star - TeacherWeb
... Light from stars that are moving toward the Earth is shifted slightly toward the blue end of the spectrum. When a source of light (like a star) is stationary, the wavelengths of light remain the same distance apart. When a source of light is moving toward you, the wavelengths of light get closer tog ...
... Light from stars that are moving toward the Earth is shifted slightly toward the blue end of the spectrum. When a source of light (like a star) is stationary, the wavelengths of light remain the same distance apart. When a source of light is moving toward you, the wavelengths of light get closer tog ...
Exploring Stars - Discovery Education
... 1. Talk about the life of a star. A good way to introduce this topic is to show Exploring Stars. After watching the program, talk about the different types of stars found in the universe. What are stars? What are they made of? How is a red star different from a blue star? Discuss and review the life ...
... 1. Talk about the life of a star. A good way to introduce this topic is to show Exploring Stars. After watching the program, talk about the different types of stars found in the universe. What are stars? What are they made of? How is a red star different from a blue star? Discuss and review the life ...
Spectral Classification
... B stars are extremely luminous and blue. As O and B stars are so powerful, they live for a very short time. They do not stray far from the area in which they were formed as they don't have the time. They therefore tend to cluster together in what we call OB1 associations. and contains all of the con ...
... B stars are extremely luminous and blue. As O and B stars are so powerful, they live for a very short time. They do not stray far from the area in which they were formed as they don't have the time. They therefore tend to cluster together in what we call OB1 associations. and contains all of the con ...
PHYS-638-07f: Problem set #0 Solutions
... magnitude (i.e. dimmer stars have bigger m), we have m⊙,new = m⊙ + 2.5 log(F⊙ /F⊙ , new) = −26.7 + 2.5 log(18002 ) = −10.4 . ...
... magnitude (i.e. dimmer stars have bigger m), we have m⊙,new = m⊙ + 2.5 log(F⊙ /F⊙ , new) = −26.7 + 2.5 log(18002 ) = −10.4 . ...
Islip Invitational 2013 Astronomy Examination Student
... b. When a group of stars form, they remove so much material from the cloud that only a big empty place is left, into which new matter from other clouds falls, creating more stars. c. When massive stars form, their UV radiation and later their final explosions compress the gas in the cloud and cause ...
... b. When a group of stars form, they remove so much material from the cloud that only a big empty place is left, into which new matter from other clouds falls, creating more stars. c. When massive stars form, their UV radiation and later their final explosions compress the gas in the cloud and cause ...
Star luminosity info and HR diagram
... from us, from several light-years to over 1,000 lightyears. Telescopes show the light of stars millions or billions of light-years away. Today, when we talk about a star’s brightness, we might mean one of two things: its intrinsic brightness or its apparent brightness. When astronomers speak of the ...
... from us, from several light-years to over 1,000 lightyears. Telescopes show the light of stars millions or billions of light-years away. Today, when we talk about a star’s brightness, we might mean one of two things: its intrinsic brightness or its apparent brightness. When astronomers speak of the ...
Sky Diary - Society for Popular Astronomy
... observation but, Saturn in particular, may be found and observed in daylight as long as sensible precautions are taken to ensure the Sun can never enter the field of view of either the telescope or the finder-scope. Jupiter is just too close to the Sun for this to be safely attempted. Which brings u ...
... observation but, Saturn in particular, may be found and observed in daylight as long as sensible precautions are taken to ensure the Sun can never enter the field of view of either the telescope or the finder-scope. Jupiter is just too close to the Sun for this to be safely attempted. Which brings u ...
Slide 1
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
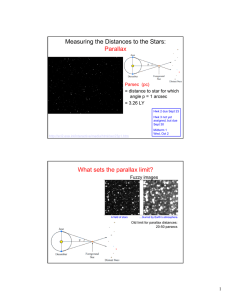
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... Hipparcos (1989-1993): 100-200 parsecs (1σ =1 milliarcsec = 1kpc) ...
