starevolution - Global Change Program
... Heavier stars evolve into supergiants, and it is the nuclear reactions in the interiors of these stars that gave rise to the heavy elements in the universe. Such massive stars start by burning hydrogen into helium in the core, then helium to carbon, and then carbon to heavier elements, all the way u ...
... Heavier stars evolve into supergiants, and it is the nuclear reactions in the interiors of these stars that gave rise to the heavy elements in the universe. Such massive stars start by burning hydrogen into helium in the core, then helium to carbon, and then carbon to heavier elements, all the way u ...
Astronomy 112: Physics of Stars Problem set 1 solutions 1
... that will lie along our line of sight? We will call these v1,LOS and v2,LOS . You may neglect the constant offset to v1,LOS and v2,LOS that comes from the motion of the binary’s center of mass relative to Earth. Solution: This is just vector geometry. If the magnitude of the velocity vector for star ...
... that will lie along our line of sight? We will call these v1,LOS and v2,LOS . You may neglect the constant offset to v1,LOS and v2,LOS that comes from the motion of the binary’s center of mass relative to Earth. Solution: This is just vector geometry. If the magnitude of the velocity vector for star ...
Comets, asteroids, and meteors oh my!
... • Chunks of ice and dust whose orbits are usually very long, narrow ellipses. – Ellipses are elongated narrow circles – Think of it as a squashed oval. • About the size of a mountain, so rather large • We don’t see them very often. • Comet in Greek means “long-haired star” ...
... • Chunks of ice and dust whose orbits are usually very long, narrow ellipses. – Ellipses are elongated narrow circles – Think of it as a squashed oval. • About the size of a mountain, so rather large • We don’t see them very often. • Comet in Greek means “long-haired star” ...
Red Giants - Faculty Web Pages
... Those two groups are not the same! The nearby stars in the sky are mostly dim Type-M stars. The bright stars in the sky, on the other hand, tend to be Type O, B or A stars, with a few Type-M stars tossed in for good measure. Today we'll be focusing on those few Type-M stars that are amongst the brig ...
... Those two groups are not the same! The nearby stars in the sky are mostly dim Type-M stars. The bright stars in the sky, on the other hand, tend to be Type O, B or A stars, with a few Type-M stars tossed in for good measure. Today we'll be focusing on those few Type-M stars that are amongst the brig ...
lecture22
... •Life time of a star is determined by its mass. •Nature makes more low-mass stars than highmass stars. Low-mass stars also live longer. That is why there are a lot more low-mass stars. What happens after the main sequence (when hydrogen in the core runs out)? ...
... •Life time of a star is determined by its mass. •Nature makes more low-mass stars than highmass stars. Low-mass stars also live longer. That is why there are a lot more low-mass stars. What happens after the main sequence (when hydrogen in the core runs out)? ...
Astronomy Club of Asheville June 2016 Sky Events
... June 2016 Sky Events – the Planets June 2016 provides 3 planets that will brighten the early evening skies. Jupiter will dominate the southwest while Mars and Saturn will reign in the southeast. Against the background of the constellation Leo, Jupiter is best viewed this month well before midnig ...
... June 2016 Sky Events – the Planets June 2016 provides 3 planets that will brighten the early evening skies. Jupiter will dominate the southwest while Mars and Saturn will reign in the southeast. Against the background of the constellation Leo, Jupiter is best viewed this month well before midnig ...
AmiraPoster3
... where a is the separation of the centres of mass of the two stars, qe is the eclipse half angle and b is the ratio of radius of the optical companion to that of its Roche-lobe, RL. ...
... where a is the separation of the centres of mass of the two stars, qe is the eclipse half angle and b is the ratio of radius of the optical companion to that of its Roche-lobe, RL. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... they imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and ...
... they imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and ...
Black Hole
... You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. In 1974, J. H. Taylor and R. Hulse (Princeton University) discovered a 0.059 s pulsa ...
... You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. In 1974, J. H. Taylor and R. Hulse (Princeton University) discovered a 0.059 s pulsa ...
Document
... Horizontal branch stars toward the blue end have relatively thin hydrogen shells.The envelopes are radiative. These stars undergo a dynamical instability causing pulsations over periods of a few hours. They are known as RR Lyrae variables. Intermediate mass helium burning stars may also undergo puls ...
... Horizontal branch stars toward the blue end have relatively thin hydrogen shells.The envelopes are radiative. These stars undergo a dynamical instability causing pulsations over periods of a few hours. They are known as RR Lyrae variables. Intermediate mass helium burning stars may also undergo puls ...
