Document
... J0108-1431 (J0108 for short), located only 770 light years from us. The elongated object immediately to its upper right is a background galaxy that is unrelated to the pulsar. Since J0108 is located a long way from the plane of our galaxy, many distant galaxies are visible in the larger-scale optica ...
... J0108-1431 (J0108 for short), located only 770 light years from us. The elongated object immediately to its upper right is a background galaxy that is unrelated to the pulsar. Since J0108 is located a long way from the plane of our galaxy, many distant galaxies are visible in the larger-scale optica ...
Star formation - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... • Stars are “born” when the core gets hot enough to begin nuclear fusion. • When fusion begins, its outward push generates enough pressure to stop gravitational contraction of the forming star and its size stabilizes. This is called hydrostatic equilibrium. • This balance of fusion vs. gravitational ...
... • Stars are “born” when the core gets hot enough to begin nuclear fusion. • When fusion begins, its outward push generates enough pressure to stop gravitational contraction of the forming star and its size stabilizes. This is called hydrostatic equilibrium. • This balance of fusion vs. gravitational ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... Cataclysmics, also known as dwarf novae, are binary stars in close orbit about one another. One of them is Sunlike, the other a compact white dwarf star with an appetite. Their embrace is so tight — 100,000 miles for SS Cygni according to some estimates — that the dwarf's powerful gravity strips mat ...
... Cataclysmics, also known as dwarf novae, are binary stars in close orbit about one another. One of them is Sunlike, the other a compact white dwarf star with an appetite. Their embrace is so tight — 100,000 miles for SS Cygni according to some estimates — that the dwarf's powerful gravity strips mat ...
the stars - Uni Heidelberg
... Stars have different colors and luminosities. Following this tutorial we will learn what star luminosity and color are, and which information about stellar evolution we can obtain from them. 2 Stars: magnitude and color Looking at the sky with naked eye most stars appear of the same color. We see st ...
... Stars have different colors and luminosities. Following this tutorial we will learn what star luminosity and color are, and which information about stellar evolution we can obtain from them. 2 Stars: magnitude and color Looking at the sky with naked eye most stars appear of the same color. We see st ...
A Study of the Spectroscopic Variability of Select RV Tauri... Charles Kurgatt , Donald K. Walter , Steve Howell
... RV Tauri and Semi-Regular stars are examples of variable stars, a star that is unable to maintain a steady apparent brightness. These changes in brightness may have many causes such as eclipses, stellar rotation, and pulsation. The two types studied here vary in brightness due to pulsations in the p ...
... RV Tauri and Semi-Regular stars are examples of variable stars, a star that is unable to maintain a steady apparent brightness. These changes in brightness may have many causes such as eclipses, stellar rotation, and pulsation. The two types studied here vary in brightness due to pulsations in the p ...
THE STARS G. Iafrate(a), M. Ramella(a) and V. Bologna(b) (a) INAF
... Stars have different colors and luminosities. Following this tutorial we will learn what star luminosity and color are, and which information about stellar evolution we can obtain from them. 2 Stars: magnitude and color Looking at the sky with naked eye most stars appear of the same color. We see st ...
... Stars have different colors and luminosities. Following this tutorial we will learn what star luminosity and color are, and which information about stellar evolution we can obtain from them. 2 Stars: magnitude and color Looking at the sky with naked eye most stars appear of the same color. We see st ...
Unit 1: The Big Picture
... which are – visible in the Southern Hemisphere – Look like clouds detached from Milky Way – Believed to be pulling apart due to gravitational pull from Milky Way ...
... which are – visible in the Southern Hemisphere – Look like clouds detached from Milky Way – Believed to be pulling apart due to gravitational pull from Milky Way ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... Barnard’s star is now at 5.9 ly, we would have to move it to 5.9/3.981 = 1.48 ly. Barnard’s star is actually moving towards us at 107 km/s, and in about 10,000 years it will pass within 3.8 ly of us; after that its distance will increase again. When it is 3.8 ly away it will be the nearest star. Wil ...
... Barnard’s star is now at 5.9 ly, we would have to move it to 5.9/3.981 = 1.48 ly. Barnard’s star is actually moving towards us at 107 km/s, and in about 10,000 years it will pass within 3.8 ly of us; after that its distance will increase again. When it is 3.8 ly away it will be the nearest star. Wil ...
Wien`s Law and Temperature
... 5. Now add another curve for the 3,500 K star. How does this new curve compare to the others? What does this tell you about the energy production in stars? (This is related to the area under the curve) Notice that a blue star with a peak wavelength in the UV is much less luminous in the red, but is ...
... 5. Now add another curve for the 3,500 K star. How does this new curve compare to the others? What does this tell you about the energy production in stars? (This is related to the area under the curve) Notice that a blue star with a peak wavelength in the UV is much less luminous in the red, but is ...
