Test 1 - Brock physics
... (d) dark, because they contain a significant amount of dark matter that can be detected using CCDs attached to radio telescopes. 7. Giant molecular clouds are relatively cool because (a) they are in cooler parts of the galaxy. (b) they have high solar-type winds, which cool them effectively, much li ...
... (d) dark, because they contain a significant amount of dark matter that can be detected using CCDs attached to radio telescopes. 7. Giant molecular clouds are relatively cool because (a) they are in cooler parts of the galaxy. (b) they have high solar-type winds, which cool them effectively, much li ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... But interstellar molecular clouds are enormous, often containing up to a million solar masses of gas (and 1% dust--it is just part of the ISM. That is a lot of self-gravity! The most massive clouds have gravity that can overcome the thermal pressure trying to resist gravity, and the cloud must colla ...
... But interstellar molecular clouds are enormous, often containing up to a million solar masses of gas (and 1% dust--it is just part of the ISM. That is a lot of self-gravity! The most massive clouds have gravity that can overcome the thermal pressure trying to resist gravity, and the cloud must colla ...
Lecture 9: Stellar Spectra
... Lines get broader as the pressure increases. Larger stars are puffier, which means lower pressure, so that Larger Stars have Narrower Lines Since larger stars are brighter at a given temperature, this measures relative stellar luminosity for stars of the same temperature. See Figure 19-15 ...
... Lines get broader as the pressure increases. Larger stars are puffier, which means lower pressure, so that Larger Stars have Narrower Lines Since larger stars are brighter at a given temperature, this measures relative stellar luminosity for stars of the same temperature. See Figure 19-15 ...
New meteor shower could light up night sky May 23 –... May 22, 2014 Doug Duncan
... director of CU- Boulder’s Fiske Planetarium, excited to see how many meteors will streak across the night sky. CUT 1 “In my whole life I have never seen a new meteor shower. We have the old, dependable meteor shows. Every August 11 and 12, for instance, we get the Perseid Meteor Shower. And now, all ...
... director of CU- Boulder’s Fiske Planetarium, excited to see how many meteors will streak across the night sky. CUT 1 “In my whole life I have never seen a new meteor shower. We have the old, dependable meteor shows. Every August 11 and 12, for instance, we get the Perseid Meteor Shower. And now, all ...
PRE-LAB
... Well, you could specify the position of a star in terms of ALTITUDE and AZIMUTH. However, this is messy because ALTITUDE and AZIMUTH change throughout the night. Also, they depend on your position , (i.e., your HORIZON and your latitude) on the EARTH. Clearly, we need a better method to describe the ...
... Well, you could specify the position of a star in terms of ALTITUDE and AZIMUTH. However, this is messy because ALTITUDE and AZIMUTH change throughout the night. Also, they depend on your position , (i.e., your HORIZON and your latitude) on the EARTH. Clearly, we need a better method to describe the ...
Star Evolution
... Red dwarfs: the small, faint, end of the main sequence stars White dwarfs: remnants of star with less than 8 solar masses Black dwarfs: White dwarfs that have cooled to invisibility Brown dwarfs: less than 0.08Msun=80 Jupiters; never burn Hydrogen Planets are less massive than 13 Jupiters & cannot b ...
... Red dwarfs: the small, faint, end of the main sequence stars White dwarfs: remnants of star with less than 8 solar masses Black dwarfs: White dwarfs that have cooled to invisibility Brown dwarfs: less than 0.08Msun=80 Jupiters; never burn Hydrogen Planets are less massive than 13 Jupiters & cannot b ...
Lecture 11
... • An alternative unit of astronomical distance is the Light Year (ly). • 1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year. • 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: – 0.31 pc ...
... • An alternative unit of astronomical distance is the Light Year (ly). • 1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year. • 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: – 0.31 pc ...
charts_set_8
... RS for a 3 MSun object is 9 km. Event horizon: imaginary sphere around object, with radius RS . Event horizon ...
... RS for a 3 MSun object is 9 km. Event horizon: imaginary sphere around object, with radius RS . Event horizon ...
Chapter 5 Galaxies and Star Systems
... Galaxy. One orbit of the solar system takes about 225 to 250 million years at a speed of half a million miles per hour. The solar system has orbited 20 to 25 times since it formed 4.6 billion years ago. The center of our galaxy is located about 28,000 light-years away, beyond the constellation Sagi ...
