General Astronomy - Stockton University
... The angle is so small that there is really no measureable difference between D and that between the star and earth ...
... The angle is so small that there is really no measureable difference between D and that between the star and earth ...
Stellar Census
... Most of the apparently bright stars are the hot and luminous A- and Btype stars The bright-star sample includes a few of the very hot O-type stars All but one of the K-type stars in the bright-star sample are giants or supergiant stars All of the M-type stars are giants or supergiants 22 March 2005 ...
... Most of the apparently bright stars are the hot and luminous A- and Btype stars The bright-star sample includes a few of the very hot O-type stars All but one of the K-type stars in the bright-star sample are giants or supergiant stars All of the M-type stars are giants or supergiants 22 March 2005 ...
Proficiency Step #5--
... from ancient times belongs to the Roman Ptolemy of Alexandria, who grouped 1022 stars into 48 constellations during the 2nd century A.D. Although Ptolemy's Almagest does not include the constellations which may only be seen from the southern hemisphere, it forms the basis for the modern list of 88 c ...
... from ancient times belongs to the Roman Ptolemy of Alexandria, who grouped 1022 stars into 48 constellations during the 2nd century A.D. Although Ptolemy's Almagest does not include the constellations which may only be seen from the southern hemisphere, it forms the basis for the modern list of 88 c ...
Stellarium01 Starter Part A B Doc - ASTR101
... Start Stellarium. Use “Current Location” listed above by going to the Icon Bar at the left-hand side of the screen and find the Location window icon (shortcut key= “F6”, in some linux it is fn-f6) and click on it. Scroll through the list of locations in the window until you find the current location ...
... Start Stellarium. Use “Current Location” listed above by going to the Icon Bar at the left-hand side of the screen and find the Location window icon (shortcut key= “F6”, in some linux it is fn-f6) and click on it. Scroll through the list of locations in the window until you find the current location ...
uniview glossary - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... Saturn was named for the Roman god of agriculture and lies 885 million miles from the Sun, (9.6 AU). Saturn takes 29.5 years to orbit, but only 10.7 hours to rotate (day). Its diameter is 75,000 miles, making it the second largest planet. Its mass is 95 times that of Earth. It is the second of the f ...
... Saturn was named for the Roman god of agriculture and lies 885 million miles from the Sun, (9.6 AU). Saturn takes 29.5 years to orbit, but only 10.7 hours to rotate (day). Its diameter is 75,000 miles, making it the second largest planet. Its mass is 95 times that of Earth. It is the second of the f ...
June 2015 - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Of all multiple star systems consisting of at least three stars, perhaps the finest and most celebrated of all is Epsilon (ε Lyr) Lyrae. Epsilon Lyrae is located in the constellation of Lyra close to the bright star Vega (mag. 0.0). For northern hemisphere observers Vega dazzles brilliantly during t ...
... Of all multiple star systems consisting of at least three stars, perhaps the finest and most celebrated of all is Epsilon (ε Lyr) Lyrae. Epsilon Lyrae is located in the constellation of Lyra close to the bright star Vega (mag. 0.0). For northern hemisphere observers Vega dazzles brilliantly during t ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Outline
... Hipparcos H-R Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell (M_V, B-V) diagram for the 16631 single stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue with relative distance precision better than 10% and sigma_(B-V) less than or equal to 0.025 mag. Colors indicate number of stars in a cell of 0.01 mag in (B-V) and 0.05 mag in V magn ...
... Hipparcos H-R Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell (M_V, B-V) diagram for the 16631 single stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue with relative distance precision better than 10% and sigma_(B-V) less than or equal to 0.025 mag. Colors indicate number of stars in a cell of 0.01 mag in (B-V) and 0.05 mag in V magn ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
HR Diagram Explorer
... An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, B-V, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y-ax ...
... An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around the diagram. The options panel allows you control the variables plotted on the x-axis: (temperature, B-V, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y-ax ...
celestial sphere
... constellations from the outside inward rather than from the inside outward. Several hundred stars have been plotted on the globe as well as the great circles representing the hour circles for every hour from 0 to 23 hours. The celestial equator, ecliptic, and parallels of declination for every tenth ...
... constellations from the outside inward rather than from the inside outward. Several hundred stars have been plotted on the globe as well as the great circles representing the hour circles for every hour from 0 to 23 hours. The celestial equator, ecliptic, and parallels of declination for every tenth ...
Surveying the Stars
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
tut35 Magnitudes
... versus daylight sky’s 6.5 magnitude/arcsecond2 has sufficient contrast to be visible just before sunset or just after sunrise. The full Moon’s size and 3.6 magnitude/arcsecond2 makes for an easy daylight sighting. At greatest elongation, Venus’ magnitude/arcsecond2 is 1.9. The large contrast with th ...