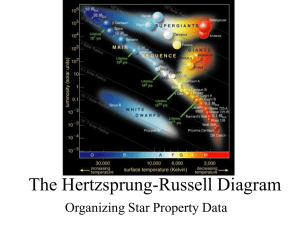
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
five minute episode script
... DISTINCTIVE BELT OF THREE STARS. IF YOU LOOK A LITTLE CLOSER YOU'LL SEE STARS OF DIFFERENT BRIGHTNESS AND COLOR. DEAN: STAR COLOR IS AN INDICATION OF ITS TEMPERATURE - BLUE STARS BEING THE HOTTEST AND RED STARS BEING THE COLDEST. YOU CAN REALLY SEE THE COLORS OF THE BRIGHTEST STARS LIKE THOSE IN ORI ...
... DISTINCTIVE BELT OF THREE STARS. IF YOU LOOK A LITTLE CLOSER YOU'LL SEE STARS OF DIFFERENT BRIGHTNESS AND COLOR. DEAN: STAR COLOR IS AN INDICATION OF ITS TEMPERATURE - BLUE STARS BEING THE HOTTEST AND RED STARS BEING THE COLDEST. YOU CAN REALLY SEE THE COLORS OF THE BRIGHTEST STARS LIKE THOSE IN ORI ...
Lecture 9
... • Brightest stars have luminosities 1 million times that of the Sun • Dim stars are a lot more common than bright stars ...
... • Brightest stars have luminosities 1 million times that of the Sun • Dim stars are a lot more common than bright stars ...
Astronomy Notes: Deep Space
... Becomes either white dwarf, neutron star or black hole, depending on how much mass it had. http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/navigation/chapter28.cfm ...
... Becomes either white dwarf, neutron star or black hole, depending on how much mass it had. http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/navigation/chapter28.cfm ...
Candles in the Dark
... that the Milky Way was the whole Universe, so M31 was presumably a relatively small and nearby object. Hubble calculated from the variation of his Andromeda Cepheid how far away it was and came up with the answer of more than 900 000 light years (better modern measurements give the accepted figure o ...
... that the Milky Way was the whole Universe, so M31 was presumably a relatively small and nearby object. Hubble calculated from the variation of his Andromeda Cepheid how far away it was and came up with the answer of more than 900 000 light years (better modern measurements give the accepted figure o ...
Final Exam: Chs 4-5, 12-17
... d. electrons inside a star resist being pushed closer together than a certain limit. ____ 50. What causes the core of a high-mass star to collapse? a. An excess of hydrogen atoms causes an explosion that crushes the star’s core. b. When the iron core becomes sufficiently massive, the electrons merge ...
... d. electrons inside a star resist being pushed closer together than a certain limit. ____ 50. What causes the core of a high-mass star to collapse? a. An excess of hydrogen atoms causes an explosion that crushes the star’s core. b. When the iron core becomes sufficiently massive, the electrons merge ...
Ch2a
... The Elevation of the North Pole Star The north pole star is always at an elevation, or altitude, a, above the northern horizon, that is equal to the latitude, of the observer. Circumpolar stars are stars which are always in view. They never set below the horizon. All stars with declinations ...
... The Elevation of the North Pole Star The north pole star is always at an elevation, or altitude, a, above the northern horizon, that is equal to the latitude, of the observer. Circumpolar stars are stars which are always in view. They never set below the horizon. All stars with declinations ...
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tra ...
... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tra ...
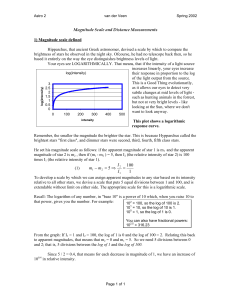
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... Hipparchus, that ancient Greek astronomer, devised a scale by which to compare the brightness of stars he observed in the night sky. Ofcourse, he had no telescope back then, so he based it entirely on the way the eye distinguishes brightness levels of light. Your eyes see LOGARITHMICALLY. That means ...
... Hipparchus, that ancient Greek astronomer, devised a scale by which to compare the brightness of stars he observed in the night sky. Ofcourse, he had no telescope back then, so he based it entirely on the way the eye distinguishes brightness levels of light. Your eyes see LOGARITHMICALLY. That means ...
Space ppt
... Types of Galaxies • Galaxies are classified by their shape. • Developed by Edwin Hubble • 3 Types of Galaxies – A. Spiral – B. Elliptical – C. Irregular ...
... Types of Galaxies • Galaxies are classified by their shape. • Developed by Edwin Hubble • 3 Types of Galaxies – A. Spiral – B. Elliptical – C. Irregular ...
The Transfer Equation
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.