8.1 Stars
... the atoms in the star’s core to compress and collapse. When an atom collapses, it forms neutrons, particles that are at the centre of most atoms already. When the star’s core becomes little more than a ball of neutrons only about 15 km across, it is called a neutron star. Neutron stars are made of ...
... the atoms in the star’s core to compress and collapse. When an atom collapses, it forms neutrons, particles that are at the centre of most atoms already. When the star’s core becomes little more than a ball of neutrons only about 15 km across, it is called a neutron star. Neutron stars are made of ...
A Brief guide to the night Skies for those who know nothing
... for most stars. A star begins life as a cloud of dust and gas called a NEBULA. Triggered by some mechanism which scientists have not fully understood, the star begins to collapse under its own gravitational attraction. Once started, the process continues very rapidly, exerting pressure on the materi ...
... for most stars. A star begins life as a cloud of dust and gas called a NEBULA. Triggered by some mechanism which scientists have not fully understood, the star begins to collapse under its own gravitational attraction. Once started, the process continues very rapidly, exerting pressure on the materi ...
w 2012-01-13 Stellar Life Cycle
... Planetary nebulae are shells of gas thrown out by some stars near the end of their lives. Our Sun will probably produce a planetary nebula in about 5 billion years. They have nothing at all to do with planets; the terminology was invented because they often look a little like planets in small telesc ...
... Planetary nebulae are shells of gas thrown out by some stars near the end of their lives. Our Sun will probably produce a planetary nebula in about 5 billion years. They have nothing at all to do with planets; the terminology was invented because they often look a little like planets in small telesc ...
Chapter 29: Stars - Mr. Pelton Science
... • Astronomers use two units to measure long distances. • The light-year (ly): the distance light travels in one year (9.461x1012 km) • A parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly ...
... • Astronomers use two units to measure long distances. • The light-year (ly): the distance light travels in one year (9.461x1012 km) • A parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly ...
SPA 302: THE EVOLUTION OF STARS LECTURE 1: BASICS OF
... 1.3.2 Brightness and Luminosity of Stars The luminosity of a star, denoted by L, is one of the most important characteristics of stars. It is measured in Watts (W) or as a multiple of the Sun's luminosity Lʘ and it is the amount of energy emitted per unit are of a star surface per second. However, i ...
... 1.3.2 Brightness and Luminosity of Stars The luminosity of a star, denoted by L, is one of the most important characteristics of stars. It is measured in Watts (W) or as a multiple of the Sun's luminosity Lʘ and it is the amount of energy emitted per unit are of a star surface per second. However, i ...
Stars
... The key to locating the North Star in the night sky is to first find the Big Dipper, a constellation of stars known as Ursa Major.. The Big Dipper is perhaps the best known group of stars in the northern sky and is easy to distinguish from all others. Also known as the Great Bear, the Big Dipper is ...
... The key to locating the North Star in the night sky is to first find the Big Dipper, a constellation of stars known as Ursa Major.. The Big Dipper is perhaps the best known group of stars in the northern sky and is easy to distinguish from all others. Also known as the Great Bear, the Big Dipper is ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... needle of light with the hint of a central bulge. Moderate apertures begin to show a dark dust lane. The North Galactic Pole is located a few degrees to the East. NGC4826 (M64) (8.6) sg. This bright galaxy is located almost halfway between M53 and NGC4565. Nicknamed the "Black-eye galaxy" because of ...
... needle of light with the hint of a central bulge. Moderate apertures begin to show a dark dust lane. The North Galactic Pole is located a few degrees to the East. NGC4826 (M64) (8.6) sg. This bright galaxy is located almost halfway between M53 and NGC4565. Nicknamed the "Black-eye galaxy" because of ...
CONSTELLATIONS
... Autumnal Equinox / September 21 THE PLANETS As you have seen, the dashed line on the planisphere marks the ecliptic. As our Earth moves around in its orbit, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets also appear along this line. The ecliptic therefore represents the plane of the solar system. Of the nine pl ...
... Autumnal Equinox / September 21 THE PLANETS As you have seen, the dashed line on the planisphere marks the ecliptic. As our Earth moves around in its orbit, the Sun, the Moon, and the planets also appear along this line. The ecliptic therefore represents the plane of the solar system. Of the nine pl ...
