Project 8 : Stellar Spectra: Classification
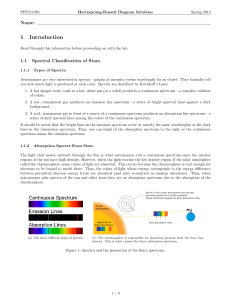
... Absorption lines occur when an electron absorbs energy from the spectrum to move up the energy levels in the atom. Since hydrogen has only one electron, this electron is usually in the ground state. But as the temperature rises, the average electron gains m ...
... Absorption lines occur when an electron absorbs energy from the spectrum to move up the energy levels in the atom. Since hydrogen has only one electron, this electron is usually in the ground state. But as the temperature rises, the average electron gains m ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
... luminosity), with the same temperature as cooler main sequence stars, have greater surface areas (larger radii). Also, stars that have the same luminosity as dimmer main sequence stars, but are to the left of them (hotter) on the H-R diagram, have smaller surface areas (smaller radii). Bright, cool ...
... luminosity), with the same temperature as cooler main sequence stars, have greater surface areas (larger radii). Also, stars that have the same luminosity as dimmer main sequence stars, but are to the left of them (hotter) on the H-R diagram, have smaller surface areas (smaller radii). Bright, cool ...
classifying stars
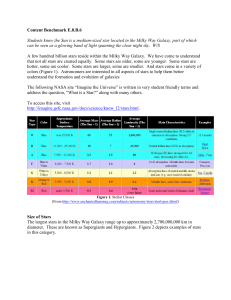
... The brightness of a star depends on its size, temperature and distance from the earth. Some stars appear brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them ...
... The brightness of a star depends on its size, temperature and distance from the earth. Some stars appear brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them ...
Constellation Catalog
... Instructions for locating the constellation: Best time for seeing Aries the Ram. The best time to behold the Mighty Ram is at the opposite end of the year, when the Earth is on the other side of the sun. In late October, this constellation rises in the east at sunset, reaches its highest point in t ...
... Instructions for locating the constellation: Best time for seeing Aries the Ram. The best time to behold the Mighty Ram is at the opposite end of the year, when the Earth is on the other side of the sun. In late October, this constellation rises in the east at sunset, reaches its highest point in t ...
Ch 11a (Measuring Stars 10-28-10)
... IV. Stellar sizes (radius) Luminosity is proportional to surface area (how large) x temperature (how hot): L= 4R2T4 If we can measure the Luminosity and the temperature of a star we can tell how large its ...
... IV. Stellar sizes (radius) Luminosity is proportional to surface area (how large) x temperature (how hot): L= 4R2T4 If we can measure the Luminosity and the temperature of a star we can tell how large its ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
... Conjunction – An alignment of two celestial bodies such that they present the least angular separation as viewed from Earth. Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to ...
Stellar Evolution – Cosmic Cycles of Formation and Destruction
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
Stellar Magnitudes & Distances
... • Take the difference in magnitudes between two stars. • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
... • Take the difference in magnitudes between two stars. • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
The Relationship Between a Star`s Brightness and its Distance
... • Take the difference in magnitudes between two stars. • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
... • Take the difference in magnitudes between two stars. • Raise 2.512 to that power. • Example: How many times brighter is Polaris (a 2nd magnitude star) than a barely-visible 6th magnitude star? • 6 - 2 = 4. So 2.5124 = 39.8 times. Polaris is almost 40 times brighter than the faintest visible star! ...
3.2 Spectra and Spectral Classification
... (a) absolute magnitude or luminosity and (b) spectral type or effective temperature (sometimes also color index) That means there exist different forms of this diagram, usually ● log L versus spectral type ● log L versus log T ● M versus B-V ...
... (a) absolute magnitude or luminosity and (b) spectral type or effective temperature (sometimes also color index) That means there exist different forms of this diagram, usually ● log L versus spectral type ● log L versus log T ● M versus B-V ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
... Several stars show periodic changes in their apparent magnitudes. This was first thought to be caused by dark spots on a rotating star’s surface: When the dark spots were turned towards us, the star appeared fainter, when the spots were turned away from us, the star appeared brighter. Today we know ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... When iron is heated it starts first to glow deep red, going through yellow and finally being bright white, at the same time its luminosity also increases. The same is in principle true for stars; the luminosity only depends on their surface temperature (color) and their emitting area (or rather thei ...
