Star Birth
... – Molecular H is hard to detect, since they do not emit light (radiation) – However, carbon monoxide present in these clouds emit millimeter wavelength light, and thus can be detected by radio telescopes. – these giant clouds have masses ranging from 105 - 106M. ...
... – Molecular H is hard to detect, since they do not emit light (radiation) – However, carbon monoxide present in these clouds emit millimeter wavelength light, and thus can be detected by radio telescopes. – these giant clouds have masses ranging from 105 - 106M. ...
Notes_ stars and sun
... • Blue Giants- These are the hottest of the giant stars. Because they burn fuel so fast, they burn out in between 10,000- 100,000 years. • These stars are incredibly bright. When they die, they explode in what is called a supernova. • Super Giant Stars- are the largest of the giant stars. If the ...
... • Blue Giants- These are the hottest of the giant stars. Because they burn fuel so fast, they burn out in between 10,000- 100,000 years. • These stars are incredibly bright. When they die, they explode in what is called a supernova. • Super Giant Stars- are the largest of the giant stars. If the ...
Properties of Stars
... Death of Medium-Mass Stars • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, mediummass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called plane ...
... Death of Medium-Mass Stars • Stars with masses similar to the sun evolve in essentially the same way as low-mass stars. • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, mediummass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called plane ...
Print Activity - Let`s Talk Science
... 7. You’ve found the North Star! If you face towards the North Star, you will be facing north. What’s happening? A constellation is a group of stars in the sky that form a fixed pattern in relation to each other, as viewed from the Earth. Astronomers currently recognize 88 constellations in the North ...
... 7. You’ve found the North Star! If you face towards the North Star, you will be facing north. What’s happening? A constellation is a group of stars in the sky that form a fixed pattern in relation to each other, as viewed from the Earth. Astronomers currently recognize 88 constellations in the North ...
Conceptobasico.pdf
... January 1, 2000 has no special designation or significance. The brightness of the stars was first estimated by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus in the second century B.C. Hipparchus' system divided the stars into five magnitude classes. The brightest stars were first magnitude, and the faintest stars ...
... January 1, 2000 has no special designation or significance. The brightness of the stars was first estimated by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus in the second century B.C. Hipparchus' system divided the stars into five magnitude classes. The brightest stars were first magnitude, and the faintest stars ...
Stars: flux, luminosity, color, and temperature
... • Luminosity - A star produces light – the total amount of energy that a star puts out as light each second is called its Luminosity. • Flux - If we have a light detector (eye, camera, telescope) we can measure the light produced by the star – the total amount of energy intercepted by the detector d ...
... • Luminosity - A star produces light – the total amount of energy that a star puts out as light each second is called its Luminosity. • Flux - If we have a light detector (eye, camera, telescope) we can measure the light produced by the star – the total amount of energy intercepted by the detector d ...
Luminosity Classes
... These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
... These are called Variable Stars. The change in luminosity is due to a change in size. (Though temperature changes too.) ...
Stars
... • Stars are much larger and brighter than the sun • look like tiny points of light to us because they are much farther away from Earth than the sun is. ...
... • Stars are much larger and brighter than the sun • look like tiny points of light to us because they are much farther away from Earth than the sun is. ...
Document
... planet has to dominate the neighborhood around its orbit. Pluto has been demoted to be a “Dwarf planet” (2006) because it does not dominate its neighborhood. Charon, its large “moon,” is only about half the size of Pluto, while all the true planets are far larger than their moons. ...
... planet has to dominate the neighborhood around its orbit. Pluto has been demoted to be a “Dwarf planet” (2006) because it does not dominate its neighborhood. Charon, its large “moon,” is only about half the size of Pluto, while all the true planets are far larger than their moons. ...
Lecture 5: The H-R diagram, standard candles and cosmic distances
... • The greater the mass of a MS star, the greater its luminosity (and also the greater its radius and surface temperature) • The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for mainsequence stars. It is found that L scales strongly with mass, approximately as ...
... • The greater the mass of a MS star, the greater its luminosity (and also the greater its radius and surface temperature) • The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for mainsequence stars. It is found that L scales strongly with mass, approximately as ...
January 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... beginning of the month the positions of the stars will be a bit further to the left (east) and at the end of the month they will be further to the right (west). Dominating the sky at this time of the year is the beautiful and very interesting constellation of Orion (The Hunter). The distinct line of ...
... beginning of the month the positions of the stars will be a bit further to the left (east) and at the end of the month they will be further to the right (west). Dominating the sky at this time of the year is the beautiful and very interesting constellation of Orion (The Hunter). The distinct line of ...
the lives of stars
... star, has been a main sequence star for about 5 billion years. It will continue to shine without changing for about 5 billion more years. Really large stars burn through their supply of hydrogen very quickly, so they ‘live fast and die young’! These very large stars may only be on the main sequence ...