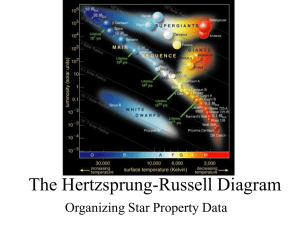
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Neutron Star - Perry Local Schools
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
July - astra
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
Where to begin the adventure with variable stars?
... because they belong to constellations that are visible all year round in the northern hemisphere. They are located in relation to one another in the following way: ...
... because they belong to constellations that are visible all year round in the northern hemisphere. They are located in relation to one another in the following way: ...
STAR TYPES
... A Mira variable star is a variable star whose brightness and size cycle over a very long time period, in the order of many months. Miras are pulsating red giants that vary in magnitude as much as a factor of many hundred (by 6 or 8 magnitudes). Mira variables were named after the star Mira, whose va ...
... A Mira variable star is a variable star whose brightness and size cycle over a very long time period, in the order of many months. Miras are pulsating red giants that vary in magnitude as much as a factor of many hundred (by 6 or 8 magnitudes). Mira variables were named after the star Mira, whose va ...
The Night Sky May 2016 - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... The constellation Leo is now in the south-eastern sky in the evening. One of the few constellations that genuinely resembles its name, it looks likes one of the Lions in Trafalgar Square, with its mane and head forming an arc (called the Sickle) to the upper right, with Regulus in the position of it ...
... The constellation Leo is now in the south-eastern sky in the evening. One of the few constellations that genuinely resembles its name, it looks likes one of the Lions in Trafalgar Square, with its mane and head forming an arc (called the Sickle) to the upper right, with Regulus in the position of it ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... The diameter of Alpha Centauri A is 1.71 x 109 meters. The Sun’s diameter is 1.39 x 109 meters as determined from the table in the text’s appendix. Thus, Alpha Centauri A is slightly larger than the Sun with a diameter of 1.23 solar diameters. Alpha Centauri B is (60/85) = 0.706 times smaller than A ...
... The diameter of Alpha Centauri A is 1.71 x 109 meters. The Sun’s diameter is 1.39 x 109 meters as determined from the table in the text’s appendix. Thus, Alpha Centauri A is slightly larger than the Sun with a diameter of 1.23 solar diameters. Alpha Centauri B is (60/85) = 0.706 times smaller than A ...
Nov 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
... The planets are best observed with a telescope using magnifithat were born out of the same nebula cloud. A group often forms cations from 50x to 200x. The five naked-eye planets are Mera pretty pattern. The Pleiades and Praesepe are great examples. cury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. Venus is ext ...
Sequencing the Stars
... seem to be too bright. These are nearby stars that don’t belong to the globular cluster but just happen to be in the field of view. I like globular clusters so much that I tend to revisit my favorites each year and retake their picture. Hence, I can compare pairs of HR-diagrams of the same cluster t ...
... seem to be too bright. These are nearby stars that don’t belong to the globular cluster but just happen to be in the field of view. I like globular clusters so much that I tend to revisit my favorites each year and retake their picture. Hence, I can compare pairs of HR-diagrams of the same cluster t ...
worksheet
... stars with different starting masses. ☆ Select a different starting mass for your star in the ‘Star Properties’ banner. ☆ Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram tab, click play to watch your new stars evolution. ☆ Try out a few different masses then answer the following questions. 1. Using the Hertzspr ...
... stars with different starting masses. ☆ Select a different starting mass for your star in the ‘Star Properties’ banner. ☆ Use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram tab, click play to watch your new stars evolution. ☆ Try out a few different masses then answer the following questions. 1. Using the Hertzspr ...
Star Formation, HR Diagram, and the Main Sequence (Professor
... Every M dwarf ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... Every M dwarf ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... – So…A smaller star has less fuel, but its rate of fusion is not as fast. Therefore, smaller stars live longer than larger stars because their rate of fuel consumption is not as rapid. ...
... – So…A smaller star has less fuel, but its rate of fusion is not as fast. Therefore, smaller stars live longer than larger stars because their rate of fuel consumption is not as rapid. ...