... When iron is heated it starts first to glow deep red, going through yellow and finally being bright white, at the same time its luminosity also increases. The same is in principle true for stars; the luminosity only depends on their surface temperature (color) and their emitting area (or rather thei ...
PDF format
... They are located only near the center of the galaxy. Their stars are among the oldest in the universe. They are located only in the disk of the galaxy. Their stars are among the youngest in the universe. B and C ...
... They are located only near the center of the galaxy. Their stars are among the oldest in the universe. They are located only in the disk of the galaxy. Their stars are among the youngest in the universe. B and C ...
Unit 13―The “Fixed” Stars
... 186. Classification by magnitudes. Stars that can only be made visible by means of a telescope are generally called telescopic and those that can be visible to the unaided eye are called lucid. (Have you ever heard someone state, “Now let me make this lucidly clear?”) As soon as telescopes started m ...
... 186. Classification by magnitudes. Stars that can only be made visible by means of a telescope are generally called telescopic and those that can be visible to the unaided eye are called lucid. (Have you ever heard someone state, “Now let me make this lucidly clear?”) As soon as telescopes started m ...
J: Chapter 4: Stars and Galaxies
... Sunspots Areas of the Sun’s surface that appear dark because they are cooler than surrounding areas are called sunspots. Ever since Galileo Galilei viewed sunspots with a telescope, scientists have been studying them. Because scientists could observe the movement of individual sunspots, shown in Fig ...
... Sunspots Areas of the Sun’s surface that appear dark because they are cooler than surrounding areas are called sunspots. Ever since Galileo Galilei viewed sunspots with a telescope, scientists have been studying them. Because scientists could observe the movement of individual sunspots, shown in Fig ...
Properties of Stars - Montana State University Extended University
... In order to better understand how stars are constructed, astronomers look for correlations between stellar properties. The easiest way to do this is make a plot of one intrinsic property vs. another intrinsic property. An intrinsic property is one that does not depend on the distance the star is fro ...
... In order to better understand how stars are constructed, astronomers look for correlations between stellar properties. The easiest way to do this is make a plot of one intrinsic property vs. another intrinsic property. An intrinsic property is one that does not depend on the distance the star is fro ...
A Stars
... • B Stars (15-30,000 K): Most of H is ionized, so only very weak H lines. • A Stars (10,000 K): Ideal excitation conditions, strongest H lines. • G Stars (6000 K): Too cool, little excited H, so only weak H lines. ...
... • B Stars (15-30,000 K): Most of H is ionized, so only very weak H lines. • A Stars (10,000 K): Ideal excitation conditions, strongest H lines. • G Stars (6000 K): Too cool, little excited H, so only weak H lines. ...
The Sculptor dwarf irregular galaxy SDIG: present and past
... indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of other late-type galaxies, suggesting that SDIG has faded by less than a magnitude in B since it stopped forming stars. Highly luminous red stars have been discovered ...
... indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of other late-type galaxies, suggesting that SDIG has faded by less than a magnitude in B since it stopped forming stars. Highly luminous red stars have been discovered ...
What is the minimum size of a star that will go supernova? A. Half
... This star, whose name means “Female Warrior,” is not only part of the constellation Orion, but was also a villain in the Harry Potter books. A. Bellatrix B. Vega C. Castor Answer: A. Bellatrix The star that’s the right hand of Orion means "female warrior" in Greek. Bellatrix is a hot blu ...
... This star, whose name means “Female Warrior,” is not only part of the constellation Orion, but was also a villain in the Harry Potter books. A. Bellatrix B. Vega C. Castor Answer: A. Bellatrix The star that’s the right hand of Orion means "female warrior" in Greek. Bellatrix is a hot blu ...
in BRIGHTEST STARS
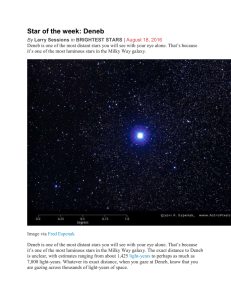
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
Pattern recognition of star constellations for spacecraft
... The star catalogue includes the declination, right ascension, and magnitude of the stars as detected by the CCD-camera. It includes the 1539 brightest stars, and it is based on the PPM catalogue [4]. It is compiled with the following corrections of the raw star data: ...
... The star catalogue includes the declination, right ascension, and magnitude of the stars as detected by the CCD-camera. It includes the 1539 brightest stars, and it is based on the PPM catalogue [4]. It is compiled with the following corrections of the raw star data: ...