27.1: Characteristics of Stars
... Measure the shift between the two locations. The closer a nearby star the greater the shift. This only works for stars that are closer than 1000 light-years. ...
... Measure the shift between the two locations. The closer a nearby star the greater the shift. This only works for stars that are closer than 1000 light-years. ...
Spectral analysis for the RV Tau star R Sct: In this section, we will
... default) the latest few week time period or (what we usually need to do) a light curve covering the date of our specific spectroscopic observation of interest (see Fig. 3). Since these stars vary, it is important to get the apparent magnitude for the specific date of observation. The dates used by a ...
... default) the latest few week time period or (what we usually need to do) a light curve covering the date of our specific spectroscopic observation of interest (see Fig. 3). Since these stars vary, it is important to get the apparent magnitude for the specific date of observation. The dates used by a ...
Part 1
... Measuring Brightness: History • Photometry - the measure of brightness • Hipparchus (150 B.C.) – catalog of 1000 stars – included position & brightness – Magnitude = brightness • brightest stars were first magnitude • faintest stars were sixth magnitude • estimated by eye (logarithmic response) ...
... Measuring Brightness: History • Photometry - the measure of brightness • Hipparchus (150 B.C.) – catalog of 1000 stars – included position & brightness – Magnitude = brightness • brightest stars were first magnitude • faintest stars were sixth magnitude • estimated by eye (logarithmic response) ...
Astro 10 Practice Test 2
... c. Mostly helium, with the rest being mostly various heavy elements, and a very small proportion of hydrogen. d. Mostly iron, similar to the hot iron core of the Earth, with a little bit of helium and some heavier elements. 17. On a clear autumn night, you spend some time examining the glowing HII r ...
... c. Mostly helium, with the rest being mostly various heavy elements, and a very small proportion of hydrogen. d. Mostly iron, similar to the hot iron core of the Earth, with a little bit of helium and some heavier elements. 17. On a clear autumn night, you spend some time examining the glowing HII r ...
Geography
... find the Big Dipper. Draw a straight line between the two stars of the Big Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... find the Big Dipper. Draw a straight line between the two stars of the Big Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
Photometry
... this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an apparent magnitude (m), which is simply a measure of how bright the stars look from Earth. ...
... this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an apparent magnitude (m), which is simply a measure of how bright the stars look from Earth. ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
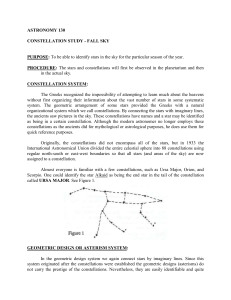
... Deneb (in Cygnus) and Altair (in Aquila). These three constellations make good reference points for the rest of the fall sky. Note in the eastern sky a large area defined roughly by four stars in a great square. This is the body of the constellation of Pegasus, which is connected to Andromeda. Make ...
... Deneb (in Cygnus) and Altair (in Aquila). These three constellations make good reference points for the rest of the fall sky. Note in the eastern sky a large area defined roughly by four stars in a great square. This is the body of the constellation of Pegasus, which is connected to Andromeda. Make ...
08 September: How far away are the closest stars?
... enormous • If the distance between the Earth and Sun were shrunk to 1 cm (0.4 inches), Alpha Centauri would be 2.75 km (1.7 miles) away ...
... enormous • If the distance between the Earth and Sun were shrunk to 1 cm (0.4 inches), Alpha Centauri would be 2.75 km (1.7 miles) away ...
Lecture notes -- pdf file - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... Modern scientific method: units of power/area Demo ...
... Modern scientific method: units of power/area Demo ...
2.64 3.26156 8.61 pc ly × =
... Thus Polaris is about 49.6 times farther from us than Sirius. From Appendix 5 of the textbook, Sirius is 8.58 ly from Earth so Polaris is 8.58 ly X 49.6 = 425 ly away. 13.49. Proxima Centauri, the star nearest the Earth other than the Sun, has a parallax of 0.772 arcseconds. How long does it take li ...
... Thus Polaris is about 49.6 times farther from us than Sirius. From Appendix 5 of the textbook, Sirius is 8.58 ly from Earth so Polaris is 8.58 ly X 49.6 = 425 ly away. 13.49. Proxima Centauri, the star nearest the Earth other than the Sun, has a parallax of 0.772 arcseconds. How long does it take li ...
Exercise 4
... (b) C > D > E > A > B (Largest m to smallest m, i.e. dimmest to brightest, i.e. least luminous to most luminous since the objects are at the same distance from the Earth) (c) B > A > E > D > C (Using m–M = 5 log d/10, the largest m-M corresponds the farthest star) ...
... (b) C > D > E > A > B (Largest m to smallest m, i.e. dimmest to brightest, i.e. least luminous to most luminous since the objects are at the same distance from the Earth) (c) B > A > E > D > C (Using m–M = 5 log d/10, the largest m-M corresponds the farthest star) ...