... star, has been a main sequence star for about 5 billion years. It will continue to shine without changing for about 5 billion more years. Really large stars burn through their supply of hydrogen very quickly, so they ‘live fast and die young’! These very large stars may only be on the main sequence ...
Slide 1
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
... helium. At these temperatures most of the hydrogen is ionized, so the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. ...
Stars
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... Life span of a star depends on its size. – Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars – Main sequence may last only a few hundred thousand years – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
AST101_lect_12
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
Luminosity - UCF Physics
... Parallax and distance. p = parallax angle in arcseconds d (in parsecs) = 1/p ...
... Parallax and distance. p = parallax angle in arcseconds d (in parsecs) = 1/p ...
Apparent Magnitude
... (hot and bright) to the lower-right (cooler and less bright), called the main sequence. In the lower-left is where white dwarfs are found, and above the main sequence are the subgiants, giants and supergiants. The Sun is found on the main sequence at luminosity 1 and temperature 5780K (spectral type ...
... (hot and bright) to the lower-right (cooler and less bright), called the main sequence. In the lower-left is where white dwarfs are found, and above the main sequence are the subgiants, giants and supergiants. The Sun is found on the main sequence at luminosity 1 and temperature 5780K (spectral type ...
May
... NGC4656 is a type SBm barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici (KAY-neez- vë-NAT-ih-si). Popularly known as the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the key features are the angled tilt of the disk and the apparent offset of the core. If observing at low magnification look in the same field of view ...
... NGC4656 is a type SBm barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici (KAY-neez- vë-NAT-ih-si). Popularly known as the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the key features are the angled tilt of the disk and the apparent offset of the core. If observing at low magnification look in the same field of view ...
H-R Diagram Lab
... d. Is the relationship of brightness to temperature for these stars puzzling, or does it make sense? Explain. 5. Using the same graph, plot the stars from Group 3. 6. Once you have plotted the stars from Group 3, answer the following questions. Label this group of questions as “Group 3 Questions.” a ...
... d. Is the relationship of brightness to temperature for these stars puzzling, or does it make sense? Explain. 5. Using the same graph, plot the stars from Group 3. 6. Once you have plotted the stars from Group 3, answer the following questions. Label this group of questions as “Group 3 Questions.” a ...
CONSTELLATIONS OF THE SOUTHERN SKY VOLANS
... English astronomer John Herschel proposed shortening it to just Volans. Francis Baily adopted this suggestion in his British Association Catalogue of 1845, and it has been known as that ever since. Volans is the 76th constellation in size, occupying an area of 141 square degrees. It is located in th ...
... English astronomer John Herschel proposed shortening it to just Volans. Francis Baily adopted this suggestion in his British Association Catalogue of 1845, and it has been known as that ever since. Volans is the 76th constellation in size, occupying an area of 141 square degrees. It is located in th ...
Sample multiple choice questions for Exam 2
... 37. The final stellar remnant of a one solar mass star is a a) white dwarf. b) neutron star. c) pulsar. d) black hole. e) main sequence star. 38. Neutron stars are thought to form from a) 1 Msun stars. b) 5 Msun stars. c) 10 Msun stars. d) 50 Msun stars. e) all stars; mass has nothing to do with it. ...
... 37. The final stellar remnant of a one solar mass star is a a) white dwarf. b) neutron star. c) pulsar. d) black hole. e) main sequence star. 38. Neutron stars are thought to form from a) 1 Msun stars. b) 5 Msun stars. c) 10 Msun stars. d) 50 Msun stars. e) all stars; mass has nothing to do with it. ...
CYGNUS CONSTELLATION, the Swan Cygnus is
... Alpha Cygni, called Deneb, is the brightest star in Cygnus. It is a white supergiant star of spectral type A2Iae that varies between magnitudes 1.21 and 1.29, one of the largest and most luminous A-class stars known. It is located about 3200 light-years away (an A-type star is a main-sequence (hydro ...
... Alpha Cygni, called Deneb, is the brightest star in Cygnus. It is a white supergiant star of spectral type A2Iae that varies between magnitudes 1.21 and 1.29, one of the largest and most luminous A-class stars known. It is located about 3200 light-years away (an A-type star is a main-sequence (hydro ...
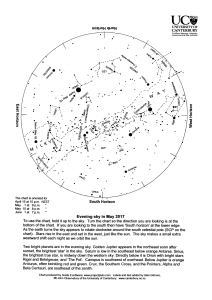
1705 Star Charts
... the galaxy, the pancake of billions of stars of which the sun is just one. The thick hub of the galaxy, 30 000 light years away, is in Sagittarius. The nearby outer edge is by Orion where the Milky Way is faintest. A scan along the Milky Way with binoculars shows many clusters of stars and some glow ...
... the galaxy, the pancake of billions of stars of which the sun is just one. The thick hub of the galaxy, 30 000 light years away, is in Sagittarius. The nearby outer edge is by Orion where the Milky Way is faintest. A scan along the Milky Way with binoculars shows many clusters of stars and some glow ...