... versus daylight sky’s 6.5 magnitude/arcsecond2 has sufficient contrast to be visible just before sunset or just after sunrise. The full Moon’s size and 3.6 magnitude/arcsecond2 makes for an easy daylight sighting. At greatest elongation, Venus’ magnitude/arcsecond2 is 1.9. The large contrast with th ...
Globular Clusters
... 47 Tuc, NGC 104. (15,000ly away). Often described as THE best glob in the sky! Easily visible to the naked eye, right beside the Small Magellanic Cloud. Sharply concentrated in the centre. A 4" scope will start to resolve it, and in a 6" scope or bigger, on a good night, it will resolve into a spec ...
... 47 Tuc, NGC 104. (15,000ly away). Often described as THE best glob in the sky! Easily visible to the naked eye, right beside the Small Magellanic Cloud. Sharply concentrated in the centre. A 4" scope will start to resolve it, and in a 6" scope or bigger, on a good night, it will resolve into a spec ...
color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
... surface area of a sphere is given by 4R2, where R is the radius of the sphere, or in the case of a light it’s the distance between you and the light bulb. So as you get further away from the light, the area of the sphere the light is spread over goes up faster, as the square of that distance. So, t ...
... surface area of a sphere is given by 4R2, where R is the radius of the sphere, or in the case of a light it’s the distance between you and the light bulb. So as you get further away from the light, the area of the sphere the light is spread over goes up faster, as the square of that distance. So, t ...
second grade - Math/Science Nucleus
... people would look into the night sky and wonder what was in "outer space." They developed stories on the groups of stars. Astronomers use 88 constellations to divide up the heavens. 2. Give each student one of the constellations and have them imagine what the constellation may look like in the sky. ...
... people would look into the night sky and wonder what was in "outer space." They developed stories on the groups of stars. Astronomers use 88 constellations to divide up the heavens. 2. Give each student one of the constellations and have them imagine what the constellation may look like in the sky. ...
Binocular Objects (MS Word)
... Sagittarius contains more Messier objects than any other constellation. The best way to identify them is to take them one by one. The beginner will have to be careful not to confuse the various objects. The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the M ...
... Sagittarius contains more Messier objects than any other constellation. The best way to identify them is to take them one by one. The beginner will have to be careful not to confuse the various objects. The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the M ...
Astronomy and Survey of Information
... Detecting planets around multiple star systems introduces additional technical difficulties, which may be why so far (as of July 2005) only one such planet has been found: HD 188753 Ab. HD 188753 Ab is the first known planet in a triple star system. It has been discovered by a Polish astronomer work ...
... Detecting planets around multiple star systems introduces additional technical difficulties, which may be why so far (as of July 2005) only one such planet has been found: HD 188753 Ab. HD 188753 Ab is the first known planet in a triple star system. It has been discovered by a Polish astronomer work ...
13.5 The HR Diagram By the early 1900s, astronomers had learned
... We find from such measurements that all stars have nearly the same composition of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, with a trace of the heavier elements. Most have surface temperatures between about 3000 and 30,000 K and masses between about 0.1 and 30 M⊙. The HR diagram offers a simple, pictorial ...
... We find from such measurements that all stars have nearly the same composition of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, with a trace of the heavier elements. Most have surface temperatures between about 3000 and 30,000 K and masses between about 0.1 and 30 M⊙. The HR diagram offers a simple, pictorial ...
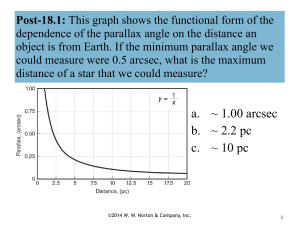
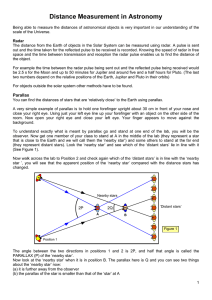
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
Stars - cayugascience
... extremely long. All stars form inside a collapsing nebula, a cloud of dust and gases. A nebula’s collapse can be triggered by a disturbance such as the gravitational attraction of a nearby star or the shockwave from an exploding star. Inside a collapsing nebula, the region with the greatest amount o ...
... extremely long. All stars form inside a collapsing nebula, a cloud of dust and gases. A nebula’s collapse can be triggered by a disturbance such as the gravitational attraction of a nearby star or the shockwave from an exploding star. Inside a collapsing nebula, the region with the greatest amount o ...