ASTR 1050: Survey of Astronomy
... a. By measuring the wavelength with the most intense light and applying Wien's law b. By measuring the strengths of the absorption lines from different elements c. By measuring the distance and magnitude and applying the inverse square law of light d. a. and b. e. a and c. f. b and c. 33. A star’s a ...
... a. By measuring the wavelength with the most intense light and applying Wien's law b. By measuring the strengths of the absorption lines from different elements c. By measuring the distance and magnitude and applying the inverse square law of light d. a. and b. e. a and c. f. b and c. 33. A star’s a ...
Dec 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... 4 b to measure distance and Spectroscopic parallax makes use of the formula so requires knowledge of luminosity and apparent brightness; apparent brightness can easily be measured with a CCD camera; the luminosity can be determined if we know the temperature of the star (obtained form its spectrum) ...
... 4 b to measure distance and Spectroscopic parallax makes use of the formula so requires knowledge of luminosity and apparent brightness; apparent brightness can easily be measured with a CCD camera; the luminosity can be determined if we know the temperature of the star (obtained form its spectrum) ...
Binary Orbits
... • Observations of the orbits can be used to determine parameters e.g. period and line of sight velocities – masses – done in optical and X-ray • Fact that a large fraction of stars are found in binaries indicate stars are formed in groups through gravitational collapse of ...
... • Observations of the orbits can be used to determine parameters e.g. period and line of sight velocities – masses – done in optical and X-ray • Fact that a large fraction of stars are found in binaries indicate stars are formed in groups through gravitational collapse of ...
M = 5.5 - The Millstone
... stellar distance (by other means). Absolute magnitude, M, expresses the brightness of a star as it would be if it were placed 10 parsecs away. Since all stars would be placed at the same distance, absolute magnitudes show differences in actual luminosities. It is a measure based on stellar analysis ...
... stellar distance (by other means). Absolute magnitude, M, expresses the brightness of a star as it would be if it were placed 10 parsecs away. Since all stars would be placed at the same distance, absolute magnitudes show differences in actual luminosities. It is a measure based on stellar analysis ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... located in the upper right-hand corner of the H-R diagram. As the central core of a main sequence star with a mass from ~0.8 to 8 solar masses runs out of hydrogen, radiation pressure no longer balances gravity and the star begins to collapse. There is still hydrogen in the outer layers surrounding ...
... located in the upper right-hand corner of the H-R diagram. As the central core of a main sequence star with a mass from ~0.8 to 8 solar masses runs out of hydrogen, radiation pressure no longer balances gravity and the star begins to collapse. There is still hydrogen in the outer layers surrounding ...
neutron star - Livonia Public Schools
... Death of Massive Stars • stars that are over three times the sun’s mass have relatively short life spans, which end in a supernova event. • A supernova is an exploding massive star that increases in brightness many thousands of times. • The massive star’s interior condenses and may produce a hot, ...
... Death of Massive Stars • stars that are over three times the sun’s mass have relatively short life spans, which end in a supernova event. • A supernova is an exploding massive star that increases in brightness many thousands of times. • The massive star’s interior condenses and may produce a hot, ...
Lecture 19 Brightness Units
... are all due to absorption by atoms starting from the second energy state. – The only way an atom gets into this state is by being hit by a neighbor, and the neighbors at these temperatures are not moving fast enough. Balmer lines are weak. Mar 3, 2006 ...
... are all due to absorption by atoms starting from the second energy state. – The only way an atom gets into this state is by being hit by a neighbor, and the neighbors at these temperatures are not moving fast enough. Balmer lines are weak. Mar 3, 2006 ...
reach for the stars
... Section Id: Answer the following questions about open and globular clusters. (10 pts total) 1. Stars in clusters are bound together by what? (1 pt) Gravity 2. Which type of cluster is often found in the halo of galaxies? (1 pt) Globular clusters 3. Where is the other type of cluster usually found? ...
... Section Id: Answer the following questions about open and globular clusters. (10 pts total) 1. Stars in clusters are bound together by what? (1 pt) Gravity 2. Which type of cluster is often found in the halo of galaxies? (1 pt) Globular clusters 3. Where is the other type of cluster usually found? ...
Constellations - Mayo Dark Sky Park
... could slay any creature on Earth. There are many legends of his special powers such as walking on water, and various stories of how he was killed. One story is that Diana, the archer-goddess with whom Orion was a favourite was tricked into firing the arrow that killed Orion. The story goes like this ...
... could slay any creature on Earth. There are many legends of his special powers such as walking on water, and various stories of how he was killed. One story is that Diana, the archer-goddess with whom Orion was a favourite was tricked into firing the arrow that killed Orion. The story goes like this ...
1) The following questions refer to the HR diagram
... A) it amplifies the contrast with red giants. B) they are both very hot and very small. C) they are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity wh ...
... A) it amplifies the contrast with red giants. B) they are both very hot and very small. C) they are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. D) they are the end-products of small, low-mass stars. E) they are the opposite of black holes. 22) What happens to the surface temperature and luminosity wh ...