... Galaxy. One orbit of the solar system takes about 225 to 250 million years at a speed of half a million miles per hour. The solar system has orbited 20 to 25 times since it formed 4.6 billion years ago. The center of our galaxy is located about 28,000 light-years away, beyond the constellation Sagi ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... young stars are nearly spherical. New stars are created when knots of dust and gas collapse. In the nebula, however, this process stopped when the young central stars reached their full power. The radiation they produce is so strong that it prevents new stars from forming. ...
... young stars are nearly spherical. New stars are created when knots of dust and gas collapse. In the nebula, however, this process stopped when the young central stars reached their full power. The radiation they produce is so strong that it prevents new stars from forming. ...
Quantum Well Electron Gain Structures and Infrared
... Mercury/Venus too hot Earth – just right Mars – was OK once (?), but now cold Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune too cold (though some moons may be OK) ...
... Mercury/Venus too hot Earth – just right Mars – was OK once (?), but now cold Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune too cold (though some moons may be OK) ...
Naked Eye, Binocular, or Small Backyard Telescope Night Sky
... Basic Scientific Content Information about what you can see in the night sky with your naked eye, binoculars, or a small telescope: 1.) The Moon – The Moon is the only natural satelli ...
... Basic Scientific Content Information about what you can see in the night sky with your naked eye, binoculars, or a small telescope: 1.) The Moon – The Moon is the only natural satelli ...
Astronomy
... 14. Which particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? A) Protons (only) B) Neutrons (only) C) Protons and neutrons, but not electrons D) Protons, neutrons, and electrons, but not neutrinos E) Protons, neutrons, electrons, and neutrinos 15. Why is the helium burning stage of a star so much shorter ...
... 14. Which particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? A) Protons (only) B) Neutrons (only) C) Protons and neutrons, but not electrons D) Protons, neutrons, and electrons, but not neutrinos E) Protons, neutrons, electrons, and neutrinos 15. Why is the helium burning stage of a star so much shorter ...
Groups of Stars
... amounts of gas and dust to form new stars. They are spherical and have a dense concentration of stars in the center. Can contain more than a million stars. Usually do not have short-lived blue stars because these stars have already died ...
... amounts of gas and dust to form new stars. They are spherical and have a dense concentration of stars in the center. Can contain more than a million stars. Usually do not have short-lived blue stars because these stars have already died ...
Chapter 8 powerpoint presentation
... How many of the H atoms are in each of the excitation levels, n=1, n=2, etc, described by the Boltzmann equation and secondly, how many of the H atoms are completely ionized, for if the H atoms are ionized they can not produce any absorption lines. This is described by the Saha equation. ...
... How many of the H atoms are in each of the excitation levels, n=1, n=2, etc, described by the Boltzmann equation and secondly, how many of the H atoms are completely ionized, for if the H atoms are ionized they can not produce any absorption lines. This is described by the Saha equation. ...
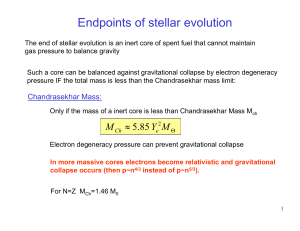
Hot-plate model of stars Test 2 & grades • Public viewing sessions
... surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. ...
... surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. ...
THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... point on this dome right above our head is known as zenith. The lower boundary of this dome is the horizon. As the surface is 2-dimensional, to specify the position of any star on this dome we need two coordinates. We usually use a spherical polar coordinate system and ignore ‘r’. One system is the ...
... point on this dome right above our head is known as zenith. The lower boundary of this dome is the horizon. As the surface is 2-dimensional, to specify the position of any star on this dome we need two coordinates. We usually use a spherical polar coordinate system and ignore ‘r’. One system is the ...
Sermon Notes
... bringing destruction to anything that is in his way. It is a picture of Christ bringing destruction to the wicked in His judgment. We only see the front half of the bull and he seems to be coming out of Aries – The Lamb/or Ram. We see the Lamb giving rise to the Bull that comes forth in judgment. Th ...
... bringing destruction to anything that is in his way. It is a picture of Christ bringing destruction to the wicked in His judgment. We only see the front half of the bull and he seems to be coming out of Aries – The Lamb/or Ram. We see the Lamb giving rise to the Bull that comes forth in judgment. Th ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.