Ch 28 Class Notes
... Thus, distance from Earth no longer becomes a factor in how bright a star is. Remember, very bright stars that are very far from Earth may appear to be very faint to us. For example: Since our sun is so close to Earth, it has an apparent magnitude of –26.7. However, the sun has an absolute magnitude ...
... Thus, distance from Earth no longer becomes a factor in how bright a star is. Remember, very bright stars that are very far from Earth may appear to be very faint to us. For example: Since our sun is so close to Earth, it has an apparent magnitude of –26.7. However, the sun has an absolute magnitude ...
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars and Galaxies
... The Magnitude System Ptolemy Broke Stars into 5 magnitude groups m=1 the brightest, m=5 the faintest In 1700’s it was found this was a logarithmic scale, as that is how the naked eye responds. Also, faintest were about 100x fainter than brightest. Break the factor of 100 into 5 equal factors: Start ...
... The Magnitude System Ptolemy Broke Stars into 5 magnitude groups m=1 the brightest, m=5 the faintest In 1700’s it was found this was a logarithmic scale, as that is how the naked eye responds. Also, faintest were about 100x fainter than brightest. Break the factor of 100 into 5 equal factors: Start ...
Stars - Academic Computer Center
... • Binary stars provide a means of determining the masses of stars. • Other properties can also sometimes be determined from binary stars. ...
... • Binary stars provide a means of determining the masses of stars. • Other properties can also sometimes be determined from binary stars. ...
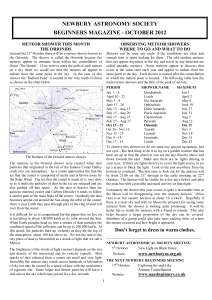
October 2012 - astronomy for beginners
... overhead is Deneb the brightest star in the constellation of Cygnus (the Swan). Look towards the west (right) about the width of your two clenched fists when held up at arm’s length. You will see another bright star this is Vega the brightest star in the constellation of Lyra (the Lyre). From these ...
... overhead is Deneb the brightest star in the constellation of Cygnus (the Swan). Look towards the west (right) about the width of your two clenched fists when held up at arm’s length. You will see another bright star this is Vega the brightest star in the constellation of Lyra (the Lyre). From these ...
Document
... • The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime. – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity. • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars.. • High-ma ...
... • The length of time a star spends fusing hydrogen into helium is called its main sequence lifetime. – Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence. – Lifetime depends on the star’s mass and luminosity. • More luminous stars burn their energy more rapidly than less luminous stars.. • High-ma ...
Stellar Evolution Simulation
... In this activity, you will be tracing the lifecycle of several different types of stars. First, go onto http://www.planetseed.com/laboratory/virtual-experiment-build-your-own-star. You will want to keep this website open as it lists some terms that you might not be familiar with. Read through the pa ...
... In this activity, you will be tracing the lifecycle of several different types of stars. First, go onto http://www.planetseed.com/laboratory/virtual-experiment-build-your-own-star. You will want to keep this website open as it lists some terms that you might not be familiar with. Read through the pa ...
Newfoundland Sky in Summer
... room than in a dark one. The sun itself i s a star. Other stars are bigger and brighter than the sun but are much fainter because they are so far away. Some stars look brighter than others, but these are not necessarily the biggest, and many of the largest stars cannot be seen at all. One of the lar ...
... room than in a dark one. The sun itself i s a star. Other stars are bigger and brighter than the sun but are much fainter because they are so far away. Some stars look brighter than others, but these are not necessarily the biggest, and many of the largest stars cannot be seen at all. One of the lar ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... as determined from the table in the text’s appendix. Thus, Alpha Centauri A is slightly larger than the Sun with a diameter of 1.23 solar diameters. Alpha Centauri B is (60/85) = 0.706 times smaller than Alpha Centauri A. based on the ratio of their angular sizes (and the fact that they are at the s ...
... as determined from the table in the text’s appendix. Thus, Alpha Centauri A is slightly larger than the Sun with a diameter of 1.23 solar diameters. Alpha Centauri B is (60/85) = 0.706 times smaller than Alpha Centauri A. based on the ratio of their angular sizes (and the fact that they are at the s ...
AJAstroProject
... million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec exposure through the V-filter. ...
... million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec exposure through the V-filter. ...
Neutron Star - Perry Local Schools
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
November 2005 - Otterbein University
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Hall Scorpius constellation (11) Jacob Hall Physics 1040, sec 002
... is the same color as the planet Mars. Antares is a red supergiant with a radius about 800 times that of the Sun. It is classified as a variable star; its apparent magnitude varies between 0.9 and 1.8. It has a hot blue companion star about 2.9 arcseconds away. (2) Antares is the 16th brightest star ...
... is the same color as the planet Mars. Antares is a red supergiant with a radius about 800 times that of the Sun. It is classified as a variable star; its apparent magnitude varies between 0.9 and 1.8. It has a hot blue companion star about 2.9 arcseconds away. (2) Antares is the 16th brightest star ...
