Black Holes, Part 9, Star Eaters
... emission spectrum would be shifted upwards into the high-energy bands, way past the UV band, into the hard-x-rays band. The extreme energy emission takes the resulting spectrum far outside the visible band. ...
... emission spectrum would be shifted upwards into the high-energy bands, way past the UV band, into the hard-x-rays band. The extreme energy emission takes the resulting spectrum far outside the visible band. ...
Formation of Stars
... UV and optical radiation. At the end of stage 2, the fragments are ~100 times the size of the solar system. Stage 3: The cloud fragment develops a hot core - from 100 K to 104 K. The gas density increases much faster in the core than at the surface. A photosphere develops. Size is about the size o ...
... UV and optical radiation. At the end of stage 2, the fragments are ~100 times the size of the solar system. Stage 3: The cloud fragment develops a hot core - from 100 K to 104 K. The gas density increases much faster in the core than at the surface. A photosphere develops. Size is about the size o ...
The Ultraluminous X-ray Source in Holmberg IX and its Environment
... mass black holes (IMBHs) having 102 to 105 solar masses (Colbert & Mushotzky 1999) or non-isotropic emission beamed into our line-of-sight (King et al. 2001). Here, we are interested in one of these objects, Holmberg IX X-1, located at a distance of 3.6 Mpc in a dwarf galaxy companion of M81. Miller ...
... mass black holes (IMBHs) having 102 to 105 solar masses (Colbert & Mushotzky 1999) or non-isotropic emission beamed into our line-of-sight (King et al. 2001). Here, we are interested in one of these objects, Holmberg IX X-1, located at a distance of 3.6 Mpc in a dwarf galaxy companion of M81. Miller ...
intergalactic move
... to cross from one side to the other. It is shaped like a whirlpool: it has bands of stars that spiral around the centre, which astronomers call the Galaxy’s ‘arms’. We live in the outer parts of the Milky Way, in one of these arms. This is a quiet part of our Galaxy, where even the closest stars liv ...
... to cross from one side to the other. It is shaped like a whirlpool: it has bands of stars that spiral around the centre, which astronomers call the Galaxy’s ‘arms’. We live in the outer parts of the Milky Way, in one of these arms. This is a quiet part of our Galaxy, where even the closest stars liv ...
Islip Invitational 2013 Astronomy Examination Student
... 9. Spectra from neutral atoms compared with spectra from ionized atoms of the same element a. Are slightly blueshifted. b. Are the same. c. Are slightly redshifted. d. Have different sets of spectral lines. e. Have the same sets of spectral lines but different widths for those lines. 10. Suppose you ...
... 9. Spectra from neutral atoms compared with spectra from ionized atoms of the same element a. Are slightly blueshifted. b. Are the same. c. Are slightly redshifted. d. Have different sets of spectral lines. e. Have the same sets of spectral lines but different widths for those lines. 10. Suppose you ...
How Stars and Planets are Born
... • How does rotation and revolution happen? • Everything is in motion • Random directions of motion get averaged out ...
... • How does rotation and revolution happen? • Everything is in motion • Random directions of motion get averaged out ...
A Dart Board for the Bored An eye opening offer from the editors of
... Pole. Because of this, it can be seen all night an all year round. The two brightest stars of Cassiopeia point to Alderamin, the brightest star in Cepheus. Although the Milky Way runs slightly through Cepheus, it contains no Messier objects or other interesting deep sky objects. A star cluster and f ...
... Pole. Because of this, it can be seen all night an all year round. The two brightest stars of Cassiopeia point to Alderamin, the brightest star in Cepheus. Although the Milky Way runs slightly through Cepheus, it contains no Messier objects or other interesting deep sky objects. A star cluster and f ...
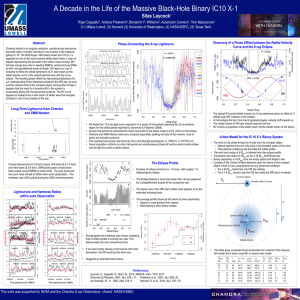
A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
Mirrored Image Sep06.pub - High Desert Astronomical Society
... west of Cebalrai (Beta Ophiuchi) near coordinates (17:57:48.5 +04:41:36.2, ICRS 2000.0). The star was named after its discoverer, noted astronomer Edward Emerson Barnard (1857-1923), who found in 1916 that the star has the largest known proper motion of all known stars (10.3 arcseconds per year). Th ...