... Hipparcos (1989-1993): 100-200 parsecs (1σ =1 milliarcsec = 1kpc) ...
17_LectureOutline
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
... Measuring Stellar Masses in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured usi ...
Star Formation
... 4) The collapsing gas becomes a young stellar object with an accretion disk and jets 4) When the young stellar object begins fusing hydrogen into helium it becomes a true star ...
... 4) The collapsing gas becomes a young stellar object with an accretion disk and jets 4) When the young stellar object begins fusing hydrogen into helium it becomes a true star ...
giant molecular clouds
... Open Clusters of Stars (2) Large, dense cluster of (yellow and red) stars in the foreground; ~ 50 million years old ...
... Open Clusters of Stars (2) Large, dense cluster of (yellow and red) stars in the foreground; ~ 50 million years old ...
Crux The Southern Cross
... There are many stars in the sky that when viewed through a telescope appear as two dots. It is common for two stars to be locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not int ...
... There are many stars in the sky that when viewed through a telescope appear as two dots. It is common for two stars to be locked together gravitationally to form a binary star system. Sometimes double stars may only appear close together from our vantage point on earth. If in reality they do not int ...
Stars
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
The Origin of Stars
... 4) Once the compression begins, the star falls together under its own gravity (protostar). A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not ...
... 4) Once the compression begins, the star falls together under its own gravity (protostar). A protostar looks starlike after the surrounding gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not ...
earth & space science
... Classifying Stars Main sequence is the location on the H-R diagram where most stars lie; it has a diagonal pattern from the lower right to the upper left. One way scientists classify stars is by plotting the surface temperatures of stars against their ...
... Classifying Stars Main sequence is the location on the H-R diagram where most stars lie; it has a diagonal pattern from the lower right to the upper left. One way scientists classify stars is by plotting the surface temperatures of stars against their ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF STARS
... A Newborn Star: When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction in which hydrogen atoms are converted to helium atoms plus energy. This energy (radiation) production prevents further contraction of the star. Young stars emit jets of intense ra ...
... A Newborn Star: When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction in which hydrogen atoms are converted to helium atoms plus energy. This energy (radiation) production prevents further contraction of the star. Young stars emit jets of intense ra ...
Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Exercises 2
... 7. For every mass m which is swallowed by a black hole (via an accretion disk, say), an amount of energy νmc2 is liberated, where ν is the efficiency of the process. A value of ν = 0.1 is realistic. At what rate Ṁ would a supermassive black hole have to swallow mass to produce the luminosity L = 10 ...
... 7. For every mass m which is swallowed by a black hole (via an accretion disk, say), an amount of energy νmc2 is liberated, where ν is the efficiency of the process. A value of ν = 0.1 is realistic. At what rate Ṁ would a supermassive black hole have to swallow mass to produce the luminosity L = 10 ...
Photometric Surveys and Variable stars
... Gamma Doradus stars • sp. type mid-late F, lum. class V, Pop I • P: 8h - 3d (close to P(rot)!) • sometimes multiperiodic • g-mode pulsators (n < 0) The gamma Doradus class is a new designation (early 1990’s). Before they were discovered, they were sometimes unknowingly used as comp stars! ...
... Gamma Doradus stars • sp. type mid-late F, lum. class V, Pop I • P: 8h - 3d (close to P(rot)!) • sometimes multiperiodic • g-mode pulsators (n < 0) The gamma Doradus class is a new designation (early 1990’s). Before they were discovered, they were sometimes unknowingly used as comp stars! ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... • Let’s think back to initial categories made of star image • Having made a few measurements now – let’s list the intrinsic properties of stars on the board together ...
... • Let’s think back to initial categories made of star image • Having made a few measurements now – let’s list the intrinsic properties of stars on the board together ...
Earth Science Notes
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
... in the sky Stars appear close together in the sky, however, they are actually light years from each other ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.