Name:
... around 8:00 p.m. in early January, at 7:00 p.m. in late January, and at 6:00 p.m. in early February. Use the map within one hour of these prescribed times to find constellations and bright stars in the outdoor nighttime sky. Look carefully at the sky map. The outer circle represents the horizon. Alo ...
... around 8:00 p.m. in early January, at 7:00 p.m. in late January, and at 6:00 p.m. in early February. Use the map within one hour of these prescribed times to find constellations and bright stars in the outdoor nighttime sky. Look carefully at the sky map. The outer circle represents the horizon. Alo ...
Properties of Supernovae
... The student will use CCD images of the Crab Nebula, a Hubble Space Telescope image of SN1987a, and a CCD image of supernova 1993j to examine a number of characteristics of supernovae and their remnants. Background and Theory Supernova explosions are the most powerful events in the Universe. In less ...
... The student will use CCD images of the Crab Nebula, a Hubble Space Telescope image of SN1987a, and a CCD image of supernova 1993j to examine a number of characteristics of supernovae and their remnants. Background and Theory Supernova explosions are the most powerful events in the Universe. In less ...
HR4AGN Powerpoint Presentation-a
... • So we want a color magnitude diagram for AGN so that by looking at the color of an AGN we can get its luminosity – But AGN have no fusion, why would we expect a color-magnitude relation? – The gas that accretes onto the black hole is still hot and so must follow the ...
... • So we want a color magnitude diagram for AGN so that by looking at the color of an AGN we can get its luminosity – But AGN have no fusion, why would we expect a color-magnitude relation? – The gas that accretes onto the black hole is still hot and so must follow the ...
Lecture 4: Telescopes
... Light Gathering Power - proportional to the square of the size of the mirror (area of the light bucket) Limiting magnitude for a telescope is m = 2.7 + 5 log D Where D is telescope aperture in millimeters. Resolving Power - Smallest angular separation that the telescope can resolve 4.56 / diameter o ...
... Light Gathering Power - proportional to the square of the size of the mirror (area of the light bucket) Limiting magnitude for a telescope is m = 2.7 + 5 log D Where D is telescope aperture in millimeters. Resolving Power - Smallest angular separation that the telescope can resolve 4.56 / diameter o ...
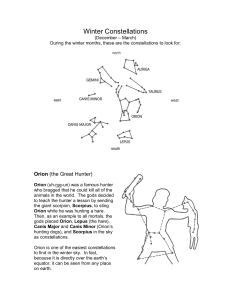
seven winter constellations
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
Teacher Guide - Astronomy Outreach at UT Austin
... This activity is an opportunity for students to learn about the fundamental characterisitcs of stars and their life cycles. Students perform a play as members of an interview with several different stars. As the play progresses, students develop an understanding of the most fundamental concepts in s ...
... This activity is an opportunity for students to learn about the fundamental characterisitcs of stars and their life cycles. Students perform a play as members of an interview with several different stars. As the play progresses, students develop an understanding of the most fundamental concepts in s ...
1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 1031 W. The apparent brightness of the star is 1.4 10–9 W m–2. These data can be used to determine the distance of the star from Earth. (i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 1031 W. The apparent brightness of the star is 1.4 10–9 W m–2. These data can be used to determine the distance of the star from Earth. (i) ...
The Sun and the Stars
... Apparent magnitude : The apparent magnitude (symbol m) is a measure of the stars brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Scale originally devised by Hipparchus and later Ptolemy. Historically , stars were divided into 6 categories according to their brightness : brightest 1st magnitude, faintest ...
... Apparent magnitude : The apparent magnitude (symbol m) is a measure of the stars brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Scale originally devised by Hipparchus and later Ptolemy. Historically , stars were divided into 6 categories according to their brightness : brightest 1st magnitude, faintest ...
Lecture 3
... Apparent magnitude : The apparent magnitude (symbol m) is a measure of the stars brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Scale originally devised by Hipparchus and later Ptolemy. Historically , stars were divided into 6 categories according to their brightness : brightest 1st magnitude, faintest ...
... Apparent magnitude : The apparent magnitude (symbol m) is a measure of the stars brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Scale originally devised by Hipparchus and later Ptolemy. Historically , stars were divided into 6 categories according to their brightness : brightest 1st magnitude, faintest ...
What tool do astronomers use to understand the evolution of stars?
... t B M B L A 1 300 300 60 Sun's lifetime ~ 10 billion years = 1010 yr = 10 Gyr. Lifetime of 5 solar mass star is 1010 yr/60 ~ 1010/102 yr = 108 yr = 102106 yr = 100 million yr = 100 Myr This is the age of the star cluster. ...
... t B M B L A 1 300 300 60 Sun's lifetime ~ 10 billion years = 1010 yr = 10 Gyr. Lifetime of 5 solar mass star is 1010 yr/60 ~ 1010/102 yr = 108 yr = 102106 yr = 100 million yr = 100 Myr This is the age of the star cluster. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.