... west of Cebalrai (Beta Ophiuchi) near coordinates (17:57:48.5 +04:41:36.2, ICRS 2000.0). The star was named after its discoverer, noted astronomer Edward Emerson Barnard (1857-1923), who found in 1916 that the star has the largest known proper motion of all known stars (10.3 arcseconds per year). Th ...
The Stars: Distance, Luminosity, Size
... The more massive a Main Sequence star is, the hotter (bluer), and more luminous. The Main Sequence is a mass sequence! ...
... The more massive a Main Sequence star is, the hotter (bluer), and more luminous. The Main Sequence is a mass sequence! ...
10438 starlight - The Described and Captioned Media Program
... patterns and differences among the stars. Why do they think some are brighter? Does it have to do with size? Distance? How do stars form? How do they die? Tell students that the program they are about to watch considers the many different things that scientists know about stars and how they gained t ...
... patterns and differences among the stars. Why do they think some are brighter? Does it have to do with size? Distance? How do stars form? How do they die? Tell students that the program they are about to watch considers the many different things that scientists know about stars and how they gained t ...
chapter9
... dust cloud; star light is reflected by the dust; reflection nebula appears blue because blue light is scattered by larger angles than red light; Same phenomenon makes the day sky appear blue (if it’s not cloudy). ...
... dust cloud; star light is reflected by the dust; reflection nebula appears blue because blue light is scattered by larger angles than red light; Same phenomenon makes the day sky appear blue (if it’s not cloudy). ...
a2Lec115
... Use mks system: length=meter, mass =kgm, time=sec Astronomical Unit (AU): Distance from the earth to the sun = semi-major axis of the orbit of Earth around Sun 1 AU = d(sun) = 1.5 x 1011 m Parsec (PC): Distance at which 1 AU subtends Angle of 1 second 1 pc (parsec) = 206625 AU = 3.086 x 1016 m = 3.2 ...
... Use mks system: length=meter, mass =kgm, time=sec Astronomical Unit (AU): Distance from the earth to the sun = semi-major axis of the orbit of Earth around Sun 1 AU = d(sun) = 1.5 x 1011 m Parsec (PC): Distance at which 1 AU subtends Angle of 1 second 1 pc (parsec) = 206625 AU = 3.086 x 1016 m = 3.2 ...
Life Histories Stars
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
2009_ASU_Exam
... closer to both stars, which star will appear brighter from the new observation point? 14) Star P is a pulsating variable star. As it pulses, the apparent magnitude of Star P changes by 5 magnitudes. Assuming that its temperature remains constant as it pulses, what is the ratio of Star P’s maximum an ...
... closer to both stars, which star will appear brighter from the new observation point? 14) Star P is a pulsating variable star. As it pulses, the apparent magnitude of Star P changes by 5 magnitudes. Assuming that its temperature remains constant as it pulses, what is the ratio of Star P’s maximum an ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... The Exploratorium grants reprint permission of this material for noncommercial, educational use only. Copyright notice must be included on all reprints. Requests for electronic or other uses should be directed to
...
... The Exploratorium grants reprint permission of this material for noncommercial, educational use only. Copyright notice must be included on all reprints. Requests for electronic or other uses should be directed to
SkyMatters Jan-2017 - CIT Blackrock Castle Observatory
... eye on in January The constellation of Taurus is easy to find using the stars in Orion’s belt. A line from the belt brings you to the bright, red star Algol that is part of a V of stars called the Hyades. Most of the stars in the Hyades are young— about 650 million years old—and this type of configu ...
... eye on in January The constellation of Taurus is easy to find using the stars in Orion’s belt. A line from the belt brings you to the bright, red star Algol that is part of a V of stars called the Hyades. Most of the stars in the Hyades are young— about 650 million years old—and this type of configu ...
10 relativity, black holes_
... Depends on the gravity between you and the object you want to escape! For a black hole, the escape velocity (inside the event horizon) is greater than the speed of light! ...
... Depends on the gravity between you and the object you want to escape! For a black hole, the escape velocity (inside the event horizon) is greater than the speed of light! ...
Science 1 (MillinerSci1)
... B. because the larger stars are a further distance away C. because the larger planets are a further distance away D. because the smaller planets are at a further distance away ...
... B. because the larger stars are a further distance away C. because the larger planets are a further distance away D. because the smaller planets are at a further distance away ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.