Melotte 20, is a bright stellar association in Perseus constellation. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue stars of spectral type B, along with the most massive member, the yellow supergiant Alpha Persei itself. Brightest members include Alpha ...
... The Alpha Persei Cluster, also know as Melotte 20, is a bright stellar association in Perseus constellation. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue stars of spectral type B, along with the most massive member, the yellow supergiant Alpha Persei itself. Brightest members include Alpha ...
here in Powerpoint format
... bA is the apparent brightness of star A bB is the apparent brightness of star B mA is the apparent magnitude of star A mB is the apparent magnitude of star B ...
... bA is the apparent brightness of star A bB is the apparent brightness of star B mA is the apparent magnitude of star A mB is the apparent magnitude of star B ...
10.1 The Solar Neighborhood Barnard`s Star
... Giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 times the Sun’s. Dwarf stars have radii equal to, or less than, the Sun’s. Supergiant stars have radii more than 100 times the Sun’s. ...
... Giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 times the Sun’s. Dwarf stars have radii equal to, or less than, the Sun’s. Supergiant stars have radii more than 100 times the Sun’s. ...
five minute episode script
... DISTINCTIVE BELT OF THREE STARS. IF YOU LOOK A LITTLE CLOSER YOU'LL SEE STARS OF DIFFERENT BRIGHTNESS AND COLOR. DEAN: STAR COLOR IS AN INDICATION OF ITS TEMPERATURE - BLUE STARS BEING THE HOTTEST AND RED STARS BEING THE COLDEST. YOU CAN REALLY SEE THE COLORS OF THE BRIGHTEST STARS LIKE THOSE IN ORI ...
... DISTINCTIVE BELT OF THREE STARS. IF YOU LOOK A LITTLE CLOSER YOU'LL SEE STARS OF DIFFERENT BRIGHTNESS AND COLOR. DEAN: STAR COLOR IS AN INDICATION OF ITS TEMPERATURE - BLUE STARS BEING THE HOTTEST AND RED STARS BEING THE COLDEST. YOU CAN REALLY SEE THE COLORS OF THE BRIGHTEST STARS LIKE THOSE IN ORI ...
Document
... the same time. • The cluster is as old as the most luminous (massive) star left on the MS. • All MS stars to the left have already used up their H fuel and are gone. • The position of the hottest, brightest star on a cluster’s main sequence is called the main sequence turnoff point. ...
... the same time. • The cluster is as old as the most luminous (massive) star left on the MS. • All MS stars to the left have already used up their H fuel and are gone. • The position of the hottest, brightest star on a cluster’s main sequence is called the main sequence turnoff point. ...
The Celestial Sphere - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Every star can be located by its RA and Dec. Ra in units of hours minutes and seconds, Dec in units of degree minutes and seconds ...
... Every star can be located by its RA and Dec. Ra in units of hours minutes and seconds, Dec in units of degree minutes and seconds ...
PHYSICS 113 Practice Questions #2
... a. a distant galaxy of stars and raw material b. a small disk of gas and dust surrounding a single star that was recently formed c. a cloud o f gas and du st illuminated by th e light of newly form ed stars within it d. the remnant of a star that exploded several thousand years ago e. an illusion ca ...
... a. a distant galaxy of stars and raw material b. a small disk of gas and dust surrounding a single star that was recently formed c. a cloud o f gas and du st illuminated by th e light of newly form ed stars within it d. the remnant of a star that exploded several thousand years ago e. an illusion ca ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
Introduction to Astronomy - Northumberland Astronomical Society
... Introduction to Astronomy Part 3 — Window on the Universe ...
... Introduction to Astronomy Part 3 — Window on the Universe ...
Sep 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... • B) The period of variability allows you to determine its absolute brightness • C) The time it takes to vary its brightness is determined by how long the light took to get to us • D) all of the above 8) If attempting to determine the distance to a nearby galaxy which is the better type of variable ...
... • B) The period of variability allows you to determine its absolute brightness • C) The time it takes to vary its brightness is determined by how long the light took to get to us • D) all of the above 8) If attempting to determine the distance to a nearby galaxy which is the better type of variable ...
Properties of Stars
... a “” symbol to plot the location of the Sun on your diagram. To which group does the Sun belong? (label it “Sun” on your graph also) 11. Compare the absolute magnitude and temperature of the Sun with those of other stars in its group. How are they the same/different? 12. Betelgeuse is 150 parsecs a ...
... a “” symbol to plot the location of the Sun on your diagram. To which group does the Sun belong? (label it “Sun” on your graph also) 11. Compare the absolute magnitude and temperature of the Sun with those of other stars in its group. How are they the same/different? 12. Betelgeuse is 150 parsecs a ...
HR Diagram Activity - Mr. Alster`s Science Classes
... Credit: Activity adapted from sir-ray.com ...
... Credit: Activity adapted from sir-ray.com ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a galaxy. When you look up into the night sky, most of the stars appear to be about the same size. However, in real ...
... atoms are fused together to create helium atoms. In the process a tremendous amount of energy is given off in the form of electromagnetic waves and heat. There are billions of stars in a galaxy. When you look up into the night sky, most of the stars appear to be about the same size. However, in real ...