* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comets and more
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Space warfare wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
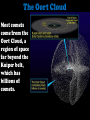
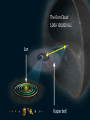
Meteoroids Meteors Meteorites Comets Asteroids. Meteoroids A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic object traveling through space Can be as small as sand or as large as 3 feet. Micrometeoroids A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid that weighs less than 1 gram (small paper clip). – Are also known as Space dust which can be found blocking the light of galaxies & Nebulae Asteroids Large space rocks. larger than 3 feet: to 600 miles across: The Tunguska Event • Historical Footage with Notes Tunguska Explosion • Narrated Explanation Russia again! 2013 Question: What is the Difference between Meteoroids, Meteors & Meteorites? Answer: Meteoroids, Meteors & Meteorites are the same object. They have different names depending on their position. Meteoroids, Meteors, and Meteorites A meteoroid is a space rock. A meteor is a space rock in the Atmosphere. A meteorite is a space rock that hit the Earth. Meteors When a space rock enters Earth’s Atmosphere, the friction as it falls through air produces heat and light. The light being created is called a meteor. The rock itself is still called a meteoroid. Meteorite A Meteorite is the rock that remains after hitting the Earth. There are three Main types: Stony Iron (Most rare) Iron (Rare) Stony (Common) Question: What is a Shooting Star? Answer: A Shooting star is a Meteor Video: What is a Shooting Star? Meteor Showers Meteor Showers are events where many meteors can be seen in the sky. Can produce between a few meteors per hour to 1,000 meteors per hour. Perseid Meteor Shower Seen from Snowy Range in Wyoming Lyrids: Meteor Shower Can be seen between April 16 – 26 each year. Usually peaks around April 22nd. Generates between 5 – 20 meteors per hour So named because they can be seen in the constellation Lyra. Perseids: Meteor Shower Can be seen from mid July to late August. Usually peaks around August 9th to 14th. Generates between 80 – 200 meteors per hour So named because they appear to originate in the constellation Perseus. However they can be seen anywhere in the sky. Video: Perseids Meteor Shower Orionids: Meteor Shower Can be seen through October 16 – 27 And peak on October 21st. Generates between 20 - 70 meteors per hour So named because they appear to originate in the constellation Orion. However they can be seen anywhere in the sky. Leonids: Meteor Shower Can be seen from November 15th – 20th. Usually peaks around November 18th. Generates between 80 – 200 meteors per hour So named because they appear to originate in the constellation Leo. However they can be seen anywhere in the sky. Geminids: Meteor Shower Can be seen between December 7th – 17th And peak on December 14th. Generates between 75 – 200 meteors per hour So named because they appear to originate in the constellation Gemini. However they can be seen anywhere in the sky. Fireballs A fireball meteor is any meteor that shines brighter than the brightest planet: Venus. Videos: Fireball over Concert Fireball over Texas Bolides / Detonating Fireballs A Bolide is a very bright fireball that explodes in the atmosphere, which is why its also called a detonating fireball. Videos: The Tunguska Event Super-Bolide: 2013 Russian Meteor Comets A Comet is a rock in space that is very icy and forms a coma and a tail. Some comets originate from the Kuiper belt. The Oort Cloud Most comets come from the Oort Cloud, a region of space far beyond the Kuiper belt, which has billions of comets. Comets: Coma’s and Tails A coma is the atmosphere of a comet & the tail is a formation of dust & gas behind it. tail Coma Comets Tail Formation A tail forms due to the heat of the Sun evaporating frozen gases and releasing dust. The tail always points away from the Sun because the Sun’s cosmic wind pushes it away. Comet Tail Formation: The tail of a comet can only be seen when it gets close enough to the Sun for it to be heated up. Video: What are Comets?