mass_spetral
... When the stars are farther apart (a is increased) they move more slowly in their orbit. Measuring the time it takes for the spectral lines to return to their starting wavelength gives us the orbital ...
... When the stars are farther apart (a is increased) they move more slowly in their orbit. Measuring the time it takes for the spectral lines to return to their starting wavelength gives us the orbital ...
procedure processing the data - Mr. Traeger`s Earth Science
... Homework for tonight! Go outside tonight after dark with your star finder and some binoculars if you have them. A small flashlight (preferably with a red filter) is also needed. Make sure to hold the star finder over your head and point the North arrow in the direction of the mountains. On a separat ...
... Homework for tonight! Go outside tonight after dark with your star finder and some binoculars if you have them. A small flashlight (preferably with a red filter) is also needed. Make sure to hold the star finder over your head and point the North arrow in the direction of the mountains. On a separat ...
Astronomy Chap 1
... North Pole? Draw a picture for each to help your answer. 3. If you watched these same stars night after night, what would change? 4. What factors ultimately explain the nightly and yearly star cycles we observe? 5. Describe a circumpolar star. What is another name for a circumpolar star? Give an exa ...
... North Pole? Draw a picture for each to help your answer. 3. If you watched these same stars night after night, what would change? 4. What factors ultimately explain the nightly and yearly star cycles we observe? 5. Describe a circumpolar star. What is another name for a circumpolar star? Give an exa ...
1 How luminous are stars?
... center of mass is in the middle, rA = rB. The more unequal the masses are, the more it shifts toward the more massive star. ...
... center of mass is in the middle, rA = rB. The more unequal the masses are, the more it shifts toward the more massive star. ...
notes
... placed it at the same distance that it currently is from our Sun (T = 5800 K) • We moved it to an M-type star (T = 3000 K) and placed it at the same distance that it currently is from our Sun • In each of these cases, where should we place the Earth to prevent these effects? ...
... placed it at the same distance that it currently is from our Sun (T = 5800 K) • We moved it to an M-type star (T = 3000 K) and placed it at the same distance that it currently is from our Sun • In each of these cases, where should we place the Earth to prevent these effects? ...
Star Classification
... with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at ...
... with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at ...
After Dark M S
... supernovas, with one supernova exploding in the Whirlpool Galaxy, M51, at the end of May and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of ...
... supernovas, with one supernova exploding in the Whirlpool Galaxy, M51, at the end of May and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of ...
Hubble Telescope Pictures
... The Sombrero Galaxy - 28 million light years from Earth - was voted best picture taken by the Hubble telescope. The dimensions of the galaxy, officially called M104, are as spectacular as its appearance. It has 800 billion suns and is 50,000 light years across. ...
... The Sombrero Galaxy - 28 million light years from Earth - was voted best picture taken by the Hubble telescope. The dimensions of the galaxy, officially called M104, are as spectacular as its appearance. It has 800 billion suns and is 50,000 light years across. ...
4th Grade Science Vocabulary Chapter 2
... Vocabulary in 4th Grade Science Ch. 2 Universe Galaxy Planet Revolve Phase Axis Comet ...
... Vocabulary in 4th Grade Science Ch. 2 Universe Galaxy Planet Revolve Phase Axis Comet ...
Prep Homework Solutions for HW due 10/04/10
... the red giant in Algol used to be the more massive star, and it evolved off the Main Sequence before its companion, but then it lost significant mass through mass transfer to the companion, so the more massive star is the less massive star now. Note: a couple of you suggested that the paradox could ...
... the red giant in Algol used to be the more massive star, and it evolved off the Main Sequence before its companion, but then it lost significant mass through mass transfer to the companion, so the more massive star is the less massive star now. Note: a couple of you suggested that the paradox could ...
planetary nebulae
... Spiral galaxies like our own are filled with interstellar dust and gas. The pink glow is caused by hydrogen excited by the radiation from young stars. ...
... Spiral galaxies like our own are filled with interstellar dust and gas. The pink glow is caused by hydrogen excited by the radiation from young stars. ...
Study Island
... food and water. She allowed the experiment to last for a few generations of mice and tested the activity levels of the different groups. There was no change in the activity levels of the mice, but she noticed that the mice in the cold environment had much darker, thicker fur than the mice in the hot ...
... food and water. She allowed the experiment to last for a few generations of mice and tested the activity levels of the different groups. There was no change in the activity levels of the mice, but she noticed that the mice in the cold environment had much darker, thicker fur than the mice in the hot ...
Binary Star Systems - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... • In a telescope, an optical double looks like a binary star system, 2 stars that are in orbit around a common center of mass. • However, they’re really far apart from each other. They just happen to be in the same part of the sky. • Mizar and Alcor are an optical double pair. ...
... • In a telescope, an optical double looks like a binary star system, 2 stars that are in orbit around a common center of mass. • However, they’re really far apart from each other. They just happen to be in the same part of the sky. • Mizar and Alcor are an optical double pair. ...
Synthetic color-magnitude diagrams: the ingredients
... field binaries within 100 parsecs from the Sun. The binary systems located in the local field has been also studied by Tout (1991), who suggested that the f(q) function can be derived by randomly extracting secondary stars from the “adopted” (observed) initial mass function; ...
... field binaries within 100 parsecs from the Sun. The binary systems located in the local field has been also studied by Tout (1991), who suggested that the f(q) function can be derived by randomly extracting secondary stars from the “adopted” (observed) initial mass function; ...
Oct 06, 2001
... C) it stops fusing hydrogen in its core and starts to expand. D) it forms planets. ...
... C) it stops fusing hydrogen in its core and starts to expand. D) it forms planets. ...
Exercise 7
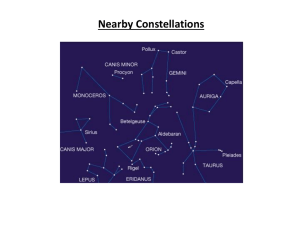
... declination (think of this as a space latitude). The declination runs from -90° (celestial south pole) to +90° (celestial north pole). Both of these coordinates are laminated to the metal pole bases. In addition, the stars have been colored according to their spectral classes; blue balls represent O ...
... declination (think of this as a space latitude). The declination runs from -90° (celestial south pole) to +90° (celestial north pole). Both of these coordinates are laminated to the metal pole bases. In addition, the stars have been colored according to their spectral classes; blue balls represent O ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.