Lecture 15: The Main Sequence
... High-Mass M-S stars have short M-S lifetimes Low-Mass M-S stars have long M-S lifetimes More massive main-sequence stars need higher pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse. Higher pressure=higher temperatures. The higher temperatures lead to greater rates of nuclear fusion wh ...
... High-Mass M-S stars have short M-S lifetimes Low-Mass M-S stars have long M-S lifetimes More massive main-sequence stars need higher pressures to support themselves against gravitational collapse. Higher pressure=higher temperatures. The higher temperatures lead to greater rates of nuclear fusion wh ...
File
... this is why they appear red to our eyes. This color is also seen in red giant stars which are larger in size and they are still colder. Station 3: Blue (Sirius & Vega) ...
... this is why they appear red to our eyes. This color is also seen in red giant stars which are larger in size and they are still colder. Station 3: Blue (Sirius & Vega) ...
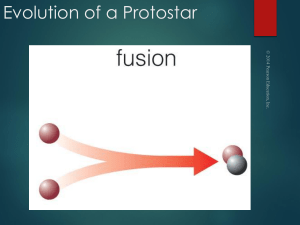
Evolution of a Protostar
... Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation. ...
... Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation. ...
Celestial Distances
... In contrast, most stars are constant in their luminosity (at least within a percent or two) ...
... In contrast, most stars are constant in their luminosity (at least within a percent or two) ...
STAAR Science Tutorial 35 TEK 8.8B: The Sun
... Sun) is Proxima Centauri, which is about 4.2 light years away from Earth. This is 263,000 times further away from Earth than our Sun. (Our Sun is 0.000016 lightyears away from Earth.) While there are 11 stars within 10 light-years of Earth, most of the other stars visible in the night sky are many t ...
... Sun) is Proxima Centauri, which is about 4.2 light years away from Earth. This is 263,000 times further away from Earth than our Sun. (Our Sun is 0.000016 lightyears away from Earth.) While there are 11 stars within 10 light-years of Earth, most of the other stars visible in the night sky are many t ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
Chapter 12 - Indiana State University
... the main sequence • Generally, 90% of a group of stars will be on the main sequence; however, a few stars will be cool but very luminous (upper right part of H-R diagram), while others will be hot and dim (lower left part of H-R ...
... the main sequence • Generally, 90% of a group of stars will be on the main sequence; however, a few stars will be cool but very luminous (upper right part of H-R diagram), while others will be hot and dim (lower left part of H-R ...
Star Fromation and ISM
... The Formation of Stars Like the Sun At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain ...
... The Formation of Stars Like the Sun At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain ...
Astronomy Webquest Part 1: Life of Stars: Go to http://www.odec.ca
... 6. What type of stars can become a white dwarf and eventually a black dwarf? __________________________________________ The Death of Massive Stars 7. For a massive star, it starts by burning ______________ & ______________. Helium atoms fuse to form _____________ & _____________. Carbon then fuses t ...
... 6. What type of stars can become a white dwarf and eventually a black dwarf? __________________________________________ The Death of Massive Stars 7. For a massive star, it starts by burning ______________ & ______________. Helium atoms fuse to form _____________ & _____________. Carbon then fuses t ...
Astronomy Worksheet
... *In general a hot star’s spectrum looks smoother than a cooler star’s spectrum. *In very hot stars (> 10,000 K) most of the Hydrogen gas in the star’s atmosphere will be ionized. Since an ionized Hydrogen atom has no electron it cannot produce any spectral lines, thus the Hydrogen lines are weak in ...
... *In general a hot star’s spectrum looks smoother than a cooler star’s spectrum. *In very hot stars (> 10,000 K) most of the Hydrogen gas in the star’s atmosphere will be ionized. Since an ionized Hydrogen atom has no electron it cannot produce any spectral lines, thus the Hydrogen lines are weak in ...
Astronomy Merit Badge Workshop
... Using a Star Finder (also called a Planisphere), go outside on a clear night, set the correct time and date, and orient yourself so that you and the Star Finder are aligned to true north.* The visible field in your Star Finder should roughly correspond to what you see in the night sky. Pick out 10 c ...
... Using a Star Finder (also called a Planisphere), go outside on a clear night, set the correct time and date, and orient yourself so that you and the Star Finder are aligned to true north.* The visible field in your Star Finder should roughly correspond to what you see in the night sky. Pick out 10 c ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.